In Italy
The coloured circles represent the total number of activities (project, products and services, outreach, collaborations) that we have in the corresponding geographical zone
Map data: © OpenStreetMap contributors
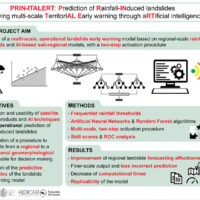
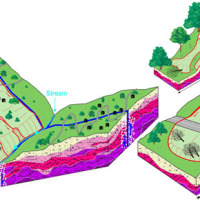
Full cOveRage, Multi-scAle and multi-sensor geomorphological map: a practical tool for TerrItOrial plaNning
 Italy is an extremely fragile territory, widely exposed to hydrogeological hazards affecting anthropic infrastructures and the natural environment. In this scenario, geomorphological maps, including the representation of the spatial distribution of landforms, have been used for a long time for the description of processes acting on the Earth’s surface. Geomorphological maps should represent the basic tool for the assessment of ...
Italy is an extremely fragile territory, widely exposed to hydrogeological hazards affecting anthropic infrastructures and the natural environment. In this scenario, geomorphological maps, including the representation of the spatial distribution of landforms, have been used for a long time for the description of processes acting on the Earth’s surface. Geomorphological maps should represent the basic tool for the assessment of ... URban GEodiversity for a Resilient Environment
 Geodiversity refers to the variety of natural abiotic features, as the natural variety of geological (rocks, minerals), geomorphological (landforms, physical processes), hydrological and soil properties. The parameter “geomorphodiversity” is a measure of the dynamics of the Earth's surface and it has a key role in conservation of biodiversity and sustainability of ecosystems. Thus, it affects evolution of the biotic world and of human life. ...
Geodiversity refers to the variety of natural abiotic features, as the natural variety of geological (rocks, minerals), geomorphological (landforms, physical processes), hydrological and soil properties. The parameter “geomorphodiversity” is a measure of the dynamics of the Earth's surface and it has a key role in conservation of biodiversity and sustainability of ecosystems. Thus, it affects evolution of the biotic world and of human life. ... Sentinel-3 Topography mission Assessment through Reference Techniques
 The Copernicus Sentinel-3 Surface Topography Mission (STM) provides extremely valuable surface elevation information over inland waters, sea ice and land ice, thanks to its SAR altimeter which retrieves high-resolution along-track elevation measurements, and to its orbit that covers high-latitude polar regions.
To ensure that these measurements can be used with confidence, and to maximize the return on investment of the Copernicus Sentinel-3 ...
The Copernicus Sentinel-3 Surface Topography Mission (STM) provides extremely valuable surface elevation information over inland waters, sea ice and land ice, thanks to its SAR altimeter which retrieves high-resolution along-track elevation measurements, and to its orbit that covers high-latitude polar regions.
To ensure that these measurements can be used with confidence, and to maximize the return on investment of the Copernicus Sentinel-3 ... I-CHANGE project
 The documented effects of climate change and environmental degradation are a threat to human societies on European and global scales. Climate change may have an impact on water availability, may increase the threat of flooding and flash-floods, and will challenge coastal regions due to rising sea levels. All this will have impacts on the economy and society. The role of citizens and their skills become important both in limiting human impacts ...
The documented effects of climate change and environmental degradation are a threat to human societies on European and global scales. Climate change may have an impact on water availability, may increase the threat of flooding and flash-floods, and will challenge coastal regions due to rising sea levels. All this will have impacts on the economy and society. The role of citizens and their skills become important both in limiting human impacts ... Laboratorio a Cielo aperto delle Grandes Jorasses per lo sviluppo di tecniche di monitoraggio di processi di instabilità in ambito glaciale
 Climate change has a powerful impact on high-altitude Alpine sectors and glaciers. This impact often turns into an increase in instability processes that can lead to very high-risk conditions. These risk conditions can significantly affect the usability of areas characterized by intense tourist flows, making risk management very ...
Climate change has a powerful impact on high-altitude Alpine sectors and glaciers. This impact often turns into an increase in instability processes that can lead to very high-risk conditions. These risk conditions can significantly affect the usability of areas characterized by intense tourist flows, making risk management very ... Remotely Piloted Aircraft Systems for emergency response
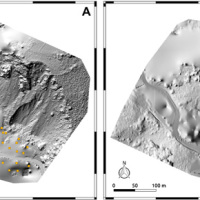 The use of remotely piloted aircraft systems (RPASs) in geosciences is often aimed at the acquisition of an image sequence to produce digital models and orthophotographs of the topographic surface. Such photogrammetric technique can be applied for rockfall hazard and risk assessment. To study rockfalls, an approach consists in the application of numerical models for the computation of rockfall trajectories. Data required for such simulations ...
The use of remotely piloted aircraft systems (RPASs) in geosciences is often aimed at the acquisition of an image sequence to produce digital models and orthophotographs of the topographic surface. Such photogrammetric technique can be applied for rockfall hazard and risk assessment. To study rockfalls, an approach consists in the application of numerical models for the computation of rockfall trajectories. Data required for such simulations ... River discharge estimation from satellite
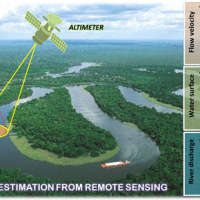 River discharge is defined as the amount of water flowing through a river over a specified period of time. Its estimate is crucial for all the operations of hydraulic structures design, the territorial planning and the flood risk assessment and management. River discharge at a specific river cross-section is not a direct measurement, but it is calculated by measuring other hydraulic quantities such as the flow velocity and the water depth, i.e. ...
River discharge is defined as the amount of water flowing through a river over a specified period of time. Its estimate is crucial for all the operations of hydraulic structures design, the territorial planning and the flood risk assessment and management. River discharge at a specific river cross-section is not a direct measurement, but it is calculated by measuring other hydraulic quantities such as the flow velocity and the water depth, i.e. ... The improvement of the expressive and learning abilities of the adult
 The researches and the experimentations carried out, in the learning field, by the IRPI Institute during the last years, started out initially in the field of geoethics, have allowed to set up principles and didactic tools that offer today practical and usable tools to significantly improve, in a relatively short period of time, the expressive, learning and assimilation capacities of students and adults.
The researches have been originally ...
The researches and the experimentations carried out, in the learning field, by the IRPI Institute during the last years, started out initially in the field of geoethics, have allowed to set up principles and didactic tools that offer today practical and usable tools to significantly improve, in a relatively short period of time, the expressive, learning and assimilation capacities of students and adults.
The researches have been originally ... How much Mar Piccolo peculiarities are due to groundwater outflow
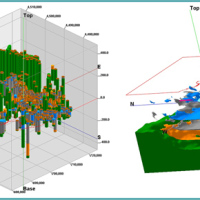 The Mar Piccolo basin is an internal sea basin located along the Ionian coast (Southern Italy), and it is surrounded primarily by fractured carbonate karstic environment.
In primarily karstic environments, infiltration is greater than runoff; in the karstic coastal Apulian aquifers, the groundwater discharge to the sea is more than two-fold greater than the surface discharge, notwithstanding the high discharges by wells. In such ...
The Mar Piccolo basin is an internal sea basin located along the Ionian coast (Southern Italy), and it is surrounded primarily by fractured carbonate karstic environment.
In primarily karstic environments, infiltration is greater than runoff; in the karstic coastal Apulian aquifers, the groundwater discharge to the sea is more than two-fold greater than the surface discharge, notwithstanding the high discharges by wells. In such ... Chronological database of sinkholes in Italy
 Sinkholes occurrence is related to the presence of an underground cavity, from which instability starts and propagate upwards until causing the collapse of the surface soil layer. The cavity may have a natural or artificial origin. Natural caves are due to presence of soluble rocks, and are typical of karst settings, where most of the sinkholes occur for dissolution processes. Man has excavated Anthropogenic cavities, for different purposes and ...
Sinkholes occurrence is related to the presence of an underground cavity, from which instability starts and propagate upwards until causing the collapse of the surface soil layer. The cavity may have a natural or artificial origin. Natural caves are due to presence of soluble rocks, and are typical of karst settings, where most of the sinkholes occur for dissolution processes. Man has excavated Anthropogenic cavities, for different purposes and ... Active alluvial fans in Calabria, Southern Italy
 Alluvial fans are known to be areas of high geomorphic activity, where debris flows and flash floods caused by intense and prolonged rainfall are a major hazard. In Calabria, southern Italy, alluvial fans are numerous. The exact age of the alluvial fans is seldom known, but most of the fans in Calabria are considered recent in age (Holocene).
Due to the significant increase in urbanization in the last two centuries, many alluvial fans are ...
Alluvial fans are known to be areas of high geomorphic activity, where debris flows and flash floods caused by intense and prolonged rainfall are a major hazard. In Calabria, southern Italy, alluvial fans are numerous. The exact age of the alluvial fans is seldom known, but most of the fans in Calabria are considered recent in age (Holocene).
Due to the significant increase in urbanization in the last two centuries, many alluvial fans are ... Automated Inclinometer System (AIS) for deep-seated ground deformation measurements
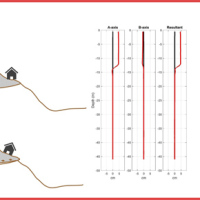 Our AIS (Automated Inclinometer System) allows for fully automatic inclinometer measurements in standard boreholes. The deep measurements have multiple applications, including (i) evaluating the rate of deep-seated ground deformation in landslide areas, (ii) evaluating the volume of deep-seated landslides, and (ii) assessing landslide hazards.
The AIS is composed of an electronic control manager, an inclinometer probe (with traditional ...
Our AIS (Automated Inclinometer System) allows for fully automatic inclinometer measurements in standard boreholes. The deep measurements have multiple applications, including (i) evaluating the rate of deep-seated ground deformation in landslide areas, (ii) evaluating the volume of deep-seated landslides, and (ii) assessing landslide hazards.
The AIS is composed of an electronic control manager, an inclinometer probe (with traditional ... Debris-flow monitoring in the Alps
 Not all that flows in creeks is water. Debris flows i.e., surges in which solid particles move together with little water, may occur in steep mountain streams, mainly as a consequence of intense rainfall. Debris flows have a high kinetic energy, and may cause major damage if they encroach buildings, roads and bridges. They are also a primary cause of landslide casualties. The video below shows an example of debris flows.
The low ...
Not all that flows in creeks is water. Debris flows i.e., surges in which solid particles move together with little water, may occur in steep mountain streams, mainly as a consequence of intense rainfall. Debris flows have a high kinetic energy, and may cause major damage if they encroach buildings, roads and bridges. They are also a primary cause of landslide casualties. The video below shows an example of debris flows.
The low ... The strong retreat of the Italian glaciers
 Between the late 19th and early 21st century, in the Alps the average air temperature has increased by about 2 °C, more than twice the increase in temperature in the northern hemisphere, of 0.8 °C. In the same period, precipitation showed a tendency towards an increase in the northern part of the Alps, and a tendency towards a decrease in the southern sector of the Alps.
Since the end of the Little Ice Age (about 1850), glaciers in the ...
Between the late 19th and early 21st century, in the Alps the average air temperature has increased by about 2 °C, more than twice the increase in temperature in the northern hemisphere, of 0.8 °C. In the same period, precipitation showed a tendency towards an increase in the northern part of the Alps, and a tendency towards a decrease in the southern sector of the Alps.
Since the end of the Little Ice Age (about 1850), glaciers in the ... ALMOND-F, an ALarm and MONitoring system for Debris-Flows
 ALMOND-F is an innovative unit for the microseismic detection of debris flows using a network of geophones.
The microseismic detection of debris flows is more complex than other types of monitoring. Use of the geophones requires: (1) the selection of the level of amplification of the signal, which depends on the distance from the stream; (2) the selection of the sampling frequency of the seismic signal, which must be sufficiently high; (3) ...
ALMOND-F is an innovative unit for the microseismic detection of debris flows using a network of geophones.
The microseismic detection of debris flows is more complex than other types of monitoring. Use of the geophones requires: (1) the selection of the level of amplification of the signal, which depends on the distance from the stream; (2) the selection of the sampling frequency of the seismic signal, which must be sufficiently high; (3) ... POLARIS: POpuLutAtion at RIsk of geo-hydrological events in Italy
 Despite the large number and frequency of landslides and floods that affect our territories, and the information on landslides and floods available also online, the subject of geo-hydrological hazards remains poorly known to the Italian citizens. The lack of understanding reflects in the limited perception of the population on the geo-hydrological risks in Italy.
One reason for the lack of understanding is the way in which the subject of ...
Despite the large number and frequency of landslides and floods that affect our territories, and the information on landslides and floods available also online, the subject of geo-hydrological hazards remains poorly known to the Italian citizens. The lack of understanding reflects in the limited perception of the population on the geo-hydrological risks in Italy.
One reason for the lack of understanding is the way in which the subject of ... Droughts, desertification and climate change in Calabria, Southern Italy
 Using long-term rainfall records obtained by the rain gauge network of the former Italian Hydrographic Service, in cooperation with colleagues in other CNR Institutes (ISAC and ISAFOM), we have studied the changes in the rainfall regimes in Calabria, Southern Italy.
Applying appropriate statistical methods, we checked the completeness of the historical records, verifying consistency and missing values in the records. We used the obtained ...
Using long-term rainfall records obtained by the rain gauge network of the former Italian Hydrographic Service, in cooperation with colleagues in other CNR Institutes (ISAC and ISAFOM), we have studied the changes in the rainfall regimes in Calabria, Southern Italy.
Applying appropriate statistical methods, we checked the completeness of the historical records, verifying consistency and missing values in the records. We used the obtained ... Detecting rainfall from the bottom up
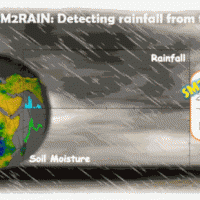 SM2RAIN is an innovative system for the estimation of the rainfall, based on measurements of the soil water content. SM2RAIN considers the soil as a natural rain gauge, and by measuring temporal variations of the soil water content, it estimates the rainfall falling on the soil, adopting a “bottom up” approach. Technically, SM2RAIN relies on the inversion of the soil water balance equation that computes the repartition of rainfall in ...
SM2RAIN is an innovative system for the estimation of the rainfall, based on measurements of the soil water content. SM2RAIN considers the soil as a natural rain gauge, and by measuring temporal variations of the soil water content, it estimates the rainfall falling on the soil, adopting a “bottom up” approach. Technically, SM2RAIN relies on the inversion of the soil water balance equation that computes the repartition of rainfall in ... Migliorare l’attenzione del pubblico per una più efficace comunicazione del rischio
 La sperimentazione ad ampio raggio condotta negli ultimi anni per testare sul campo la funzionalità e l’efficacia della procedura semplificata per la rielaborazione dei ricordi traumatici (RINOEL) ha consentito di evidenziare con sempre maggior chiarezza gli effetti esercitati da tali ricordi sull’attenzione di una persona. La capacità di concentrazione di un individuo, e dunque la sua abilità di focalizzare l’attenzione, risente ...
La sperimentazione ad ampio raggio condotta negli ultimi anni per testare sul campo la funzionalità e l’efficacia della procedura semplificata per la rielaborazione dei ricordi traumatici (RINOEL) ha consentito di evidenziare con sempre maggior chiarezza gli effetti esercitati da tali ricordi sull’attenzione di una persona. La capacità di concentrazione di un individuo, e dunque la sua abilità di focalizzare l’attenzione, risente ... Assessing sediment connectivity and availability in several mountain catchments in the Veneto Region
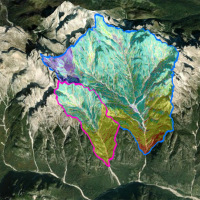 Mass wasting is a threat to residential areas and infrastructure, causing widespread destabilization in alpine stream channels, also in relation to ongoing climatic changes. Although hillslope sediment supply represents a critical factor for stream channel stability during heavy rainstorms, there is a general lack of procedures for quantifying sediment availability and composition. Moreover, we lack validated empirical models for estimating ...
Mass wasting is a threat to residential areas and infrastructure, causing widespread destabilization in alpine stream channels, also in relation to ongoing climatic changes. Although hillslope sediment supply represents a critical factor for stream channel stability during heavy rainstorms, there is a general lack of procedures for quantifying sediment availability and composition. Moreover, we lack validated empirical models for estimating ... MUltiHAzard framework for water related risks management
 The MUHA project is building upon the idea to address disaster management cycle consisting of preparedness-response-mitigation-rebuild components in the ADRION countries. It will connect the observed and modelled hazards and risks related to the integrated water cycle, by effectively join them with the existing and improved coping capacity developed by national, bilateral and EU Civil Protection ...
The MUHA project is building upon the idea to address disaster management cycle consisting of preparedness-response-mitigation-rebuild components in the ADRION countries. It will connect the observed and modelled hazards and risks related to the integrated water cycle, by effectively join them with the existing and improved coping capacity developed by national, bilateral and EU Civil Protection ... Fiber optic sensors engineering for the monitoring of structural reinforcements on unstable slopes
 Geo-Hydrological risks are one of the main sources of economic losses for our country causing a huge number of victims and damages. From 1966 to 2015, landslides and floods caused 1948 casualties, 3524 injured and more than 412,000 displaced people. The Venetian mountain has always been subject to major landslides and, almost every year, new emergencies occur with the intensification of the autumn and spring rains, which are increasing due to ...
Geo-Hydrological risks are one of the main sources of economic losses for our country causing a huge number of victims and damages. From 1966 to 2015, landslides and floods caused 1948 casualties, 3524 injured and more than 412,000 displaced people. The Venetian mountain has always been subject to major landslides and, almost every year, new emergencies occur with the intensification of the autumn and spring rains, which are increasing due to ... IntEractions between hydrodyNamics and bioTic communities in fluvial Ecosystems: advancement in the knowledge and undeRstanding of PRocesses and ecosystem sustainability by the development of novel technologieS with fIeld monitoriNg and laboratory testinG
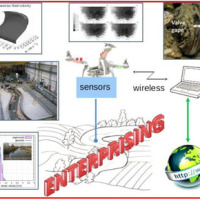 The development of an innovative system for monitoring river flows during extreme events and the impact of hydrodynamic pressures on ecosystems are two important challenges identified by the World Meteorological Organization for flood event control and by the European Commission for the European Biodiversity Strategy for the protection of ecosystems and ...
The development of an innovative system for monitoring river flows during extreme events and the impact of hydrodynamic pressures on ecosystems are two important challenges identified by the World Meteorological Organization for flood event control and by the European Commission for the European Biodiversity Strategy for the protection of ecosystems and ... Valutazione del rischio idraulico finalizzata alla individuazione di interventi di mitigazione per la ricostruzione post-sisma
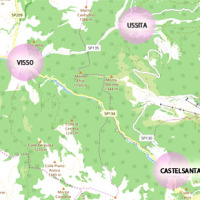 The seismic events that have affected central Italy since 24 August 2016 have caused extensive damage in the municipalities of Castelsantagelo sul Nera, Ussita and Visso (Marche Region). In order to proceed with the reconstruction, it is necessary to carry out interventions to reduce the hydraulic risk in urban ...
The seismic events that have affected central Italy since 24 August 2016 have caused extensive damage in the municipalities of Castelsantagelo sul Nera, Ussita and Visso (Marche Region). In order to proceed with the reconstruction, it is necessary to carry out interventions to reduce the hydraulic risk in urban ... Progetto ADAPT
Typify geo-hydrological events
 A Geo-hydrological event (EDId) (landslides, mass movements, floods, etc.) can result in a high social and economic impact, especially if it is generated by multiple simultaneous phenomena, when it is able to produce social hardships and economic damage characterized by important and lasting effects. The identification of the typical elements of the phenomena that can contribute to an EDId (typify) is essential to adequately define the risk ...
A Geo-hydrological event (EDId) (landslides, mass movements, floods, etc.) can result in a high social and economic impact, especially if it is generated by multiple simultaneous phenomena, when it is able to produce social hardships and economic damage characterized by important and lasting effects. The identification of the typical elements of the phenomena that can contribute to an EDId (typify) is essential to adequately define the risk ... Risk Management System (RMS)
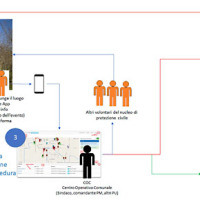 The management of emergencies, in particular those determined by natural events, is complex and must be able to use all the available cognitive elements. During emergencies, it is possible to acquire useful data regarding the processes that determine the same emergencies. These data can contribute to significantly improve planning and design of prevention ...
The management of emergencies, in particular those determined by natural events, is complex and must be able to use all the available cognitive elements. During emergencies, it is possible to acquire useful data regarding the processes that determine the same emergencies. These data can contribute to significantly improve planning and design of prevention ... Monitoring and landslides risk in the Maierato area
 The Maierato landslide (Vibo Valentia Province) is a complex movement, which involved a significant thickness of geomaterials (rocks and soils) and rapidly flowed away for one kilometre. Owing that, the surrounding zone is interested by the same geological settings that predisposed the Maierato landslide, it is useful to identify any elements indicative of the presence of instabilities that can be triggered and evolved as the Maierato ...
The Maierato landslide (Vibo Valentia Province) is a complex movement, which involved a significant thickness of geomaterials (rocks and soils) and rapidly flowed away for one kilometre. Owing that, the surrounding zone is interested by the same geological settings that predisposed the Maierato landslide, it is useful to identify any elements indicative of the presence of instabilities that can be triggered and evolved as the Maierato ...