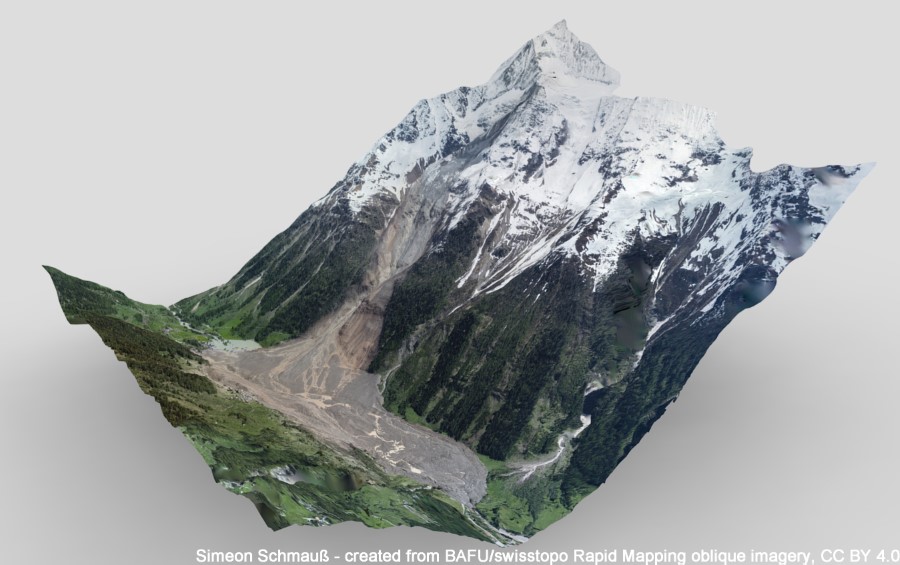
On 28 May 2025, at15:24 (CEST), the frontal part of the Birch Glacier in Valais (CH), estimated at around 3 million m3, collapsed, dragging with it over 6 million m3 of debris that had accumulated on its surface over the previous weeks, following a sequence of rockfalls from the northern slope of the Kleines Nesthorn (3335 m a.s.l.). The ice mass disintegrated immediately after detachment, giving rise to a catastrophic ice-rock avalanche with a ...
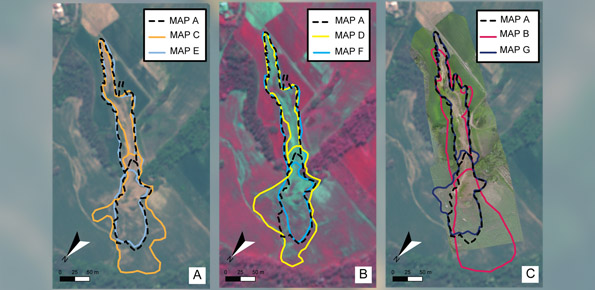
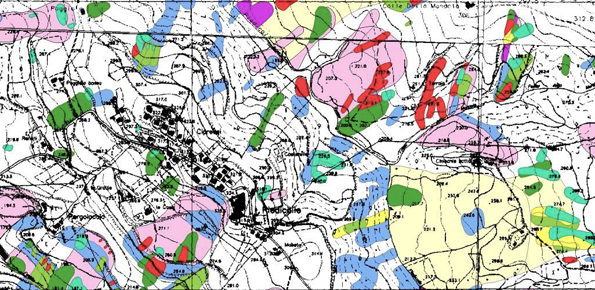
Landslides leave discernible signs on the land surface, most of which can be captured in remote sensing images. On the images the signs appear as modification of the photographic characteristics as tone, colour, mottling and texture, or/and as modification of morphological characteristics including shape, curvature, convexity and concavity. These signs are the landslide signature. Trained geomorphologists analyse remote sensing images and map ...

Worldwide, landslides pose a serious threat to the population, causing fatalities, widespread damages, and significant economic losses. Different phenomena influence the stability of slopes and can cause landslides, among which the main factor is rainfall. Rainfall is strongly controlled and influenced by climate and its variations. Therefore, it is to be expected that climate changes influence slope stability at different temporal and ...

The use of remotely piloted aircraft systems (RPASs) in geosciences is often aimed at the acquisition of an image sequence to produce digital models and orthophotographs of the topographic surface. Such photogrammetric technique can be applied for rockfall hazard and risk assessment. To study rockfalls, an approach consists in the application of numerical models for the computation of rockfall trajectories. Data required for such simulations ...

The LiDAR sensor available to the institute has recently turned seven years since the first survey executed on November 2, 2011, in the aftermath of the flood event that affected large areas of the Liguria Region, northern Italy.
The system consists of a laser head RIEGL LMS-Q680i, a medium format camera Hasselblad H3DII-39Mpixel f=50mm, an IMU IGI 256Khz, and a GNSS system Novatel-OEM4, and has since operated on many Italian areas thanks to ...
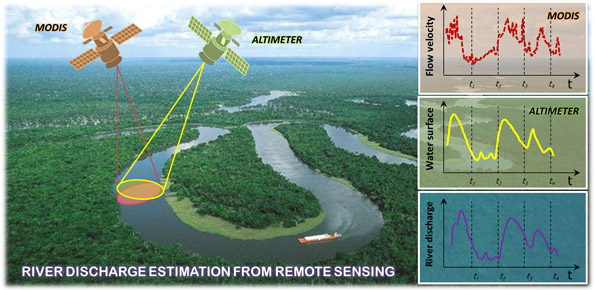
River discharge is defined as the amount of water flowing through a river over a specified period of time. Its estimate is crucial for all the operations of hydraulic structures design, the territorial planning and the flood risk assessment and management. River discharge at a specific river cross-section is not a direct measurement, but it is calculated by measuring other hydraulic quantities such as the flow velocity and the water depth, i.e. ...

The researches and the experimentations carried out, in the learning field, by the IRPI Institute during the last years, started out initially in the field of geoethics, have allowed to set up principles and didactic tools that offer today practical and usable tools to significantly improve, in a relatively short period of time, the expressive, learning and assimilation capacities of students and adults.
The researches have been originally ...

When soil behaviour is studied, whether landslide soils are concern, levee materials or foundations, the problem regarding how much and how reliable information about the soil properties we have available has to be addressed.
Understanding “what’s beneath” the visible surface is fundamental, yet complicated. Drillings are performed to analyse the stratigraphy of soils (the order and the thickness of the different soil levels) and ...

We published a book entitled “Eventi alluvionali in Calabria nel periodo 1990-1999” (Alluvial events in Calabria from 1990 to 1999)
Link to the Book»
The volume is the result of a study that lasted more than a year, and was part of long-lasting research effort to investigate historical landslide and flood events in Calabria, which started in the ‘70s of last century.
To search the information, we went to the Public Provincial ...

Landslides and floods tend to hit places that by their nature and geographic location are more likely than others to be damaged. Knowing the location of these places, and how they have been affected in the past by landslides and floods, allows to draw damage scenarios for possible future events.
For years, we have studied historical landslide and flood events in Calabria. Our investigations have allowed us to reconstruct a unique historical ...
The Mar Piccolo basin is an internal sea basin located along the Ionian coast (Southern Italy), and it is surrounded primarily by fractured carbonate karstic environment.
In primarily karstic environments, infiltration is greater than runoff; in the karstic coastal Apulian aquifers, the groundwater discharge to the sea is more than two-fold greater than the surface discharge, notwithstanding the high discharges by wells. In such ...
A landslide is the movement of a mass of rock, debris or earth along a slope under the influence of gravity.
Landslides pose serious threats in many areas of the world, and knowing their location, distribution and classification is important for land use planning. Landslide identification and mapping is a fundamental activity for an effective defence from the damage caused by landslides to the population and to structures and the ...

Sinkholes occurrence is related to the presence of an underground cavity, from which instability starts and propagate upwards until causing the collapse of the surface soil layer. The cavity may have a natural or artificial origin. Natural caves are due to presence of soluble rocks, and are typical of karst settings, where most of the sinkholes occur for dissolution processes. Man has excavated Anthropogenic cavities, for different purposes and ...

Alluvial fans are known to be areas of high geomorphic activity, where debris flows and flash floods caused by intense and prolonged rainfall are a major hazard. In Calabria, southern Italy, alluvial fans are numerous. The exact age of the alluvial fans is seldom known, but most of the fans in Calabria are considered recent in age (Holocene).
Due to the significant increase in urbanization in the last two centuries, many alluvial fans are ...
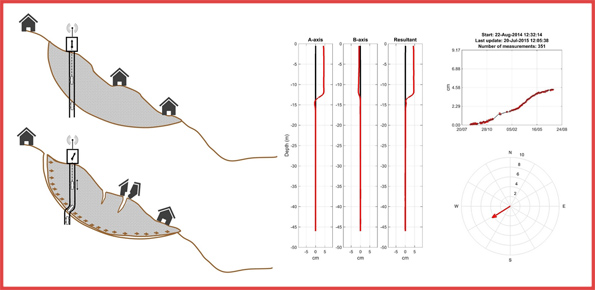
Our AIS (Automated Inclinometer System) allows for fully automatic inclinometer measurements in standard boreholes. The deep measurements have multiple applications, including (i) evaluating the rate of deep-seated ground deformation in landslide areas, (ii) evaluating the volume of deep-seated landslides, and (ii) assessing landslide hazards.
The AIS is composed of an electronic control manager, an inclinometer probe (with traditional ...

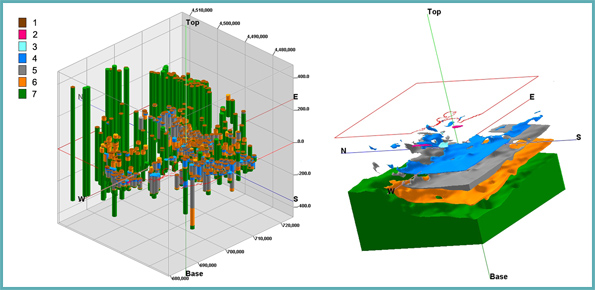
The characterization of an impact crater requires an understanding of the impact phenomena, considering the properties of the materials involved in the impact. The size and energy of the projectile control the width and depth of the crater. Related to impact craters is the formation of mass concentrations, or mascons, which produce intense positive gravity anomalies. One of the largest mascons is in the Isidis Planitia, Mars.
Using the ...

Not all that flows in creeks is water. Debris flows i.e., surges in which solid particles move together with little water, may occur in steep mountain streams, mainly as a consequence of intense rainfall. Debris flows have a high kinetic energy, and may cause major damage if they encroach buildings, roads and bridges. They are also a primary cause of landslide casualties. The video below shows an example of debris flows.
The low ...
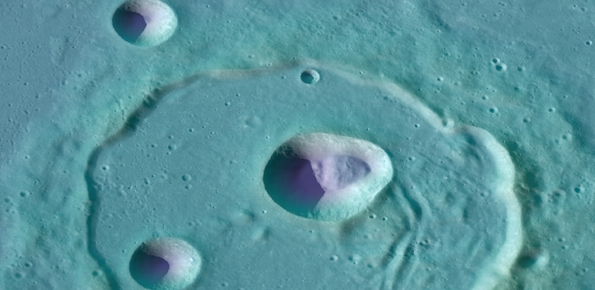
On Earth, landslides are hazardous phenomena often associated with economic damage and loss of human lives. The most common natural triggers of terrestrial landslides are intense or prolonged rainfall, earthquakes, rapid snow melting, and volcanic activity. But what are the main natural triggers of landslides on other solid bodies of the Solar System?
Since the early 70’s of the last century, landslides were observed on the surface of the ...
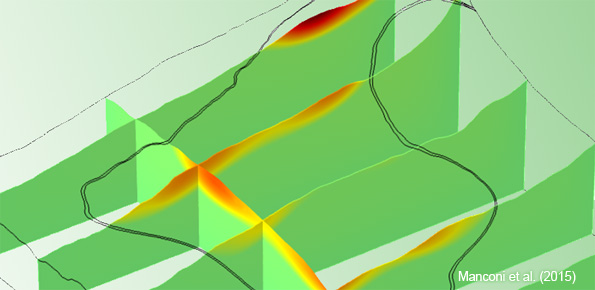
We experiment the application of 3D numerical modelling techniques for the analysis of the kinematics of slow-moving active landslides. The activity assesses the hazards posed by slow-moving landslides, determines the factors controlling the slope processes, investigates the potential evolution of the active slopes, and helps selecting appropriate slope mitigation strategies.
We exploit modern numerical modelling techniques based on finite ...
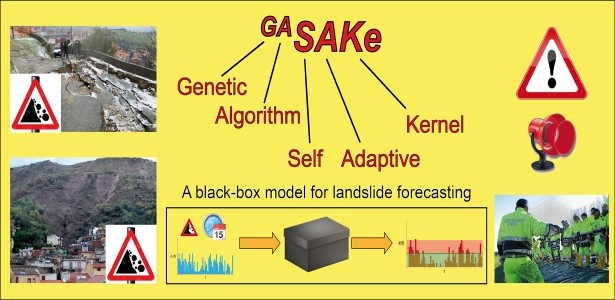
We developed GASAKe, Genetic Algorithm-based Self-Adaptive Kernel, a new model to predict the time of occurrence of rainfall induced landslides.
GASAKe predicts the time of occurrence of single landslides or groups of similar landslides, both shallow and deep-seated, using a threshold than when exceeded determines the initiation of the landslides. The triggering threshold is defined using historical information on rainfall and ...
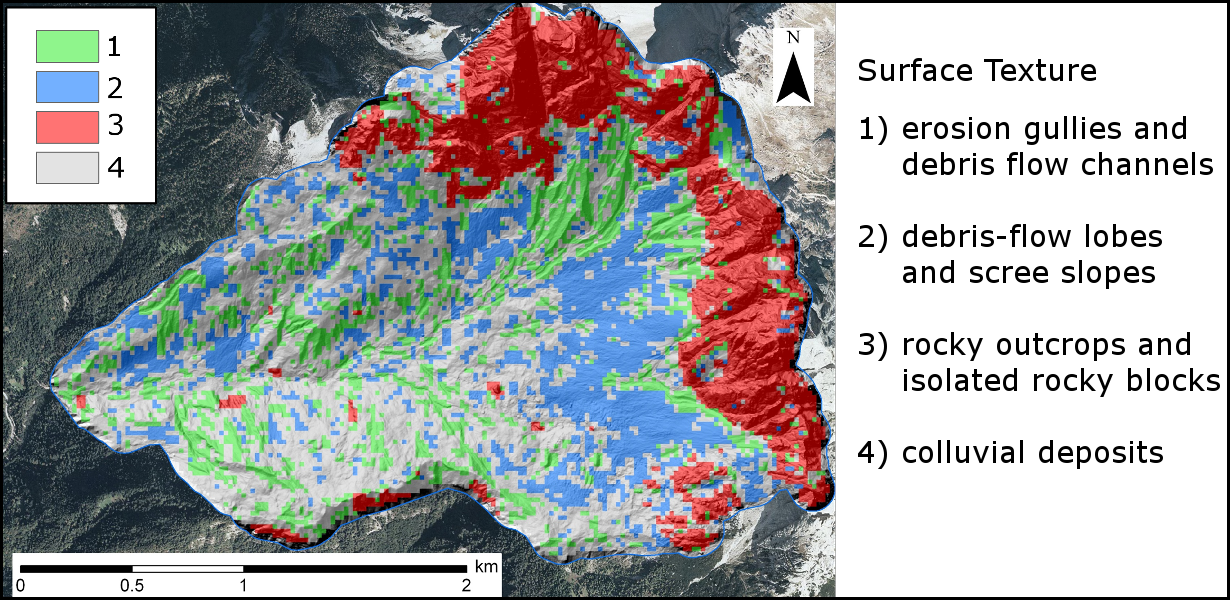
Geomorphometry complements the traditional qualitative description of landforms with a quantitative approach based on the analysis of Digital Terrain Models, which are numerical representations of the topography.
For the purpose, geomorphometry develops and exploits new algorithms in GIS (Geographical Information System) environments.
The scope of the analysis is to derive parameters (e.g., terrain slope, surface roughness), or ...
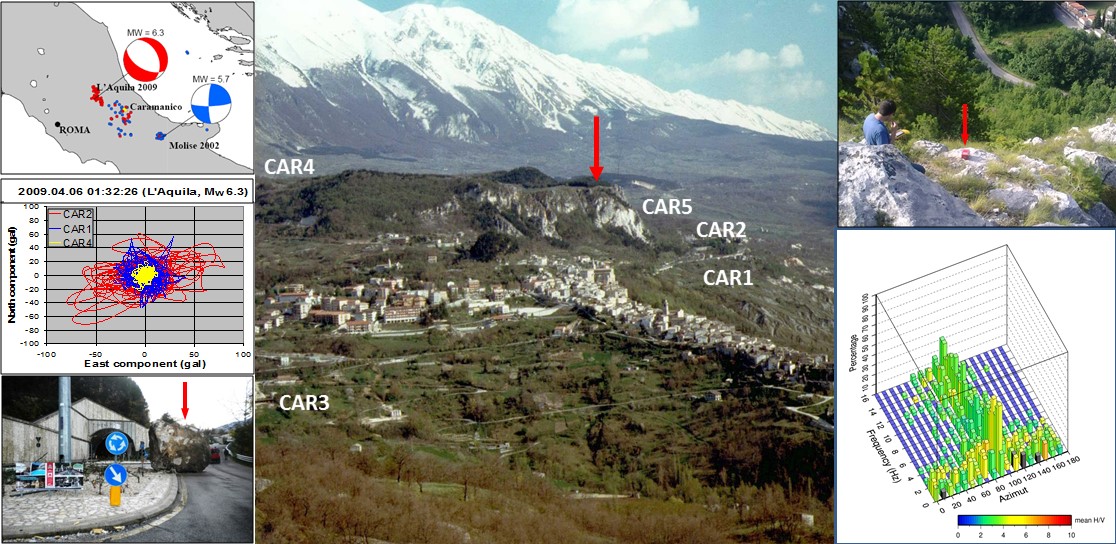

Landslides and earthquakes are important geological hazards in Italy, where mountains and hills dominate a landscape characterized by the presence of weak geological materials. The geological and morphological settings result in high susceptibility to landslides under seismic conditions. Italy is also one of the most active tectonic regions in Europe; and seismic shaking is known to have caused landslides in Italy.
Numerous historical ...
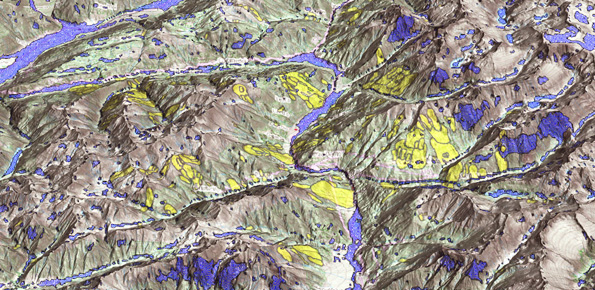
Landslide susceptibility is the propensity of a territory to generate landslides.
Many methods are available to determine landslide susceptibility, whereas only a few attempts were made to outline areas not likely to generate landslides i.e., non-susceptible landslide areas. This is surprising, because for planning purposes it is just as important (if not more important) to know where landslides are not expected than to know where landslides ...

Between the late 19th and early 21st century, in the Alps the average air temperature has increased by about 2 °C, more than twice the increase in temperature in the northern hemisphere, of 0.8 °C. In the same period, precipitation showed a tendency towards an increase in the northern part of the Alps, and a tendency towards a decrease in the southern sector of the Alps.
Since the end of the Little Ice Age (about 1850), glaciers in the ...
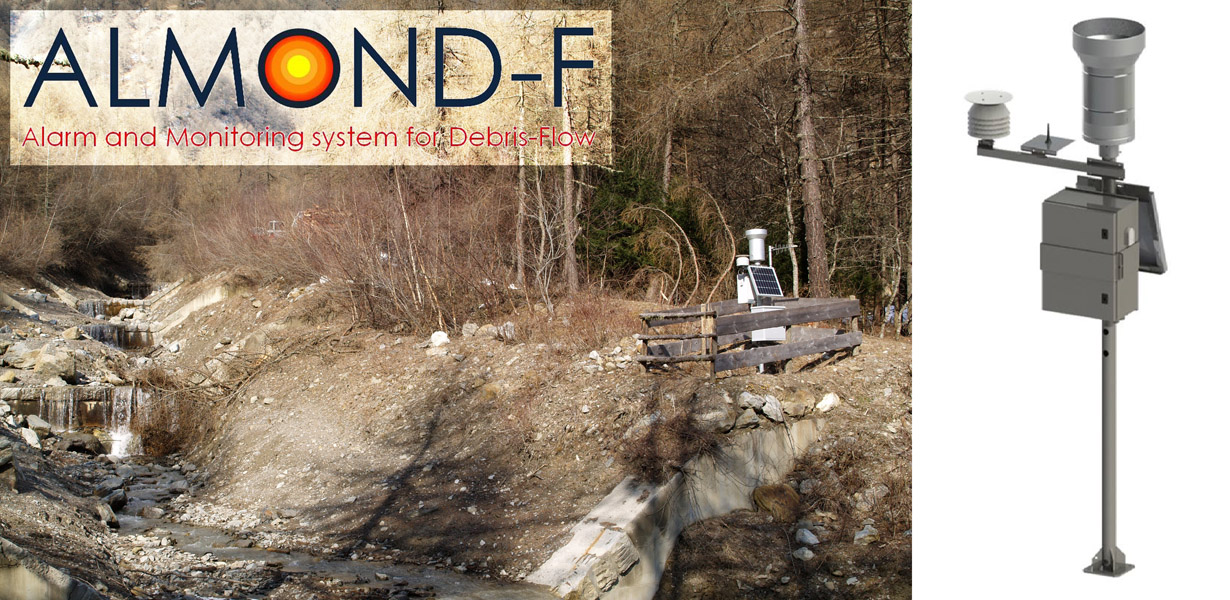

ALMOND-F is an innovative unit for the microseismic detection of debris flows using a network of geophones.
The microseismic detection of debris flows is more complex than other types of monitoring. Use of the geophones requires: (1) the selection of the level of amplification of the signal, which depends on the distance from the stream; (2) the selection of the sampling frequency of the seismic signal, which must be sufficiently high; (3) ...

Despite the large number and frequency of landslides and floods that affect our territories, and the information on landslides and floods available also online, the subject of geo-hydrological hazards remains poorly known to the Italian citizens. The lack of understanding reflects in the limited perception of the population on the geo-hydrological risks in Italy.
One reason for the lack of understanding is the way in which the subject of ...
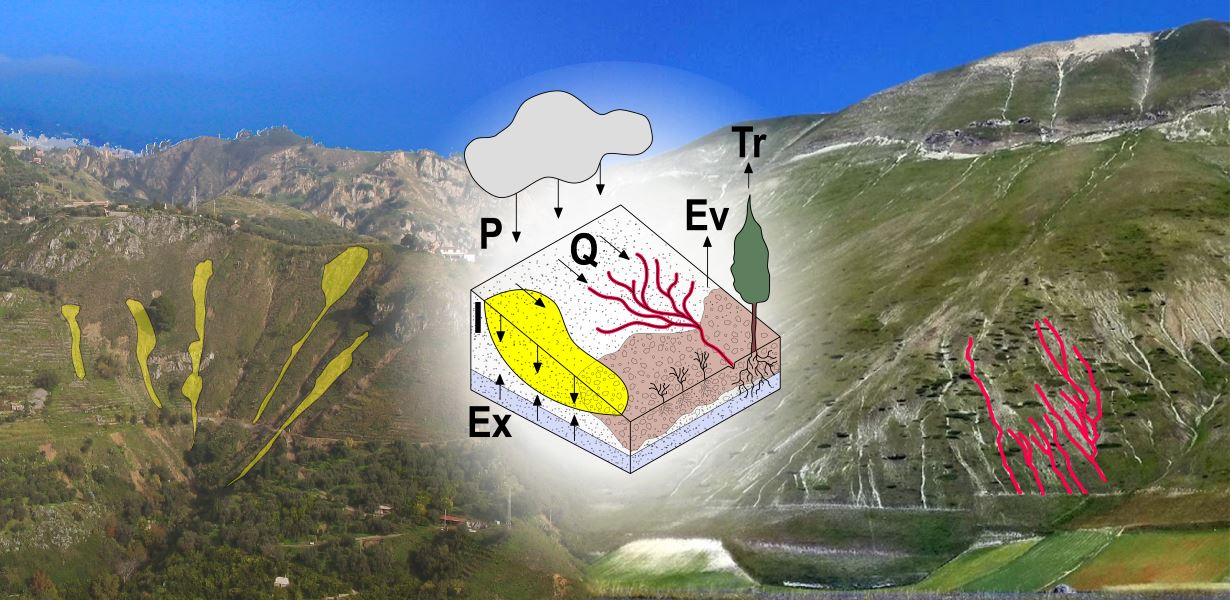
Different approaches have been proposed to model landslide and erosion processes separately. Only a few attempts have been made to model landslide and erosion jointly. Some models consider the effects of landslides on sediment yield and transport. In other cases, landslides and erosion processes are components of a landscape evolution model. However, existing models do not describe jointly the triggering mechanisms of landslide and erosion ...

Using long-term rainfall records obtained by the rain gauge network of the former Italian Hydrographic Service, in cooperation with colleagues in other CNR Institutes (ISAC and ISAFOM), we have studied the changes in the rainfall regimes in Calabria, Southern Italy.
Applying appropriate statistical methods, we checked the completeness of the historical records, verifying consistency and missing values in the records. We used the obtained ...

A recent research has been carried out by Marco Pagani, researcher of the Institute of Cognitive sciences and technologies of the Italian National Research Council (Istc-Cnr) in Rome. The research has documented, with electroencephalographic monitoring techniques (EEG), the cerebral effects deriving from the re-processing of a traumatic memory (https://www.cnr.it/it/news/5761/dall-emdr-un-aiuto-per-superare-i-traumi). In particular, the ...
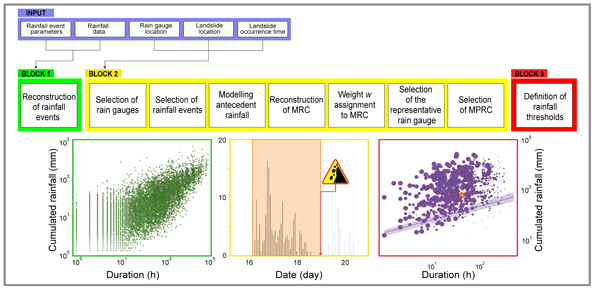
The empirical rainfall thresholds while representing a useful approach used to forecast landslide occurrence in wide areas, are affected by several uncertainties related to the rainfall and the landslide information accuracy, the reconstruction of the rainfall events responsible for the failure, and the method to calculate the thresholds. Definition of the rainfall conditions responsible for landslides is a crucial issue and may contribute to ...

It is part of the mission of the Italian National Research Council, and consequently of our Institute, the task of producing new knowledge. This aim, fundamental to the social and cultural progress of our Country, needs to be accompanied by another, equally important, target: ensure that the quality of learning and knowledge already conquered, and the quality of its retransmission to future generations are properly preserved.
Are we sure we ...

SM2RAIN is an innovative system for the estimation of the rainfall, based on measurements of the soil water content. SM2RAIN considers the soil as a natural rain gauge, and by measuring temporal variations of the soil water content, it estimates the rainfall falling on the soil, adopting a “bottom up” approach. Technically, SM2RAIN relies on the inversion of the soil water balance equation that computes the repartition of rainfall in ...
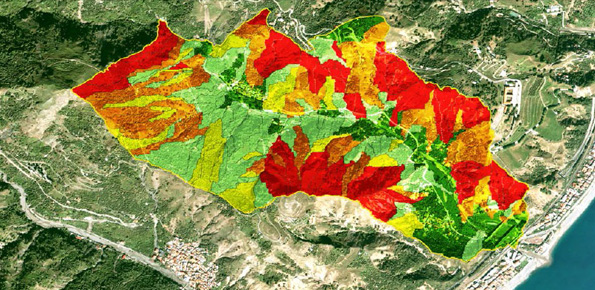
Landslide susceptibility is the likelihood of a landslide occurring in an area, given the local terrain conditions. It is the degree to which an area can be affected by future landslides i.e., an estimate of “where” landslides are more likely to occur.
Landslide susceptibility does not consider the temporal occurrence or the magnitude of the expected landslides. In mathematical language, landslide susceptibility can be expressed as the ...

La sperimentazione ad ampio raggio condotta negli ultimi anni per testare sul campo la funzionalità e l’efficacia della procedura semplificata per la rielaborazione dei ricordi traumatici (RINOEL) ha consentito di evidenziare con sempre maggior chiarezza gli effetti esercitati da tali ricordi sull’attenzione di una persona. La capacità di concentrazione di un individuo, e dunque la sua abilità di focalizzare l’attenzione, risente ...
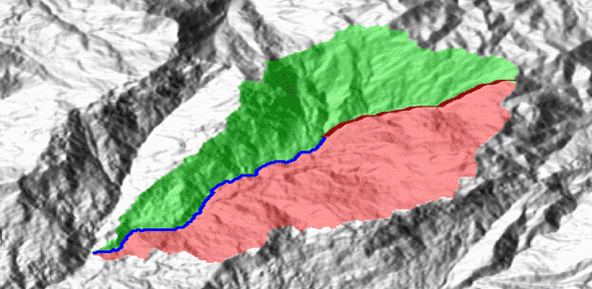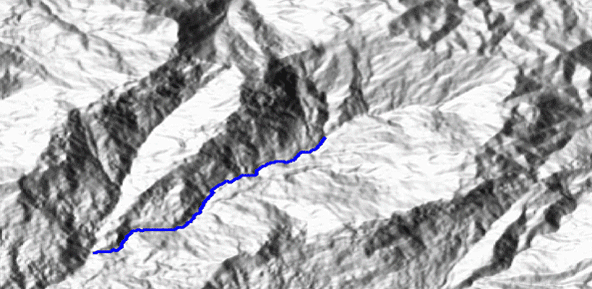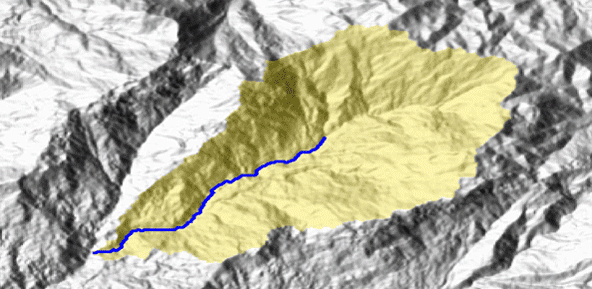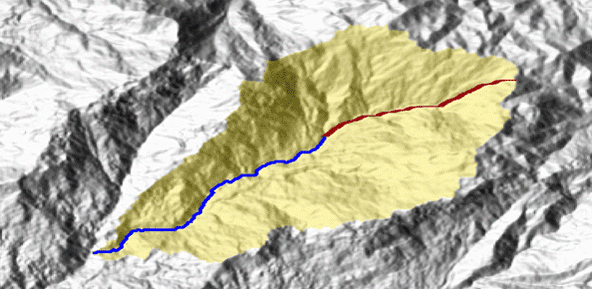
Quantitative geomorphological and environmental analysis requires the adoption of mapping units, well-defined spatial domains as basic mapping units which provide local boundaries to aggregate environmental and morphometric variables and to perform calculations. Grid cells, typically aligned with a digital elevation model, are the standard mapping unit choice. A wiser choice is represented by slope units, irregular terrain partitions delimited ...
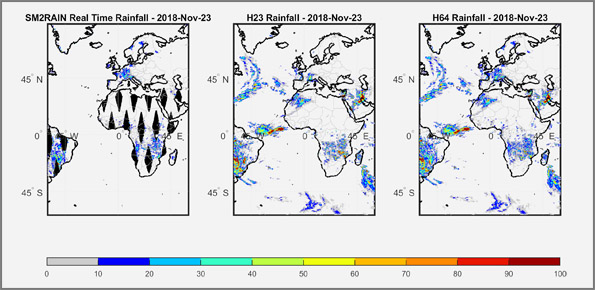
We have developed a new satellite rainfall product in near real-time. The product, called H64, is based on the integration of rainfall estimates obtained through two satellite sources. The developed algorithm combines estimates obtained by applying the SM2RAIN algorithm to satellite soil moisture data and those provided by a state-of-the-art product already operating on the full-disk area of the Meteosat satellites (60° West - 60° East, 60° ...
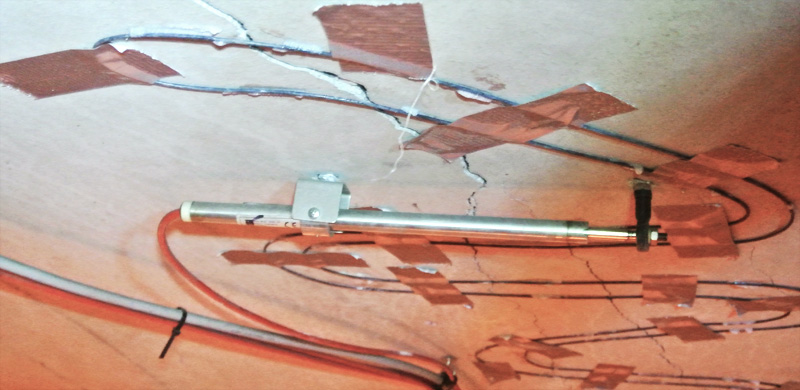
Optical fibres are generally aimed at large bandwidth transmission, and a few people know that the proposal of optical fibres as sensing elements is almost as old as their proposal as transmission media.
Over the last 25 years, fibre optic sensor technology has assumed a dominant role in several fields of applications. Fibre optic sensors (FOSs) offer several advantages compared to legacy electronic and mechanic sensors. FOSs are immune to ...

Flash floods occur in small to medium size river basins, and are characterised by fast temporal evolution. Because of their intensity and short warning times, flash floods often cause not only major economic damage, but also loss of lives.
An integrated approach to documentation and analysis of flash floods has to include the following issues:
post-flood observations aimed at estimating peak discharge and reconstructing temporal ...

Glaciers are typical of the Alpine landscape, and an important source of water. Undoubtedly fascinating, glaciers are very complex and yet surprisingly poorly known. In the Alps, many studies focus on the volumetric changes of glaciers, proving their almost systematic reduction in the current climatic period. Little is known about the daily behaviour of Alpine glaciers. This is partly due to the inhospitable and not easily accessible ...
 On 28 May 2025, at15:24 (CEST), the frontal part of the Birch Glacier in Valais (CH), estimated at around 3 million m3, collapsed, dragging with it over 6 million m3 of debris that had accumulated on its surface over the previous weeks, following a sequence of rockfalls from the northern slope of the Kleines Nesthorn (3335 m a.s.l.). The ice mass disintegrated immediately after detachment, giving rise to a catastrophic ice-rock avalanche with a ...
On 28 May 2025, at15:24 (CEST), the frontal part of the Birch Glacier in Valais (CH), estimated at around 3 million m3, collapsed, dragging with it over 6 million m3 of debris that had accumulated on its surface over the previous weeks, following a sequence of rockfalls from the northern slope of the Kleines Nesthorn (3335 m a.s.l.). The ice mass disintegrated immediately after detachment, giving rise to a catastrophic ice-rock avalanche with a ...  The use of remotely piloted aircraft systems (RPASs) in geosciences is often aimed at the acquisition of an image sequence to produce digital models and orthophotographs of the topographic surface. Such photogrammetric technique can be applied for rockfall hazard and risk assessment. To study rockfalls, an approach consists in the application of numerical models for the computation of rockfall trajectories. Data required for such simulations ...
The use of remotely piloted aircraft systems (RPASs) in geosciences is often aimed at the acquisition of an image sequence to produce digital models and orthophotographs of the topographic surface. Such photogrammetric technique can be applied for rockfall hazard and risk assessment. To study rockfalls, an approach consists in the application of numerical models for the computation of rockfall trajectories. Data required for such simulations ...  The LiDAR sensor available to the institute has recently turned seven years since the first survey executed on November 2, 2011, in the aftermath of the flood event that affected large areas of the Liguria Region, northern Italy.
The system consists of a laser head RIEGL LMS-Q680i, a medium format camera Hasselblad H3DII-39Mpixel f=50mm, an IMU IGI 256Khz, and a GNSS system Novatel-OEM4, and has since operated on many Italian areas thanks to ...
The LiDAR sensor available to the institute has recently turned seven years since the first survey executed on November 2, 2011, in the aftermath of the flood event that affected large areas of the Liguria Region, northern Italy.
The system consists of a laser head RIEGL LMS-Q680i, a medium format camera Hasselblad H3DII-39Mpixel f=50mm, an IMU IGI 256Khz, and a GNSS system Novatel-OEM4, and has since operated on many Italian areas thanks to ...  River discharge is defined as the amount of water flowing through a river over a specified period of time. Its estimate is crucial for all the operations of hydraulic structures design, the territorial planning and the flood risk assessment and management. River discharge at a specific river cross-section is not a direct measurement, but it is calculated by measuring other hydraulic quantities such as the flow velocity and the water depth, i.e. ...
River discharge is defined as the amount of water flowing through a river over a specified period of time. Its estimate is crucial for all the operations of hydraulic structures design, the territorial planning and the flood risk assessment and management. River discharge at a specific river cross-section is not a direct measurement, but it is calculated by measuring other hydraulic quantities such as the flow velocity and the water depth, i.e. ...  The researches and the experimentations carried out, in the learning field, by the IRPI Institute during the last years, started out initially in the field of geoethics, have allowed to set up principles and didactic tools that offer today practical and usable tools to significantly improve, in a relatively short period of time, the expressive, learning and assimilation capacities of students and adults.
The researches have been originally ...
The researches and the experimentations carried out, in the learning field, by the IRPI Institute during the last years, started out initially in the field of geoethics, have allowed to set up principles and didactic tools that offer today practical and usable tools to significantly improve, in a relatively short period of time, the expressive, learning and assimilation capacities of students and adults.
The researches have been originally ...  The Mar Piccolo basin is an internal sea basin located along the Ionian coast (Southern Italy), and it is surrounded primarily by fractured carbonate karstic environment.
In primarily karstic environments, infiltration is greater than runoff; in the karstic coastal Apulian aquifers, the groundwater discharge to the sea is more than two-fold greater than the surface discharge, notwithstanding the high discharges by wells. In such ...
The Mar Piccolo basin is an internal sea basin located along the Ionian coast (Southern Italy), and it is surrounded primarily by fractured carbonate karstic environment.
In primarily karstic environments, infiltration is greater than runoff; in the karstic coastal Apulian aquifers, the groundwater discharge to the sea is more than two-fold greater than the surface discharge, notwithstanding the high discharges by wells. In such ...  Sinkholes occurrence is related to the presence of an underground cavity, from which instability starts and propagate upwards until causing the collapse of the surface soil layer. The cavity may have a natural or artificial origin. Natural caves are due to presence of soluble rocks, and are typical of karst settings, where most of the sinkholes occur for dissolution processes. Man has excavated Anthropogenic cavities, for different purposes and ...
Sinkholes occurrence is related to the presence of an underground cavity, from which instability starts and propagate upwards until causing the collapse of the surface soil layer. The cavity may have a natural or artificial origin. Natural caves are due to presence of soluble rocks, and are typical of karst settings, where most of the sinkholes occur for dissolution processes. Man has excavated Anthropogenic cavities, for different purposes and ...  Alluvial fans are known to be areas of high geomorphic activity, where debris flows and flash floods caused by intense and prolonged rainfall are a major hazard. In Calabria, southern Italy, alluvial fans are numerous. The exact age of the alluvial fans is seldom known, but most of the fans in Calabria are considered recent in age (Holocene).
Due to the significant increase in urbanization in the last two centuries, many alluvial fans are ...
Alluvial fans are known to be areas of high geomorphic activity, where debris flows and flash floods caused by intense and prolonged rainfall are a major hazard. In Calabria, southern Italy, alluvial fans are numerous. The exact age of the alluvial fans is seldom known, but most of the fans in Calabria are considered recent in age (Holocene).
Due to the significant increase in urbanization in the last two centuries, many alluvial fans are ...  Our AIS (Automated Inclinometer System) allows for fully automatic inclinometer measurements in standard boreholes. The deep measurements have multiple applications, including (i) evaluating the rate of deep-seated ground deformation in landslide areas, (ii) evaluating the volume of deep-seated landslides, and (ii) assessing landslide hazards.
The AIS is composed of an electronic control manager, an inclinometer probe (with traditional ...
Our AIS (Automated Inclinometer System) allows for fully automatic inclinometer measurements in standard boreholes. The deep measurements have multiple applications, including (i) evaluating the rate of deep-seated ground deformation in landslide areas, (ii) evaluating the volume of deep-seated landslides, and (ii) assessing landslide hazards.
The AIS is composed of an electronic control manager, an inclinometer probe (with traditional ...  Not all that flows in creeks is water. Debris flows i.e., surges in which solid particles move together with little water, may occur in steep mountain streams, mainly as a consequence of intense rainfall. Debris flows have a high kinetic energy, and may cause major damage if they encroach buildings, roads and bridges. They are also a primary cause of landslide casualties. The video below shows an example of debris flows.
The low ...
Not all that flows in creeks is water. Debris flows i.e., surges in which solid particles move together with little water, may occur in steep mountain streams, mainly as a consequence of intense rainfall. Debris flows have a high kinetic energy, and may cause major damage if they encroach buildings, roads and bridges. They are also a primary cause of landslide casualties. The video below shows an example of debris flows.
The low ...  Geomorphometry complements the traditional qualitative description of landforms with a quantitative approach based on the analysis of Digital Terrain Models, which are numerical representations of the topography.
For the purpose, geomorphometry develops and exploits new algorithms in GIS (Geographical Information System) environments.
The scope of the analysis is to derive parameters (e.g., terrain slope, surface roughness), or ...
Geomorphometry complements the traditional qualitative description of landforms with a quantitative approach based on the analysis of Digital Terrain Models, which are numerical representations of the topography.
For the purpose, geomorphometry develops and exploits new algorithms in GIS (Geographical Information System) environments.
The scope of the analysis is to derive parameters (e.g., terrain slope, surface roughness), or ...  Between the late 19th and early 21st century, in the Alps the average air temperature has increased by about 2 °C, more than twice the increase in temperature in the northern hemisphere, of 0.8 °C. In the same period, precipitation showed a tendency towards an increase in the northern part of the Alps, and a tendency towards a decrease in the southern sector of the Alps.
Since the end of the Little Ice Age (about 1850), glaciers in the ...
Between the late 19th and early 21st century, in the Alps the average air temperature has increased by about 2 °C, more than twice the increase in temperature in the northern hemisphere, of 0.8 °C. In the same period, precipitation showed a tendency towards an increase in the northern part of the Alps, and a tendency towards a decrease in the southern sector of the Alps.
Since the end of the Little Ice Age (about 1850), glaciers in the ...  ALMOND-F is an innovative unit for the microseismic detection of debris flows using a network of geophones.
The microseismic detection of debris flows is more complex than other types of monitoring. Use of the geophones requires: (1) the selection of the level of amplification of the signal, which depends on the distance from the stream; (2) the selection of the sampling frequency of the seismic signal, which must be sufficiently high; (3) ...
ALMOND-F is an innovative unit for the microseismic detection of debris flows using a network of geophones.
The microseismic detection of debris flows is more complex than other types of monitoring. Use of the geophones requires: (1) the selection of the level of amplification of the signal, which depends on the distance from the stream; (2) the selection of the sampling frequency of the seismic signal, which must be sufficiently high; (3) ...  Despite the large number and frequency of landslides and floods that affect our territories, and the information on landslides and floods available also online, the subject of geo-hydrological hazards remains poorly known to the Italian citizens. The lack of understanding reflects in the limited perception of the population on the geo-hydrological risks in Italy.
One reason for the lack of understanding is the way in which the subject of ...
Despite the large number and frequency of landslides and floods that affect our territories, and the information on landslides and floods available also online, the subject of geo-hydrological hazards remains poorly known to the Italian citizens. The lack of understanding reflects in the limited perception of the population on the geo-hydrological risks in Italy.
One reason for the lack of understanding is the way in which the subject of ...  Using long-term rainfall records obtained by the rain gauge network of the former Italian Hydrographic Service, in cooperation with colleagues in other CNR Institutes (ISAC and ISAFOM), we have studied the changes in the rainfall regimes in Calabria, Southern Italy.
Applying appropriate statistical methods, we checked the completeness of the historical records, verifying consistency and missing values in the records. We used the obtained ...
Using long-term rainfall records obtained by the rain gauge network of the former Italian Hydrographic Service, in cooperation with colleagues in other CNR Institutes (ISAC and ISAFOM), we have studied the changes in the rainfall regimes in Calabria, Southern Italy.
Applying appropriate statistical methods, we checked the completeness of the historical records, verifying consistency and missing values in the records. We used the obtained ...  A recent research has been carried out by Marco Pagani, researcher of the Institute of Cognitive sciences and technologies of the Italian National Research Council (Istc-Cnr) in Rome. The research has documented, with electroencephalographic monitoring techniques (EEG), the cerebral effects deriving from the re-processing of a traumatic memory (https://www.cnr.it/it/news/5761/dall-emdr-un-aiuto-per-superare-i-traumi). In particular, the ...
A recent research has been carried out by Marco Pagani, researcher of the Institute of Cognitive sciences and technologies of the Italian National Research Council (Istc-Cnr) in Rome. The research has documented, with electroencephalographic monitoring techniques (EEG), the cerebral effects deriving from the re-processing of a traumatic memory (https://www.cnr.it/it/news/5761/dall-emdr-un-aiuto-per-superare-i-traumi). In particular, the ...  It is part of the mission of the Italian National Research Council, and consequently of our Institute, the task of producing new knowledge. This aim, fundamental to the social and cultural progress of our Country, needs to be accompanied by another, equally important, target: ensure that the quality of learning and knowledge already conquered, and the quality of its retransmission to future generations are properly preserved.
Are we sure we ...
It is part of the mission of the Italian National Research Council, and consequently of our Institute, the task of producing new knowledge. This aim, fundamental to the social and cultural progress of our Country, needs to be accompanied by another, equally important, target: ensure that the quality of learning and knowledge already conquered, and the quality of its retransmission to future generations are properly preserved.
Are we sure we ...  SM2RAIN is an innovative system for the estimation of the rainfall, based on measurements of the soil water content. SM2RAIN considers the soil as a natural rain gauge, and by measuring temporal variations of the soil water content, it estimates the rainfall falling on the soil, adopting a “bottom up” approach. Technically, SM2RAIN relies on the inversion of the soil water balance equation that computes the repartition of rainfall in ...
SM2RAIN is an innovative system for the estimation of the rainfall, based on measurements of the soil water content. SM2RAIN considers the soil as a natural rain gauge, and by measuring temporal variations of the soil water content, it estimates the rainfall falling on the soil, adopting a “bottom up” approach. Technically, SM2RAIN relies on the inversion of the soil water balance equation that computes the repartition of rainfall in ...  La sperimentazione ad ampio raggio condotta negli ultimi anni per testare sul campo la funzionalità e l’efficacia della procedura semplificata per la rielaborazione dei ricordi traumatici (RINOEL) ha consentito di evidenziare con sempre maggior chiarezza gli effetti esercitati da tali ricordi sull’attenzione di una persona. La capacità di concentrazione di un individuo, e dunque la sua abilità di focalizzare l’attenzione, risente ...
La sperimentazione ad ampio raggio condotta negli ultimi anni per testare sul campo la funzionalità e l’efficacia della procedura semplificata per la rielaborazione dei ricordi traumatici (RINOEL) ha consentito di evidenziare con sempre maggior chiarezza gli effetti esercitati da tali ricordi sull’attenzione di una persona. La capacità di concentrazione di un individuo, e dunque la sua abilità di focalizzare l’attenzione, risente ...  Quantitative geomorphological and environmental analysis requires the adoption of mapping units, well-defined spatial domains as basic mapping units which provide local boundaries to aggregate environmental and morphometric variables and to perform calculations. Grid cells, typically aligned with a digital elevation model, are the standard mapping unit choice. A wiser choice is represented by slope units, irregular terrain partitions delimited ...
Quantitative geomorphological and environmental analysis requires the adoption of mapping units, well-defined spatial domains as basic mapping units which provide local boundaries to aggregate environmental and morphometric variables and to perform calculations. Grid cells, typically aligned with a digital elevation model, are the standard mapping unit choice. A wiser choice is represented by slope units, irregular terrain partitions delimited ...  We have developed a new satellite rainfall product in near real-time. The product, called H64, is based on the integration of rainfall estimates obtained through two satellite sources. The developed algorithm combines estimates obtained by applying the SM2RAIN algorithm to satellite soil moisture data and those provided by a state-of-the-art product already operating on the full-disk area of the Meteosat satellites (60° West - 60° East, 60° ...
We have developed a new satellite rainfall product in near real-time. The product, called H64, is based on the integration of rainfall estimates obtained through two satellite sources. The developed algorithm combines estimates obtained by applying the SM2RAIN algorithm to satellite soil moisture data and those provided by a state-of-the-art product already operating on the full-disk area of the Meteosat satellites (60° West - 60° East, 60° ...  Optical fibres are generally aimed at large bandwidth transmission, and a few people know that the proposal of optical fibres as sensing elements is almost as old as their proposal as transmission media.
Over the last 25 years, fibre optic sensor technology has assumed a dominant role in several fields of applications. Fibre optic sensors (FOSs) offer several advantages compared to legacy electronic and mechanic sensors. FOSs are immune to ...
Optical fibres are generally aimed at large bandwidth transmission, and a few people know that the proposal of optical fibres as sensing elements is almost as old as their proposal as transmission media.
Over the last 25 years, fibre optic sensor technology has assumed a dominant role in several fields of applications. Fibre optic sensors (FOSs) offer several advantages compared to legacy electronic and mechanic sensors. FOSs are immune to ...  Flash floods occur in small to medium size river basins, and are characterised by fast temporal evolution. Because of their intensity and short warning times, flash floods often cause not only major economic damage, but also loss of lives.
An integrated approach to documentation and analysis of flash floods has to include the following issues:
post-flood observations aimed at estimating peak discharge and reconstructing temporal ...
Flash floods occur in small to medium size river basins, and are characterised by fast temporal evolution. Because of their intensity and short warning times, flash floods often cause not only major economic damage, but also loss of lives.
An integrated approach to documentation and analysis of flash floods has to include the following issues:
post-flood observations aimed at estimating peak discharge and reconstructing temporal ...  Glaciers are typical of the Alpine landscape, and an important source of water. Undoubtedly fascinating, glaciers are very complex and yet surprisingly poorly known. In the Alps, many studies focus on the volumetric changes of glaciers, proving their almost systematic reduction in the current climatic period. Little is known about the daily behaviour of Alpine glaciers. This is partly due to the inhospitable and not easily accessible ...
Glaciers are typical of the Alpine landscape, and an important source of water. Undoubtedly fascinating, glaciers are very complex and yet surprisingly poorly known. In the Alps, many studies focus on the volumetric changes of glaciers, proving their almost systematic reduction in the current climatic period. Little is known about the daily behaviour of Alpine glaciers. This is partly due to the inhospitable and not easily accessible ...