Which characteristics should optical satellite images have to detect and map landslides? It depends …
A proper selection of optical satellite images for landslides detection and mapping should be based on the landslide “signature”, when landslides occur in response to intense or prolonged rainfall, or earthquakes. This is the first step to get a good quality landslide inventory map
Landslides leave discernible signs on the land surface, most of which can be captured in remote sensing images. On the images the signs appear as modification of the photographic characteristics as tone, colour, mottling and texture, or/and as modification of morphological characteristics including shape, curvature, convexity and concavity. These signs are the landslide signature. Trained geomorphologists analyse remote sensing images and map landslides through heuristic interpretation of photographic and morphological characteristics.
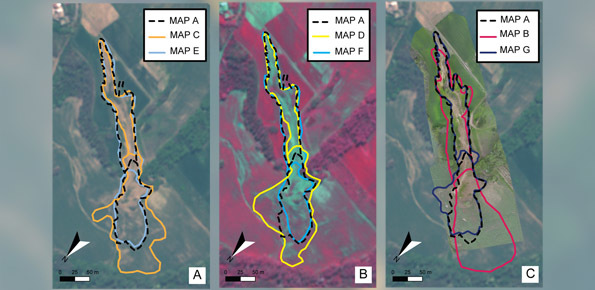
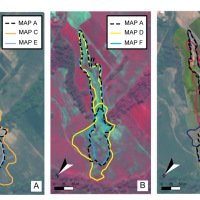
Despite a wide use of remote sensing images for landslide mapping, no attempt to evaluate how the images characteristics influence landslide identification and mapping exists. We made an experiment to determine the effects of optical image characteristics, such as spatial resolution, spectral content and image type (2D or 3D), on landslide mapping. We do so by comparing the maps prepared for one rainfall-induced landslide (Assignano landslide) in a pairwise approach, including a benchmark map. The seven maps were obtained using different techniques and images: (i) field-based reconnaissance mapping, (ii) the interpretation of ultra-resolution images taken by an optical camera on-board of a UAV, and (iii) the visual interpretation of Very High Resolution (VHR), monoscopic and stereoscopic, multispectral images taken by the WordView-2 satellite. These comparisons included an eighth map, obtained through dGPS survey, considered as the “ground truth”.
Results show that image’s characteristics to be selected for obtaining a high quality inventory map, depend on the type of landslide signature. Albeit conducted on a single landslide, the experiment results are general, and provide useful information to decide on the optimal imagery for the production of event, seasonal and multi-temporal landslide inventory maps.
Results
To perform the comparison were prepared eight separate and independent cartographic representations of the studied landslide. Comparison of the eight maps were made using the Error index proposed by Carrara et. al and published in the ITC Journal. The experiment showed that map closest to the benchmark was obtained using the higher resolution image, where the landslide signature was primarily photographical (in the landslide source and transport area). Conversely, where the landslide signature was mainly morphological (in the landslide deposit) the best mapping result was obtained using the stereoscopic i.e. 3D images.
Granting institutions
- Italian National Department of Civil Protection;
- Servizio Protezione Civile della Città Metropolitana di Torino.
To know more
Fiorucci F., Giordan D., Santangelo M., Dutto F., Rossi M., Guzzetti, F. 2018. Criteria for the optimal selection of remote sensing optical images to map event landslides. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci., 18, 405–417. https://doi.org/10.5194/nhess-18-405-2018.



 Contact person: federica fiorucci -
Contact person: federica fiorucci -