Projects
Geothermal Atlas of Southern Italy Project
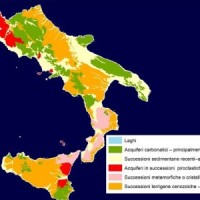 The Geothermal Atlas project is aimed at the characterization, classification and mapping of geothermal resources, conventional and unconventional types, for the production of electricity in the regions of Southern Italy. It also provides training and information stretched to increase the skills of the industry and the public's knowledge about the various aspects of geothermal energy, especially the unconventional, in order to promote the ...
The Geothermal Atlas project is aimed at the characterization, classification and mapping of geothermal resources, conventional and unconventional types, for the production of electricity in the regions of Southern Italy. It also provides training and information stretched to increase the skills of the industry and the public's knowledge about the various aspects of geothermal energy, especially the unconventional, in order to promote the ... La Ricerca ITaliana per il MARE
 UK The Italian maritime cluster represents for Italy an important economic sector contributing to 2.6% of national GDP, 11% of production in the industry of transport, and using almost 1% of the units of work identified in the country, share as high as 2% including the impact of upstream and downstream, for a total of around 480,000 employees (Cluster and maritime development in Italy and in the regions CENSIS - September 2011). In the European ...
UK The Italian maritime cluster represents for Italy an important economic sector contributing to 2.6% of national GDP, 11% of production in the industry of transport, and using almost 1% of the units of work identified in the country, share as high as 2% including the impact of upstream and downstream, for a total of around 480,000 employees (Cluster and maritime development in Italy and in the regions CENSIS - September 2011). In the European ... Assessment of water Balances and Optimisation based Target setting across EU River Basins
 ABOT is one of the Pilot projects on Development of Prevention Activities to Halt Desertification in Europe, partly funded by DG Environment of the European Commission. The objective of the pilot projects is to support the development of concrete pilot initiatives on innovative technologies, techniques or practices in order to contribute to the exchanges of good practice and innovation for halting the desertification in ...
ABOT is one of the Pilot projects on Development of Prevention Activities to Halt Desertification in Europe, partly funded by DG Environment of the European Commission. The objective of the pilot projects is to support the development of concrete pilot initiatives on innovative technologies, techniques or practices in order to contribute to the exchanges of good practice and innovation for halting the desertification in ... Sinkholes in the Marina di Lesina area
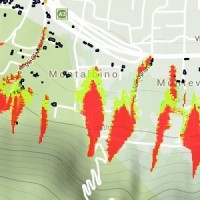
 Sinkholes are in Apulia among the main geohazards, and are at the origin of severe interactions with the anthropogenic environment, and heavy losses to society. Since several years the territory of Marina di Lesina is diffusely affected by development of sinkholes (that have caused an emergency state to be declared), mostly concentrated near the Acquarotta Channel, linking the Lesina Lake to the Adriatic ...
Sinkholes are in Apulia among the main geohazards, and are at the origin of severe interactions with the anthropogenic environment, and heavy losses to society. Since several years the territory of Marina di Lesina is diffusely affected by development of sinkholes (that have caused an emergency state to be declared), mostly concentrated near the Acquarotta Channel, linking the Lesina Lake to the Adriatic ... The Via Firenze Sinkhole of in the Municipality of Gallipoli
 Among the most recent sinkhole events, registered in Apulia region, that occurred in Via Firenze at Gallipoli on March 29, 2007, greatly raised the attention by public opinion, having affected (likely, without causing any fatalities) the built-up areas of one of the largest towns in Salento. The event pointed out to the need to carry out detailed studies on the sinkholes related to artificial ...
Among the most recent sinkhole events, registered in Apulia region, that occurred in Via Firenze at Gallipoli on March 29, 2007, greatly raised the attention by public opinion, having affected (likely, without causing any fatalities) the built-up areas of one of the largest towns in Salento. The event pointed out to the need to carry out detailed studies on the sinkholes related to artificial ... Changing Hydro-meteorological Risks as Analyzed by a New Generation of European Scientists
 The European Commission has identified the need for adaptations in risk management as a consequence to climate and environmental changes in several documents. The implementation of risk management measures such as disaster preparedness programmes, land-use planning, regulatory zoning and early warning systems are considered essential. Further, multi-risk assessment approaches are not used in planning practice: risk indicators are hardly used ...
The European Commission has identified the need for adaptations in risk management as a consequence to climate and environmental changes in several documents. The implementation of risk management measures such as disaster preparedness programmes, land-use planning, regulatory zoning and early warning systems are considered essential. Further, multi-risk assessment approaches are not used in planning practice: risk indicators are hardly used ... Register of the caves and artificial cavities of Apulia
 Within the framework of the project “Register of the Caves and Artificial Cavities of Apulia Region” (PO FESR 2007-2016), committed by the Ecology Service to the Apulian Speleological Federation (FSP), this latter involved CNR-IRPI to guarantee high scientific value to the documents to be produced, and to work with the cavers in the different phases of the ...
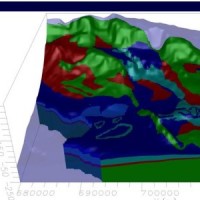
Within the framework of the project “Register of the Caves and Artificial Cavities of Apulia Region” (PO FESR 2007-2016), committed by the Ecology Service to the Apulian Speleological Federation (FSP), this latter involved CNR-IRPI to guarantee high scientific value to the documents to be produced, and to work with the cavers in the different phases of the ... Evaluating the geothermal potential in the Southern Regions of Italy
 VIGOR contributed to increasing knowledge in exploitation of geothermal resources. It was aimed at providing information useful to start exploration and utilization of geothermal energy, through reconnaissance, analyses and studies, valorise geothermal resources in Calabria, Campania, Puglia and Sicily.
In particular, geological and geothermal characterization were carried both at regional scale (i.e. maps of geothermal potential) and at the ...
VIGOR contributed to increasing knowledge in exploitation of geothermal resources. It was aimed at providing information useful to start exploration and utilization of geothermal energy, through reconnaissance, analyses and studies, valorise geothermal resources in Calabria, Campania, Puglia and Sicily.
In particular, geological and geothermal characterization were carried both at regional scale (i.e. maps of geothermal potential) and at the ... Ground Deformations Risk Scenarios: an advanced assessment service
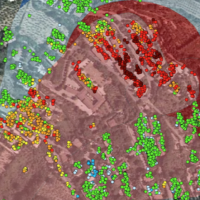 DORIS - Ground Deformations Risk Scenarios: an advanced assessment service is an advanced downstream service for the detection, mapping, monitoring and forecasting of ground deformations, at different temporal and spatial scales and in various physiographic and climatic and environments. DORIS integrates traditional and innovative Earth Observation (EO) and ground based (non-EO) data and technologies to improve our understanding of the ...
DORIS - Ground Deformations Risk Scenarios: an advanced assessment service is an advanced downstream service for the detection, mapping, monitoring and forecasting of ground deformations, at different temporal and spatial scales and in various physiographic and climatic and environments. DORIS integrates traditional and innovative Earth Observation (EO) and ground based (non-EO) data and technologies to improve our understanding of the ... DInSAR techniques for the assessment of sinkhole hazard
 Sinkholes occur as sudden collapses of the ground, related to natural cavities produced by karst processes in soluble rocks, or to man-made cavities deriving from different types of human activities in different historical ages. Sinkholes are widespread all over the world, and the related hazard is extremely high, with very severe damage to built-up areas and human infrastructures, and heavy losses to the ...
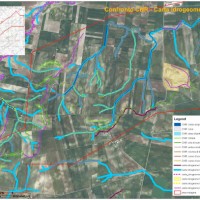
Sinkholes occur as sudden collapses of the ground, related to natural cavities produced by karst processes in soluble rocks, or to man-made cavities deriving from different types of human activities in different historical ages. Sinkholes are widespread all over the world, and the related hazard is extremely high, with very severe damage to built-up areas and human infrastructures, and heavy losses to the ... Identification of the channel network in the Autonomous Province of Trento
 The accurate representation of the channel network is fundamental in cartography. The increasing availability of high-resolution, LiDAR-derived DTMs provides an excellent topographic basis for the representation of the channel network, but requires innovative techniques for managing and processing ...
The accurate representation of the channel network is fundamental in cartography. The increasing availability of high-resolution, LiDAR-derived DTMs provides an excellent topographic basis for the representation of the channel network, but requires innovative techniques for managing and processing ... GIS technologies for managing sinkhole hazard
 The widespread sinkholes that involve large sectors of the Apulian territory are related to natural cavities produced by karst processes in soluble rocks, or to man-made cavities deriving from different types of human activities in different historical ages. The related hazard is extremely high, with very severe damage to built-up areas and human infrastructures, and heavy losses to the ...
The widespread sinkholes that involve large sectors of the Apulian territory are related to natural cavities produced by karst processes in soluble rocks, or to man-made cavities deriving from different types of human activities in different historical ages. The related hazard is extremely high, with very severe damage to built-up areas and human infrastructures, and heavy losses to the ... Glacial hazards in the western Alps
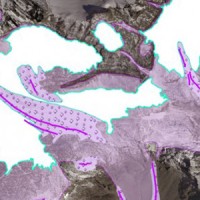 The project is included in Operative Program of the European cross-border territorial cooperation "Alcotra 2007-2013". It brings together specialized scientific expertise Italian and French that deal to study the mountain and its dangerousness. It is divided into a part of studies conducted on the entire framework of the Western Alps and in actions on the pilot sites identified by the ...
The project is included in Operative Program of the European cross-border territorial cooperation "Alcotra 2007-2013". It brings together specialized scientific expertise Italian and French that deal to study the mountain and its dangerousness. It is divided into a part of studies conducted on the entire framework of the Western Alps and in actions on the pilot sites identified by the ... Investigation of postglacial fault zones using DInSAR
 Fennoscandia bears witness of the Pleistocene glaciation in the form of a series of large geological faults. Pärvie which is the longest runs for 150 km. No information is available on its state of activity and no surface deformations data have ever been collected. The length of the fault and its location, make the traditional monitoring techniques unfeasible and ...
Fennoscandia bears witness of the Pleistocene glaciation in the form of a series of large geological faults. Pärvie which is the longest runs for 150 km. No information is available on its state of activity and no surface deformations data have ever been collected. The length of the fault and its location, make the traditional monitoring techniques unfeasible and ... Hazards in karst areas and mitigation strategies
 The high fragility of karst terrains, and the deriving vulnerability to a number of possible events, together with the presence of significant natural (first and foremost, groundwater), landscape and historical resources, are at the origin of the project activities, aimed at the safeguard of karst environments and the mitigation of the related ...
The high fragility of karst terrains, and the deriving vulnerability to a number of possible events, together with the presence of significant natural (first and foremost, groundwater), landscape and historical resources, are at the origin of the project activities, aimed at the safeguard of karst environments and the mitigation of the related ... Continuous monitoring of the seismogenic Paganica fault (AQ) after the April 6 2009 L’Aquila earthquake
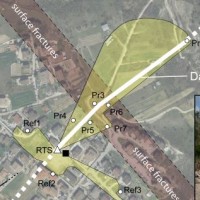 The L’Aquila earthquake occurred the 6th April 2009, causing several casualties and damages to a large number of buildings and infrastructures. The event was a 6.3 moment magnitude (Mw). In the days following the earthquake, several aftershocks with Mw>4 affected the same general area. In total, within an area of about 50 km radius from L’Aquila town, the seismic sequence counted ca. 2×104 events in about one year. Among the severely ...
The L’Aquila earthquake occurred the 6th April 2009, causing several casualties and damages to a large number of buildings and infrastructures. The event was a 6.3 moment magnitude (Mw). In the days following the earthquake, several aftershocks with Mw>4 affected the same general area. In total, within an area of about 50 km radius from L’Aquila town, the seismic sequence counted ca. 2×104 events in about one year. Among the severely ... Updating the list of Apulian municipalities with presence of man-made cavities
 The widespread occurrence of sinkholes related to man-made cavities in Apulia highlights the need to perform a careful reconnaissance of the artificial caves over the whole region, and of their stability conditions. Knowledge of the presence and typology of artificial cavity, and of its main features, is a mandatory step for the mitigation of the sinkhole ...
The widespread occurrence of sinkholes related to man-made cavities in Apulia highlights the need to perform a careful reconnaissance of the artificial caves over the whole region, and of their stability conditions. Knowledge of the presence and typology of artificial cavity, and of its main features, is a mandatory step for the mitigation of the sinkhole ... Cassini Extended Mission
The project, funded by ASI under the coordination of INAF (Istituto di Astrofisica Spaziale), involved Italian research groups active in data analysis from Cassini-Huygens probe, orbiting around Saturn and its ...
Design and restore underground
 Puglia is one of the italian region with a higher density of hypogean sites of great value from the archaeological historical and artistic point of view. Many of them are in so precarious conditions that it is not possible to comprehend the precise history of the places and to define restoration interventions for their utilization and ...
Puglia is one of the italian region with a higher density of hypogean sites of great value from the archaeological historical and artistic point of view. Many of them are in so precarious conditions that it is not possible to comprehend the precise history of the places and to define restoration interventions for their utilization and ... Long-term Permafrost Monitoring Network
 Permafrost is very sensitive to climate change and the risks associated with its degradation affect traffic routes, settlements and infrastructure. Data on the distribution of permafrost are inconsistent and there is no common strategy to tackle this problem. Local administrators should have the means to manage the risks associated with the degradation of the ...
Permafrost is very sensitive to climate change and the risks associated with its degradation affect traffic routes, settlements and infrastructure. Data on the distribution of permafrost are inconsistent and there is no common strategy to tackle this problem. Local administrators should have the means to manage the risks associated with the degradation of the ... Database of post-wildfire debris-flow activity in Mediterranean ecosystems
 Wildfires can have profound effects on the hydrologic response of watersheds, and debris-flow activity is among the most destructive consequences of these effects. The continued high likelihood of catastrophic wildfires in Mediterranean climates has created the need to develop methods to identify and quantify potential debris flow hazards from burned ...
Wildfires can have profound effects on the hydrologic response of watersheds, and debris-flow activity is among the most destructive consequences of these effects. The continued high likelihood of catastrophic wildfires in Mediterranean climates has created the need to develop methods to identify and quantify potential debris flow hazards from burned ... Mountain Risks: from prediction to management and governance
 The observed increase in disastrous events over the last decades, associated with a low perception of risk by the communities involved, along with the lack of efficient, socially accepted and environmentally sound remedial measures are amongst the motivation behind this research project. The adaptation of a combined multi-risk-oriented analysis, in which the investigations focus more on the interdependence of events rather than on single event, ...
The observed increase in disastrous events over the last decades, associated with a low perception of risk by the communities involved, along with the lack of efficient, socially accepted and environmentally sound remedial measures are amongst the motivation behind this research project. The adaptation of a combined multi-risk-oriented analysis, in which the investigations focus more on the interdependence of events rather than on single event, ... Progetto Presídi
 Il progetto presidi soddisfa un’esigenza normativa (D.P.C.M. 27/02/2004) e conoscitiva della Protezione Civile Regionale del Piemonte; diventa uno strumento funzionale all’aggiornamento dei punti di criticità idrogeologica del territorio, individuati e verificati dopo una complessa indagine retrospettiva e lunga concertazione di diversi Enti territoriali competenti, e al loro monitoraggio durante le fasi parossistiche di eventi di piena o ...
Il progetto presidi soddisfa un’esigenza normativa (D.P.C.M. 27/02/2004) e conoscitiva della Protezione Civile Regionale del Piemonte; diventa uno strumento funzionale all’aggiornamento dei punti di criticità idrogeologica del territorio, individuati e verificati dopo una complessa indagine retrospettiva e lunga concertazione di diversi Enti territoriali competenti, e al loro monitoraggio durante le fasi parossistiche di eventi di piena o ... Hydrometeorological data resources and technologies for effective flash flood forecasting
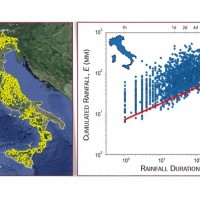
 Flash-floods develop at space and time scales that conventional observation systems for rainfall and river discharge are not able to monitor. Consequently, the atmospheric and hydrological generating mechanisms of flash-floods are poorly understood, leading to highly uncertain forecasts of these ...
Flash-floods develop at space and time scales that conventional observation systems for rainfall and river discharge are not able to monitor. Consequently, the atmospheric and hydrological generating mechanisms of flash-floods are poorly understood, leading to highly uncertain forecasts of these ... Albanian International Center on Marine Sciences
 The project CISM faces problems related to marine Albanian waters in view of the Adriatic basin, which must meet various environmental problems in other portions of the Adriatic Sea, which are still influenced by the contribution of Albanian waters. CISM is not only a time of growth of the scientific culture of Albania, but also a landmark in the international scenario of the Adriatic ...
The project CISM faces problems related to marine Albanian waters in view of the Adriatic basin, which must meet various environmental problems in other portions of the Adriatic Sea, which are still influenced by the contribution of Albanian waters. CISM is not only a time of growth of the scientific culture of Albania, but also a landmark in the international scenario of the Adriatic ... Vulnerability maps for monitoring and management of groundwater resources in the Archimed area
Monitoring, Forecasting and Best Practices for FLOOD Mitigation & Prevention in the CADSES Region
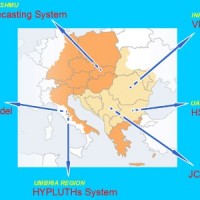 Hydrometeorological monitoring and flood forecasting are indispensable in preventing hydraulic hazard and ensuring civil protection. Implementing a sustainable plan to combat floods requires further activities, such as best practices for agricultural, forestry and land use management in flood risk areas. Methodologies must be developped within a transnational context, transending local ...
Hydrometeorological monitoring and flood forecasting are indispensable in preventing hydraulic hazard and ensuring civil protection. Implementing a sustainable plan to combat floods requires further activities, such as best practices for agricultural, forestry and land use management in flood risk areas. Methodologies must be developped within a transnational context, transending local ... Karst sinkholes in urban areas in Florida
 Sinkholes are among the main features of karst areas, and are extremely widespread in Florida, one of the sites most known for their occurrence and the likely interaction with the built-up environment. The Tampa area, in turn, shows an high frequency of events, which origin derives from different types of ...
Sinkholes are among the main features of karst areas, and are extremely widespread in Florida, one of the sites most known for their occurrence and the likely interaction with the built-up environment. The Tampa area, in turn, shows an high frequency of events, which origin derives from different types of ... Prevention, Information and Early Warning pre-operational services to support the management of risks
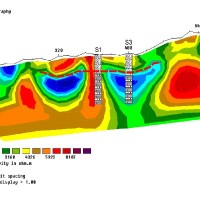 PREVIEW is an integrated project by the European Commission 6th Framework Programme, led by the EURORISK Consortium, a multi-disciplinary European Team of committing Actors of the domain: Civil Protections and Environmental Bodies; Scientific communities and Service operators, at national and regional level, for Meteorology, Hydrology, Seismology, Volcanology and GIS services based on Space data; and Industry. The project was organized around a ...
PREVIEW is an integrated project by the European Commission 6th Framework Programme, led by the EURORISK Consortium, a multi-disciplinary European Team of committing Actors of the domain: Civil Protections and Environmental Bodies; Scientific communities and Service operators, at national and regional level, for Meteorology, Hydrology, Seismology, Volcanology and GIS services based on Space data; and Industry. The project was organized around a ... Extreme Events Causes and Consequences
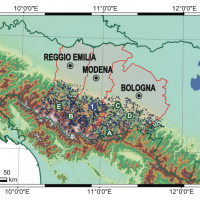 Extreme events are a key manifestation of complex systems, in both the natural and human world. Their economic and social consequences are a matter of enormous concern. Much of science has concentrated, until recently, on understanding the mean behaviour of physical, biological or social systems and their “normal” variability. Extreme events, due to their rarity, have been hard to study and even harder to predict. E2-C2 developed methods ...
Extreme events are a key manifestation of complex systems, in both the natural and human world. Their economic and social consequences are a matter of enormous concern. Much of science has concentrated, until recently, on understanding the mean behaviour of physical, biological or social systems and their “normal” variability. Extreme events, due to their rarity, have been hard to study and even harder to predict. E2-C2 developed methods ...