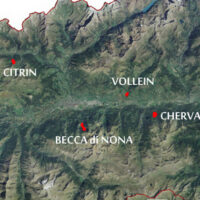
The Aosta Valley is a small alpine region affected by numerous landslides, varying in size and type, ranging from isolated rock falls to rotational/translational slides up to extensive deep landslides. The study of such landslides, functional to a more effective risk management and to guarantee adequate safety standards, represents a primary necessity for a mountain territory like this ...
Geological-geotechnical monitoring systems are one of the most effective tools for landslide characterization, both in terms of landslide detection and for monitoring purposes. The regional monitoring network of Regione Lombardia represents an exemplary case in Italy, with as many as 44 landslides monitored, of which more than half in real time.
The management of monitoring networks and early warning systems represents a complex component, in ...
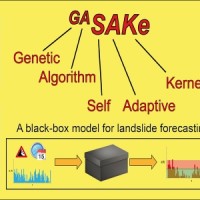
We developed GASAKe, Genetic Algorithm-based Self-Adaptive Kernel, a new model to predict the time of occurrence of rainfall induced landslides.
GASAKe predicts the time of occurrence of single landslides or groups of similar landslides, both shallow and deep-seated, using a threshold than when exceeded determines the initiation of the landslides. The triggering threshold is defined using historical information on rainfall and ...

ALMOND-F is an innovative unit for the microseismic detection of debris flows using a network of geophones.
The microseismic detection of debris flows is more complex than other types of monitoring. Use of the geophones requires: (1) the selection of the level of amplification of the signal, which depends on the distance from the stream; (2) the selection of the sampling frequency of the seismic signal, which must be sufficiently high; (3) ...
In recent years, following short and intense meteoric events, along the railway line of the Department of Reggio Calabria, there have been a series of interruptions in correspondence of basins below 3-4 km2. Based on the current procedures for risk mitigation in RFI, in the event of a "red alert" issued by the Civil Protection, RFI management locate along the railway line personal in correspondence of the area in question. This procedure is ...
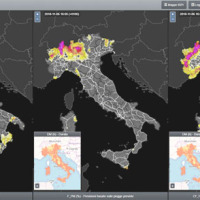
SANF-RFI is a landslide early warning system along the RFI national railway Infrastructure. The system forecasts the possible occurrence of landslides by comparing rainfall measurements and forecasts with empirical rainfall thresholds for the possible occurrence of landslides. Specifically, the system consists of three components: (i) for rainfall and other data input and storage, (ii) for data processing and analysis, and (iii) for the ...
Since 2013, CNR IRPI went in with the collection of information on rainfall events that have resulted in landslides in the Liguria region. Rainfall thresholds can be used in early warning systems for the prediction of the occurrence of rainfall-induced landslides. To respond to a request of the Italian national Department for Civil Protection (DPC), CNR IRPI designed and developed SANF, an Italian acronym for National Early Warning System for ...

Among all types of landslide phenomena present in Alpine environment, the rockfalls are certainly the most impacting, because they also are extremely widespread. Rockfall are very difficult to monitor and they are often managed exclusively through the execution of active or passive works aimed at risk mitigation. Due to the rockfalls impulsive behavior, it is a difficult task to locate them a priori. The problem of rockfalls can be approached ...

The Apulia region is affected by multiple types of geo-hydrological instability processes such as sinkholes, flash floods and landslides.
Landsliding mainly affects the north-western sector of the Region (bordering with Apennine chain) and the sea rocky cliffs.
The sub-Appennine Daunia portion of the Region is exposed to landslide risk due to hydro-geological setup of the soil/rock deposits, the poor mechanical properties of the ...
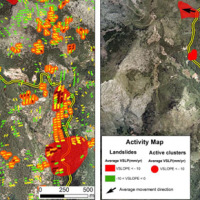
The project is focused on monitoring geohazard-associated ground deformations, a key prevention action specifically addressed to urban areas and critical infrastructures. The project will propose a procedure to produce maps to assess continuously the potential impact of geohazard activity. These maps will provide inputs to support early warning, giving information on the stability of the monitored areas and to evaluate the expected ...

The project is focused on flood forecasting and hydraulic risk, i.e. the assessment of the effects of flooding in flood-prone areas also involving the vulnerability assessment of the hydraulic structures (dams, leaves, bridges, etc.).
The effects of flood events are not completely eliminated by structural measures, therefore it is necessary to develop complementary non-structural measures, such as real-time Flood Forecasting and Warning ...
In Italy, landslides are triggered by intense and/or prolonged rainfall. The spatial and temporal forecast of multiple landslides triggered by rainfall in wide areas relies primarily on empirical rainfall thresholds. It is widely believed that the thresholds are influenced by the local topographic (morphological), lithological, soil, and climatic settings. For this reason, it is necessary to define local rainfall thresholds. Reliable local ...

In India, as in many other areas in Asia and in the world, landslides are abundant and frequent, and they represent a serious hazard to the local population. The aim of LANDSLIP is to develop tools, including operational systems, to contribute to reducing impacts of hydrologically related landslide multi-hazards and to building resilience to landslides in vulnerable and hazard-prone areas of ...

With more than 5 million people affected, more than 1000 killed, and with estimated total damages exceeding 4.5 billion Euros just in Europe and during the last decade, floods are among the most disruptive natural events threatening our Society. Due to increase in extreme weather events and rapid socio-economic developments in vulnerable locations, the risks connected to floods in general are growing rapidly, and the awareness of these risks ...
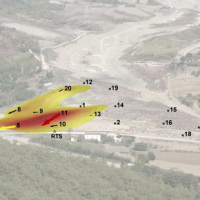
The 3DA software is a new procedure that allows retrieving in near-real-time 3D surface deformation models starting from data acquired via robotized total stations or others system that acquire the surface displacements. The measurements are first pre-processed and then implemented on 3D maps that include vector arrows representative of the intensities and of the real directions of motion in a given system of coordinates. The 3D surface ...
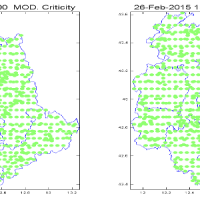
Real time evaluation of the rainfall and soil moisture conditions over the analysis grid point, and the combination with the available vulnerability and susceptibility information for the definition of the dynamic risk ...

Following the recent technological development, the role of landslides monitoring has become increasingly important, especially for the study and management of large landslides in emergency scenarios. In the last decades, CNR IRPI developed a range of skills dedicated to the design, installation and management of monitoring systems that can be considered for a technical and scientific support in many national emergencies. CNR IRPI can apply ...
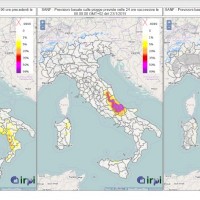
SANF is a landslide early warning system based on the comparison between rainfall measurements and forecasts and empirical rainfall thresholds. Specifically, the system consists of three components: (i) for rainfall and other data input and storage, (ii) for data processing and analysis, and (iii) for the production and delivery of the ...

In Italy rainfall are among the main causes of trigger of shallow landslides, that yearly cause fatalities, damage, and severe economic losses. Identification of the amount of rainfall needed to trigger landslides, and the forecasting of rainfall-induced landslides, are of interest for the scientific community, as well as for the whole ...
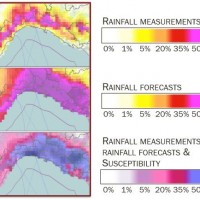
In Italy, landslides are triggered by intense and/or prolonged rainfall. The spatial and temporal forecast of multiple landslides triggered by rainfall in wide areas relies primarily on empirical rainfall thresholds. It is widely believed that the thresholds are influenced by the local topographic (morphological), lithological, soil, and climatic settings. For this reason, it is necessary to define local rainfall thresholds. Reliable local ...

Monitoring of debris flows in instrumented areas is carried out since many years in different Countries worldwide. It is still missing, however, an adequate standardization of methodologies, instrumentations and procedures. The instrumented areas are also employed for testing warning systems. Even though these latter have been more and more employed, a systematic experimentation of these systems has not yet been carried ...

The Mont de La Saxe landslide affects the south-western side of Mont de La Saxe near Courmayeur, Valle d'Aosta. This landslide at present can be considered one of the most critical active landslides in the Italian Alps. The estimated unstable mass is more than eight millions of cubic meters and the main elements at risk are the hamlets of La Palud and Entreves, and the motorway access to the international tunnel of the Mont ...
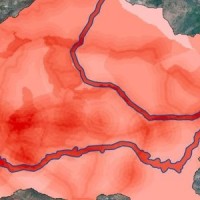
FLIRE is a demonstration project aiming to the development of an integrated Decision Support System (DSS) for both flash floods and forest fires risk assessment and management. The DSS tool will be designed by using state of art tools, technologies and methods and taking into account prevention, adaptation and interaction issues. The final model will be online available to key stakeholders and relevant authorities (local and national) for the ...
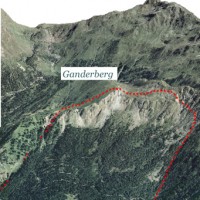
A Deep-seated Gravitational Slope Deformation (DGSD) affects the south-west flank of mount Ganderberg (Moso in Passiria – BZ). The continuous displacements of the landslide induce secondary hazardous phenomena. A 800.000 m3 rock slab shows signs of incipient movement; a detachment could create a natural barrier on the river ...

At the beginning of November 2010 exceptional rainfall events stroke the Veneto Region causing the re-activation of the Rotolon landslide which is a serious threat to the town of Recoaro Terme, Vicenza, ...

Following the run aground off near the "Isola del Giglio" (Tuscany, Italy, January 13, 2012) of the cruise vessel "Costa Concordia", a monitoring system for handling the security of the SAR (Search and Rescue) operations and for the control of the ships' movements/deformations during the subsequent defueling and recovery phases has been progressively installed and ...
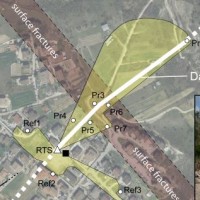
The L’Aquila earthquake occurred the 6th April 2009, causing several casualties and damages to a large number of buildings and infrastructures. The event was a 6.3 moment magnitude (Mw). In the days following the earthquake, several aftershocks with Mw>4 affected the same general area. In total, within an area of about 50 km radius from L’Aquila town, the seismic sequence counted ca. 2×104 events in about one year. Among the severely ...
 ALMOND-F is an innovative unit for the microseismic detection of debris flows using a network of geophones.
The microseismic detection of debris flows is more complex than other types of monitoring. Use of the geophones requires: (1) the selection of the level of amplification of the signal, which depends on the distance from the stream; (2) the selection of the sampling frequency of the seismic signal, which must be sufficiently high; (3) ...
ALMOND-F is an innovative unit for the microseismic detection of debris flows using a network of geophones.
The microseismic detection of debris flows is more complex than other types of monitoring. Use of the geophones requires: (1) the selection of the level of amplification of the signal, which depends on the distance from the stream; (2) the selection of the sampling frequency of the seismic signal, which must be sufficiently high; (3) ...  In recent years, following short and intense meteoric events, along the railway line of the Department of Reggio Calabria, there have been a series of interruptions in correspondence of basins below 3-4 km2. Based on the current procedures for risk mitigation in RFI, in the event of a "red alert" issued by the Civil Protection, RFI management locate along the railway line personal in correspondence of the area in question. This procedure is ...
In recent years, following short and intense meteoric events, along the railway line of the Department of Reggio Calabria, there have been a series of interruptions in correspondence of basins below 3-4 km2. Based on the current procedures for risk mitigation in RFI, in the event of a "red alert" issued by the Civil Protection, RFI management locate along the railway line personal in correspondence of the area in question. This procedure is ...  Among all types of landslide phenomena present in Alpine environment, the rockfalls are certainly the most impacting, because they also are extremely widespread. Rockfall are very difficult to monitor and they are often managed exclusively through the execution of active or passive works aimed at risk mitigation. Due to the rockfalls impulsive behavior, it is a difficult task to locate them a priori. The problem of rockfalls can be approached ...
Among all types of landslide phenomena present in Alpine environment, the rockfalls are certainly the most impacting, because they also are extremely widespread. Rockfall are very difficult to monitor and they are often managed exclusively through the execution of active or passive works aimed at risk mitigation. Due to the rockfalls impulsive behavior, it is a difficult task to locate them a priori. The problem of rockfalls can be approached ...  The Apulia region is affected by multiple types of geo-hydrological instability processes such as sinkholes, flash floods and landslides.
Landsliding mainly affects the north-western sector of the Region (bordering with Apennine chain) and the sea rocky cliffs.
The sub-Appennine Daunia portion of the Region is exposed to landslide risk due to hydro-geological setup of the soil/rock deposits, the poor mechanical properties of the ...
The Apulia region is affected by multiple types of geo-hydrological instability processes such as sinkholes, flash floods and landslides.
Landsliding mainly affects the north-western sector of the Region (bordering with Apennine chain) and the sea rocky cliffs.
The sub-Appennine Daunia portion of the Region is exposed to landslide risk due to hydro-geological setup of the soil/rock deposits, the poor mechanical properties of the ...  The project is focused on flood forecasting and hydraulic risk, i.e. the assessment of the effects of flooding in flood-prone areas also involving the vulnerability assessment of the hydraulic structures (dams, leaves, bridges, etc.).
The effects of flood events are not completely eliminated by structural measures, therefore it is necessary to develop complementary non-structural measures, such as real-time Flood Forecasting and Warning ...
The project is focused on flood forecasting and hydraulic risk, i.e. the assessment of the effects of flooding in flood-prone areas also involving the vulnerability assessment of the hydraulic structures (dams, leaves, bridges, etc.).
The effects of flood events are not completely eliminated by structural measures, therefore it is necessary to develop complementary non-structural measures, such as real-time Flood Forecasting and Warning ...  With more than 5 million people affected, more than 1000 killed, and with estimated total damages exceeding 4.5 billion Euros just in Europe and during the last decade, floods are among the most disruptive natural events threatening our Society. Due to increase in extreme weather events and rapid socio-economic developments in vulnerable locations, the risks connected to floods in general are growing rapidly, and the awareness of these risks ...
With more than 5 million people affected, more than 1000 killed, and with estimated total damages exceeding 4.5 billion Euros just in Europe and during the last decade, floods are among the most disruptive natural events threatening our Society. Due to increase in extreme weather events and rapid socio-economic developments in vulnerable locations, the risks connected to floods in general are growing rapidly, and the awareness of these risks ...  The Mont de La Saxe landslide affects the south-western side of Mont de La Saxe near Courmayeur, Valle d'Aosta. This landslide at present can be considered one of the most critical active landslides in the Italian Alps. The estimated unstable mass is more than eight millions of cubic meters and the main elements at risk are the hamlets of La Palud and Entreves, and the motorway access to the international tunnel of the Mont ...
The Mont de La Saxe landslide affects the south-western side of Mont de La Saxe near Courmayeur, Valle d'Aosta. This landslide at present can be considered one of the most critical active landslides in the Italian Alps. The estimated unstable mass is more than eight millions of cubic meters and the main elements at risk are the hamlets of La Palud and Entreves, and the motorway access to the international tunnel of the Mont ...  FLIRE is a demonstration project aiming to the development of an integrated Decision Support System (DSS) for both flash floods and forest fires risk assessment and management. The DSS tool will be designed by using state of art tools, technologies and methods and taking into account prevention, adaptation and interaction issues. The final model will be online available to key stakeholders and relevant authorities (local and national) for the ...
FLIRE is a demonstration project aiming to the development of an integrated Decision Support System (DSS) for both flash floods and forest fires risk assessment and management. The DSS tool will be designed by using state of art tools, technologies and methods and taking into account prevention, adaptation and interaction issues. The final model will be online available to key stakeholders and relevant authorities (local and national) for the ...  A Deep-seated Gravitational Slope Deformation (DGSD) affects the south-west flank of mount Ganderberg (Moso in Passiria – BZ). The continuous displacements of the landslide induce secondary hazardous phenomena. A 800.000 m3 rock slab shows signs of incipient movement; a detachment could create a natural barrier on the river ...
A Deep-seated Gravitational Slope Deformation (DGSD) affects the south-west flank of mount Ganderberg (Moso in Passiria – BZ). The continuous displacements of the landslide induce secondary hazardous phenomena. A 800.000 m3 rock slab shows signs of incipient movement; a detachment could create a natural barrier on the river ...  Following the run aground off near the "Isola del Giglio" (Tuscany, Italy, January 13, 2012) of the cruise vessel "Costa Concordia", a monitoring system for handling the security of the SAR (Search and Rescue) operations and for the control of the ships' movements/deformations during the subsequent defueling and recovery phases has been progressively installed and ...
Following the run aground off near the "Isola del Giglio" (Tuscany, Italy, January 13, 2012) of the cruise vessel "Costa Concordia", a monitoring system for handling the security of the SAR (Search and Rescue) operations and for the control of the ships' movements/deformations during the subsequent defueling and recovery phases has been progressively installed and ...  The L’Aquila earthquake occurred the 6th April 2009, causing several casualties and damages to a large number of buildings and infrastructures. The event was a 6.3 moment magnitude (Mw). In the days following the earthquake, several aftershocks with Mw>4 affected the same general area. In total, within an area of about 50 km radius from L’Aquila town, the seismic sequence counted ca. 2×104 events in about one year. Among the severely ...
The L’Aquila earthquake occurred the 6th April 2009, causing several casualties and damages to a large number of buildings and infrastructures. The event was a 6.3 moment magnitude (Mw). In the days following the earthquake, several aftershocks with Mw>4 affected the same general area. In total, within an area of about 50 km radius from L’Aquila town, the seismic sequence counted ca. 2×104 events in about one year. Among the severely ... 
















