Geological-geotechnical monitoring systems are one of the most effective tools for landslide characterization, both in terms of landslide detection and for monitoring purposes. The regional monitoring network of Regione Lombardia represents an exemplary case in Italy, with as many as 44 landslides monitored, of which more than half in real time.
The management of monitoring networks and early warning systems represents a complex component, in ...
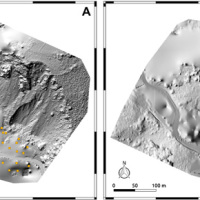
The use of remotely piloted aircraft systems (RPASs) in geosciences is often aimed at the acquisition of an image sequence to produce digital models and orthophotographs of the topographic surface. Such photogrammetric technique can be applied for rockfall hazard and risk assessment. To study rockfalls, an approach consists in the application of numerical models for the computation of rockfall trajectories. Data required for such simulations ...
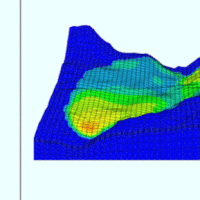
When soil behaviour is studied, whether landslide soils are concern, levee materials or foundations, the problem regarding how much and how reliable information about the soil properties we have available has to be addressed.
Understanding “what’s beneath” the visible surface is fundamental, yet complicated. Drillings are performed to analyse the stratigraphy of soils (the order and the thickness of the different soil levels) and ...
The Mar Piccolo basin is an internal sea basin located along the Ionian coast (Southern Italy), and it is surrounded primarily by fractured carbonate karstic environment.
In primarily karstic environments, infiltration is greater than runoff; in the karstic coastal Apulian aquifers, the groundwater discharge to the sea is more than two-fold greater than the surface discharge, notwithstanding the high discharges by wells. In such ...
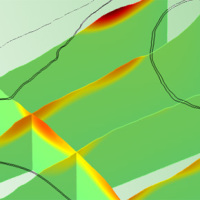
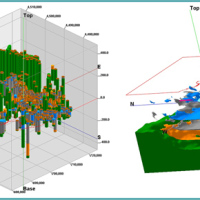
We experiment the application of 3D numerical modelling techniques for the analysis of the kinematics of slow-moving active landslides. The activity assesses the hazards posed by slow-moving landslides, determines the factors controlling the slope processes, investigates the potential evolution of the active slopes, and helps selecting appropriate slope mitigation strategies.
We exploit modern numerical modelling techniques based on finite ...
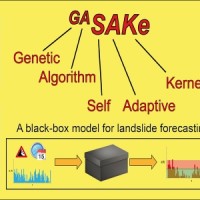
We developed GASAKe, Genetic Algorithm-based Self-Adaptive Kernel, a new model to predict the time of occurrence of rainfall induced landslides.
GASAKe predicts the time of occurrence of single landslides or groups of similar landslides, both shallow and deep-seated, using a threshold than when exceeded determines the initiation of the landslides. The triggering threshold is defined using historical information on rainfall and ...
Different approaches have been proposed to model landslide and erosion processes separately. Only a few attempts have been made to model landslide and erosion jointly. Some models consider the effects of landslides on sediment yield and transport. In other cases, landslides and erosion processes are components of a landscape evolution model. However, existing models do not describe jointly the triggering mechanisms of landslide and erosion ...
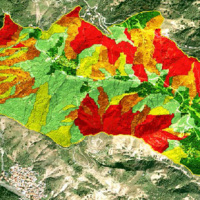
Landslide susceptibility is the likelihood of a landslide occurring in an area, given the local terrain conditions. It is the degree to which an area can be affected by future landslides i.e., an estimate of “where” landslides are more likely to occur.
Landslide susceptibility does not consider the temporal occurrence or the magnitude of the expected landslides. In mathematical language, landslide susceptibility can be expressed as the ...
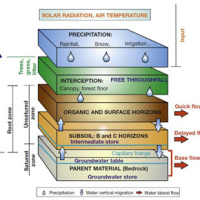
The area of interest specifically refers to the study of the following themes: extreme hydrological events and their interaction with slopes and watercourses; soil water erosion; debris flows; slope stability; triggering instability mechanisms; evolution of slope movements; monitoring systems for gravitational movements for the purpose of alerting for the mitigation of geo-hydrological risk. The activities proposed in the module are therefore ...

Past debris flows in the Rio Kortol catchment arise concerns for the safety of the village of Sauris di Sotto, and urge new studies for the assessment of hazard and the choice of risk mitigation ...
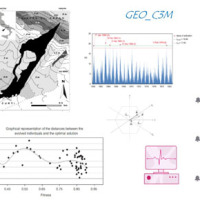
The project concerns the mitigation of natural hazards (mainly the effects on the territory and the anthropic environment caused by rains, earthquakes, volcanism, and Radon gas). The geological characterization is essential to frame the contexts and the expected phenomena. Numerical modeling and monitoring allow to predict the spatio-temporal evolution of the phenomena, and therefore to evaluate the risk for mitigation ...

Critical and depositional friction angles are characteristic for the deposition of a granular mass; the wrong angle adoption determines the ineffectiveness of a containment basin. The term is used with different meanings and measured by various procedures. The numerical simulation is a useful tool for the hazard assessment, but the definition of friction needed parameters requires insights on their ...
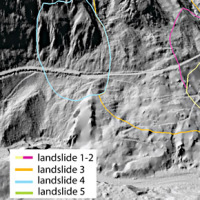
L’area del "Passo della Morte" (UD) è interessata da una situazione di grave dissesto a causa della presenza di più movimenti franosi. Questi sono caratterizzati da elevata pericolosità in relazione alle caratteristiche intrinseche dei fenomeni (volumetrie e velocità di spostamento), alla morfologia del versante ed alla geologia dell'area. La loro presenza mette a rischio la rete stradale che collega la Carnia con il Cadore e l’asta ...
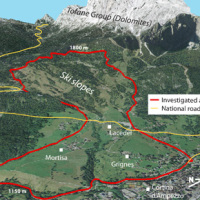
The study of the dynamics of large landslide is a heuristic process based on the integration of multiple investigation techniques: geological and geomorphological analysis, monitoring systems (traditional and innovative) and numerical models. Risk mitigation may require major interventions that call for detailed studies on the specific ...

With more than 5 million people affected, more than 1000 killed, and with estimated total damages exceeding 4.5 billion Euros just in Europe and during the last decade, floods are among the most disruptive natural events threatening our Society. Due to increase in extreme weather events and rapid socio-economic developments in vulnerable locations, the risks connected to floods in general are growing rapidly, and the awareness of these risks ...
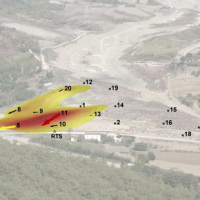
The 3DA software is a new procedure that allows retrieving in near-real-time 3D surface deformation models starting from data acquired via robotized total stations or others system that acquire the surface displacements. The measurements are first pre-processed and then implemented on 3D maps that include vector arrows representative of the intensities and of the real directions of motion in a given system of coordinates. The 3D surface ...

Italy has a tradition of scientific research and technological development on hazardous natural phenomena in general, and specifically on geo-hydrological hazards. Within the CNR, the “Progetti Finalizzati” Soil Conservation and Geodynamics (in the ’70s and ’80s), and GNDCI – the National Group for the Defence from Hydrogeological Disasters (in the ’80s and ’90s), have contributed to the advancement of knowledge ...

The hydro-meteorological monitoring is the operational tool for the measures of atmospheric, hydrologic ad hydraulic variables characterizing the hydrological cycle and it represents the grounds of IRPI’s research activities finalized to forecast, prevention and mitigation of natural hazards. Indeed, an accurate knowledge of processes at basis of natural phenomenon cannot disregard the direct measure of hydrological quantities, considering ...
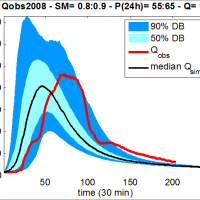
The project activities were carried out in two phases:
"dynamic scenarios of flood risk" identification through hydrologic-hydraulic modeling addressed to Civil Protection activities (2009-2011);
operational implementation of developed dynamic scenarios of flood risk and results dissemination trough web-GIS technologies, also within the context of Floods Directive 2007/60 /EC (2012-203); flood forecasting models implementation; ...
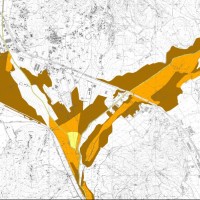
The activities of the project concern the delineation of hazard maps for return periods of 50, 100, 200 and 500 years for many reaches of interest identified in the secondary hydrographic network of Tiber ...
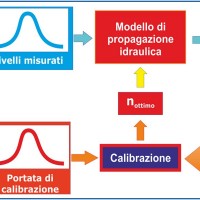
River discharge monitoring is fundamental for the study of the hydraulic regime of river flow and for the validation and calibration of rainfall-runoff models. The assessment of channel roughness coefficients associated with the measured discharges is fundamental for the calibration of flood routing models that can be used to address civil protection activities in real time. Unfortunately, the number of river flow monitoring stations in the ...
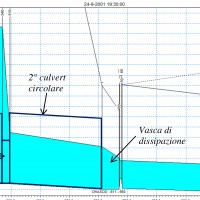
The artificial reservoirs are fundamental for water resources management, by regulating releases to meet the different users request (industrial, irrigation, hydropower, etc.), and for downstream territories floods defence through lamination of critical flood waves.
The main objective of the project concerns the review of hydrological-hydraulic studies carried out for the Montedoglio dam, on Tiber River, Casanuova dam, on Chiascio River, ...
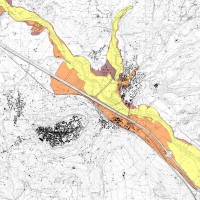
The Tiber River Basin Authority (ABT) and the Umbria Region (Service Water Resources and Hydraulic Risk), considering the verified underestimation of the flood-prone areas in the Paglia River basin provided by the Italian PAI (hydro-geological management plan) and the update of rating curves, decided to revise the hydrological study of the drainage basin in order to re-estimate the flood hazard maps for the Paglia River reach bounded upstream ...
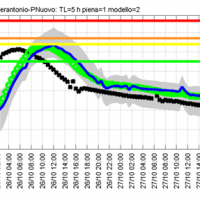
The project activities concern:
development and implementation of: 1) a semi-distributed continuous hydrological model (MISDc) for real-time soil moisture estimate and river discharge prediction in the Upper-Middle Tiber River basin; 2) a flood wave routing model (STAFOM-RCM) for stage hydrograph forecasting at some selected hydrometric stations in the Tiber River basin;
support for installation of soil moisture sensors in the ...
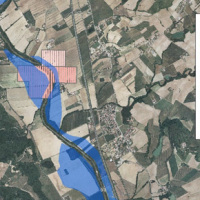
On 25-27 November 2005, the territory of central Italy was affected by heavy rainfall that hit the Tiber River basin and, mainly, the province of Perugia. The meteoric event had a significant phase with a duration of approximately 48 hours with widespread precipitation up to a maximum accumulated value higher than 100 mm. Significant increases in water levels occurred in most rivers of Upper-Middle Tiber
causing extended flooding in ...
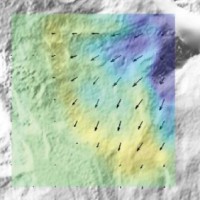
Based on the application of numerical modelling techniques, CNR – IRPI can provide consulting services on stability/instability conditions and kinematical evolution of potentially unstable slopes, underground caves, embankments, open-pit mines, landfills and any other type of natural or man-made soil/rock structure at ...

In Italy landslides and floods are frequent, widespread and dangerous phenomena, that cause fatalities and serious economic damage. In our country, landslides and floods pose major problems of scientific interest and of social and economic relevance.
The Institute is a Competence Centre for the Italian national Civil Protection Department, an Office of the Prime Minister. For the Department of Civil Protection we execute research and ...
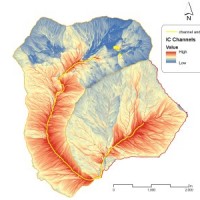
Water and sediment connectivity has emerged in recent years as a significant conceptual framework for understanding the transfer of surface water and sediment through landscapes. Connectivity can be seen both as a driver of hydrological and geomorphic processes within a catchment and as an emergent catchment property that is the result of processes acting at different ...

On December 3, 2013, a large landslide activated on the SW slope of Montescaglioso (Matera province, Basilicata), affecting an area with evidence of past instability. The landslide involved some 500 m of the main road to the village, and also interested several houses and other ...
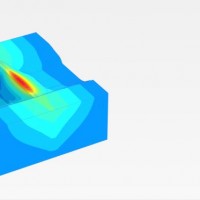
The project AIM-DAMS is aimed at developing a laboratory of integrated and advanced environmental monitoring for the control of the behavior of the earth-dams due to the different factors acting on the dams during their lifetime. Based on the integration of innovative and non-invasive sensors, as well as recent monitoring techniques and numerical modelling, the project is intended to fulfill the need of the dam management agencies of using ...
Glaciers are widely recognized as the best terrestrial indicator of climate change. Nevertheless, occurred changes, even in recent times, are often poorly known. Italy has a unique, secular history of glaciological documentation that, jointly with a rich wealth of spatial, multitemporal data, allows an accurate reconstruction of recent glacier evolution. Unfortunately, these data are dispersed and/or difficult to ...
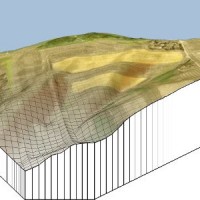
The application of distributed physically based models is possible on relatively small areas, typically hundreds or few thousands of km2. Distributed modelling of slope dynamics requires many sufficiently detailed information. Knowledge of geotechnical parameters and land use, digital terrain models, medium/high resolution cartography, temporal evolution of soil moisture conditions, are ...
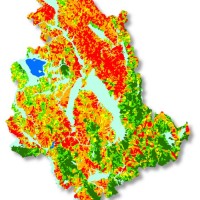
Realizzazione di modelli e carte di suscettibilità da frana tipo scorrimento per il territorio della Regione ...

The widespread sinkholes that involve large sectors of the Apulian territory are related to natural cavities produced by karst processes in soluble rocks, or to man-made cavities deriving from different types of human activities in different historical ages. The related hazard is extremely high, with very severe damage to built-up areas and human infrastructures, and heavy losses to the ...

One of the main challenges in the field of engineering geology is the comprehension of the triggering mechanisms of landslides and the forecast of possible evolutionary scenarios in order to assess the correct mitigation measures. Landslides can be initiated by a variety of triggers: from earthquakes to meteorological events, including intense or prolonged rainfall, rapid snow melting, and variations of the surface temperature conditions. ...

The observed increase in disastrous events over the last decades, associated with a low perception of risk by the communities involved, along with the lack of efficient, socially accepted and environmentally sound remedial measures are amongst the motivation behind this research project. The adaptation of a combined multi-risk-oriented analysis, in which the investigations focus more on the interdependence of events rather than on single event, ...

The Strategic Project PS_119 was aimed at developing a methodology for the landslide risk assessment, applicable at the regional scale and based on the most advanced knowledge in the fields of geology, geotechnics, structural engineering and urban planning. This assessment was based on a deterministic approach of the landslide processes and the risks related to them. The failure slope mechanisms, the structural damages due to landsliding and ...
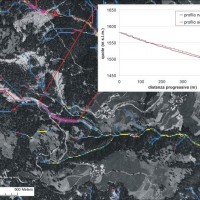
The assessment debris-flow hazard is of utmost importance in the management of alpine catchments. The analysis of morphometric variables of drainage basins and channels can contribute to preliminary assessment of debris-flow hazard at regional ...
 The use of remotely piloted aircraft systems (RPASs) in geosciences is often aimed at the acquisition of an image sequence to produce digital models and orthophotographs of the topographic surface. Such photogrammetric technique can be applied for rockfall hazard and risk assessment. To study rockfalls, an approach consists in the application of numerical models for the computation of rockfall trajectories. Data required for such simulations ...
The use of remotely piloted aircraft systems (RPASs) in geosciences is often aimed at the acquisition of an image sequence to produce digital models and orthophotographs of the topographic surface. Such photogrammetric technique can be applied for rockfall hazard and risk assessment. To study rockfalls, an approach consists in the application of numerical models for the computation of rockfall trajectories. Data required for such simulations ...  The Mar Piccolo basin is an internal sea basin located along the Ionian coast (Southern Italy), and it is surrounded primarily by fractured carbonate karstic environment.
In primarily karstic environments, infiltration is greater than runoff; in the karstic coastal Apulian aquifers, the groundwater discharge to the sea is more than two-fold greater than the surface discharge, notwithstanding the high discharges by wells. In such ...
The Mar Piccolo basin is an internal sea basin located along the Ionian coast (Southern Italy), and it is surrounded primarily by fractured carbonate karstic environment.
In primarily karstic environments, infiltration is greater than runoff; in the karstic coastal Apulian aquifers, the groundwater discharge to the sea is more than two-fold greater than the surface discharge, notwithstanding the high discharges by wells. In such ...  The area of interest specifically refers to the study of the following themes: extreme hydrological events and their interaction with slopes and watercourses; soil water erosion; debris flows; slope stability; triggering instability mechanisms; evolution of slope movements; monitoring systems for gravitational movements for the purpose of alerting for the mitigation of geo-hydrological risk. The activities proposed in the module are therefore ...
The area of interest specifically refers to the study of the following themes: extreme hydrological events and their interaction with slopes and watercourses; soil water erosion; debris flows; slope stability; triggering instability mechanisms; evolution of slope movements; monitoring systems for gravitational movements for the purpose of alerting for the mitigation of geo-hydrological risk. The activities proposed in the module are therefore ...  The project concerns the mitigation of natural hazards (mainly the effects on the territory and the anthropic environment caused by rains, earthquakes, volcanism, and Radon gas). The geological characterization is essential to frame the contexts and the expected phenomena. Numerical modeling and monitoring allow to predict the spatio-temporal evolution of the phenomena, and therefore to evaluate the risk for mitigation ...
The project concerns the mitigation of natural hazards (mainly the effects on the territory and the anthropic environment caused by rains, earthquakes, volcanism, and Radon gas). The geological characterization is essential to frame the contexts and the expected phenomena. Numerical modeling and monitoring allow to predict the spatio-temporal evolution of the phenomena, and therefore to evaluate the risk for mitigation ...  With more than 5 million people affected, more than 1000 killed, and with estimated total damages exceeding 4.5 billion Euros just in Europe and during the last decade, floods are among the most disruptive natural events threatening our Society. Due to increase in extreme weather events and rapid socio-economic developments in vulnerable locations, the risks connected to floods in general are growing rapidly, and the awareness of these risks ...
With more than 5 million people affected, more than 1000 killed, and with estimated total damages exceeding 4.5 billion Euros just in Europe and during the last decade, floods are among the most disruptive natural events threatening our Society. Due to increase in extreme weather events and rapid socio-economic developments in vulnerable locations, the risks connected to floods in general are growing rapidly, and the awareness of these risks ...  The hydro-meteorological monitoring is the operational tool for the measures of atmospheric, hydrologic ad hydraulic variables characterizing the hydrological cycle and it represents the grounds of IRPI’s research activities finalized to forecast, prevention and mitigation of natural hazards. Indeed, an accurate knowledge of processes at basis of natural phenomenon cannot disregard the direct measure of hydrological quantities, considering ...
The hydro-meteorological monitoring is the operational tool for the measures of atmospheric, hydrologic ad hydraulic variables characterizing the hydrological cycle and it represents the grounds of IRPI’s research activities finalized to forecast, prevention and mitigation of natural hazards. Indeed, an accurate knowledge of processes at basis of natural phenomenon cannot disregard the direct measure of hydrological quantities, considering ...  The project activities were carried out in two phases:
"dynamic scenarios of flood risk" identification through hydrologic-hydraulic modeling addressed to Civil Protection activities (2009-2011);
operational implementation of developed dynamic scenarios of flood risk and results dissemination trough web-GIS technologies, also within the context of Floods Directive 2007/60 /EC (2012-203); flood forecasting models implementation; ...
The project activities were carried out in two phases:
"dynamic scenarios of flood risk" identification through hydrologic-hydraulic modeling addressed to Civil Protection activities (2009-2011);
operational implementation of developed dynamic scenarios of flood risk and results dissemination trough web-GIS technologies, also within the context of Floods Directive 2007/60 /EC (2012-203); flood forecasting models implementation; ...  River discharge monitoring is fundamental for the study of the hydraulic regime of river flow and for the validation and calibration of rainfall-runoff models. The assessment of channel roughness coefficients associated with the measured discharges is fundamental for the calibration of flood routing models that can be used to address civil protection activities in real time. Unfortunately, the number of river flow monitoring stations in the ...
River discharge monitoring is fundamental for the study of the hydraulic regime of river flow and for the validation and calibration of rainfall-runoff models. The assessment of channel roughness coefficients associated with the measured discharges is fundamental for the calibration of flood routing models that can be used to address civil protection activities in real time. Unfortunately, the number of river flow monitoring stations in the ...  The artificial reservoirs are fundamental for water resources management, by regulating releases to meet the different users request (industrial, irrigation, hydropower, etc.), and for downstream territories floods defence through lamination of critical flood waves.
The main objective of the project concerns the review of hydrological-hydraulic studies carried out for the Montedoglio dam, on Tiber River, Casanuova dam, on Chiascio River, ...
The artificial reservoirs are fundamental for water resources management, by regulating releases to meet the different users request (industrial, irrigation, hydropower, etc.), and for downstream territories floods defence through lamination of critical flood waves.
The main objective of the project concerns the review of hydrological-hydraulic studies carried out for the Montedoglio dam, on Tiber River, Casanuova dam, on Chiascio River, ...  The Tiber River Basin Authority (ABT) and the Umbria Region (Service Water Resources and Hydraulic Risk), considering the verified underestimation of the flood-prone areas in the Paglia River basin provided by the Italian PAI (hydro-geological management plan) and the update of rating curves, decided to revise the hydrological study of the drainage basin in order to re-estimate the flood hazard maps for the Paglia River reach bounded upstream ...
The Tiber River Basin Authority (ABT) and the Umbria Region (Service Water Resources and Hydraulic Risk), considering the verified underestimation of the flood-prone areas in the Paglia River basin provided by the Italian PAI (hydro-geological management plan) and the update of rating curves, decided to revise the hydrological study of the drainage basin in order to re-estimate the flood hazard maps for the Paglia River reach bounded upstream ...  The project activities concern:
development and implementation of: 1) a semi-distributed continuous hydrological model (MISDc) for real-time soil moisture estimate and river discharge prediction in the Upper-Middle Tiber River basin; 2) a flood wave routing model (STAFOM-RCM) for stage hydrograph forecasting at some selected hydrometric stations in the Tiber River basin;
support for installation of soil moisture sensors in the ...
The project activities concern:
development and implementation of: 1) a semi-distributed continuous hydrological model (MISDc) for real-time soil moisture estimate and river discharge prediction in the Upper-Middle Tiber River basin; 2) a flood wave routing model (STAFOM-RCM) for stage hydrograph forecasting at some selected hydrometric stations in the Tiber River basin;
support for installation of soil moisture sensors in the ...  On 25-27 November 2005, the territory of central Italy was affected by heavy rainfall that hit the Tiber River basin and, mainly, the province of Perugia. The meteoric event had a significant phase with a duration of approximately 48 hours with widespread precipitation up to a maximum accumulated value higher than 100 mm. Significant increases in water levels occurred in most rivers of Upper-Middle Tiber
causing extended flooding in ...
On 25-27 November 2005, the territory of central Italy was affected by heavy rainfall that hit the Tiber River basin and, mainly, the province of Perugia. The meteoric event had a significant phase with a duration of approximately 48 hours with widespread precipitation up to a maximum accumulated value higher than 100 mm. Significant increases in water levels occurred in most rivers of Upper-Middle Tiber
causing extended flooding in ...  Based on the application of numerical modelling techniques, CNR – IRPI can provide consulting services on stability/instability conditions and kinematical evolution of potentially unstable slopes, underground caves, embankments, open-pit mines, landfills and any other type of natural or man-made soil/rock structure at ...
Based on the application of numerical modelling techniques, CNR – IRPI can provide consulting services on stability/instability conditions and kinematical evolution of potentially unstable slopes, underground caves, embankments, open-pit mines, landfills and any other type of natural or man-made soil/rock structure at ...  In Italy landslides and floods are frequent, widespread and dangerous phenomena, that cause fatalities and serious economic damage. In our country, landslides and floods pose major problems of scientific interest and of social and economic relevance.
The Institute is a Competence Centre for the Italian national Civil Protection Department, an Office of the Prime Minister. For the Department of Civil Protection we execute research and ...
In Italy landslides and floods are frequent, widespread and dangerous phenomena, that cause fatalities and serious economic damage. In our country, landslides and floods pose major problems of scientific interest and of social and economic relevance.
The Institute is a Competence Centre for the Italian national Civil Protection Department, an Office of the Prime Minister. For the Department of Civil Protection we execute research and ...  Water and sediment connectivity has emerged in recent years as a significant conceptual framework for understanding the transfer of surface water and sediment through landscapes. Connectivity can be seen both as a driver of hydrological and geomorphic processes within a catchment and as an emergent catchment property that is the result of processes acting at different ...
Water and sediment connectivity has emerged in recent years as a significant conceptual framework for understanding the transfer of surface water and sediment through landscapes. Connectivity can be seen both as a driver of hydrological and geomorphic processes within a catchment and as an emergent catchment property that is the result of processes acting at different ...  The project AIM-DAMS is aimed at developing a laboratory of integrated and advanced environmental monitoring for the control of the behavior of the earth-dams due to the different factors acting on the dams during their lifetime. Based on the integration of innovative and non-invasive sensors, as well as recent monitoring techniques and numerical modelling, the project is intended to fulfill the need of the dam management agencies of using ...
The project AIM-DAMS is aimed at developing a laboratory of integrated and advanced environmental monitoring for the control of the behavior of the earth-dams due to the different factors acting on the dams during their lifetime. Based on the integration of innovative and non-invasive sensors, as well as recent monitoring techniques and numerical modelling, the project is intended to fulfill the need of the dam management agencies of using ...  Glaciers are widely recognized as the best terrestrial indicator of climate change. Nevertheless, occurred changes, even in recent times, are often poorly known. Italy has a unique, secular history of glaciological documentation that, jointly with a rich wealth of spatial, multitemporal data, allows an accurate reconstruction of recent glacier evolution. Unfortunately, these data are dispersed and/or difficult to ...
Glaciers are widely recognized as the best terrestrial indicator of climate change. Nevertheless, occurred changes, even in recent times, are often poorly known. Italy has a unique, secular history of glaciological documentation that, jointly with a rich wealth of spatial, multitemporal data, allows an accurate reconstruction of recent glacier evolution. Unfortunately, these data are dispersed and/or difficult to ...  The application of distributed physically based models is possible on relatively small areas, typically hundreds or few thousands of km2. Distributed modelling of slope dynamics requires many sufficiently detailed information. Knowledge of geotechnical parameters and land use, digital terrain models, medium/high resolution cartography, temporal evolution of soil moisture conditions, are ...
The application of distributed physically based models is possible on relatively small areas, typically hundreds or few thousands of km2. Distributed modelling of slope dynamics requires many sufficiently detailed information. Knowledge of geotechnical parameters and land use, digital terrain models, medium/high resolution cartography, temporal evolution of soil moisture conditions, are ...  The widespread sinkholes that involve large sectors of the Apulian territory are related to natural cavities produced by karst processes in soluble rocks, or to man-made cavities deriving from different types of human activities in different historical ages. The related hazard is extremely high, with very severe damage to built-up areas and human infrastructures, and heavy losses to the ...
The widespread sinkholes that involve large sectors of the Apulian territory are related to natural cavities produced by karst processes in soluble rocks, or to man-made cavities deriving from different types of human activities in different historical ages. The related hazard is extremely high, with very severe damage to built-up areas and human infrastructures, and heavy losses to the ...  The observed increase in disastrous events over the last decades, associated with a low perception of risk by the communities involved, along with the lack of efficient, socially accepted and environmentally sound remedial measures are amongst the motivation behind this research project. The adaptation of a combined multi-risk-oriented analysis, in which the investigations focus more on the interdependence of events rather than on single event, ...
The observed increase in disastrous events over the last decades, associated with a low perception of risk by the communities involved, along with the lack of efficient, socially accepted and environmentally sound remedial measures are amongst the motivation behind this research project. The adaptation of a combined multi-risk-oriented analysis, in which the investigations focus more on the interdependence of events rather than on single event, ... 


















