In Europe
The coloured circles represent the total number of activities (project, products and services, outreach, collaborations) that we have in the corresponding geographical zone
Map data: © OpenStreetMap contributors
URban GEodiversity for a Resilient Environment
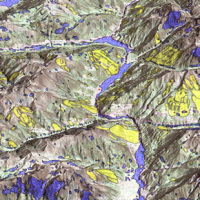
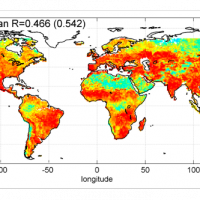
 Geodiversity refers to the variety of natural abiotic features, as the natural variety of geological (rocks, minerals), geomorphological (landforms, physical processes), hydrological and soil properties. The parameter “geomorphodiversity” is a measure of the dynamics of the Earth's surface and it has a key role in conservation of biodiversity and sustainability of ecosystems. Thus, it affects evolution of the biotic world and of human life. ...
Geodiversity refers to the variety of natural abiotic features, as the natural variety of geological (rocks, minerals), geomorphological (landforms, physical processes), hydrological and soil properties. The parameter “geomorphodiversity” is a measure of the dynamics of the Earth's surface and it has a key role in conservation of biodiversity and sustainability of ecosystems. Thus, it affects evolution of the biotic world and of human life. ... Sentinel-3 Topography mission Assessment through Reference Techniques
 The Copernicus Sentinel-3 Surface Topography Mission (STM) provides extremely valuable surface elevation information over inland waters, sea ice and land ice, thanks to its SAR altimeter which retrieves high-resolution along-track elevation measurements, and to its orbit that covers high-latitude polar regions.
To ensure that these measurements can be used with confidence, and to maximize the return on investment of the Copernicus Sentinel-3 ...
The Copernicus Sentinel-3 Surface Topography Mission (STM) provides extremely valuable surface elevation information over inland waters, sea ice and land ice, thanks to its SAR altimeter which retrieves high-resolution along-track elevation measurements, and to its orbit that covers high-latitude polar regions.
To ensure that these measurements can be used with confidence, and to maximize the return on investment of the Copernicus Sentinel-3 ... I-CHANGE project
 The documented effects of climate change and environmental degradation are a threat to human societies on European and global scales. Climate change may have an impact on water availability, may increase the threat of flooding and flash-floods, and will challenge coastal regions due to rising sea levels. All this will have impacts on the economy and society. The role of citizens and their skills become important both in limiting human impacts ...
The documented effects of climate change and environmental degradation are a threat to human societies on European and global scales. Climate change may have an impact on water availability, may increase the threat of flooding and flash-floods, and will challenge coastal regions due to rising sea levels. All this will have impacts on the economy and society. The role of citizens and their skills become important both in limiting human impacts ... River discharge estimation from satellite
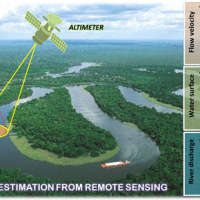 River discharge is defined as the amount of water flowing through a river over a specified period of time. Its estimate is crucial for all the operations of hydraulic structures design, the territorial planning and the flood risk assessment and management. River discharge at a specific river cross-section is not a direct measurement, but it is calculated by measuring other hydraulic quantities such as the flow velocity and the water depth, i.e. ...
River discharge is defined as the amount of water flowing through a river over a specified period of time. Its estimate is crucial for all the operations of hydraulic structures design, the territorial planning and the flood risk assessment and management. River discharge at a specific river cross-section is not a direct measurement, but it is calculated by measuring other hydraulic quantities such as the flow velocity and the water depth, i.e. ... Automated Inclinometer System (AIS) for deep-seated ground deformation measurements
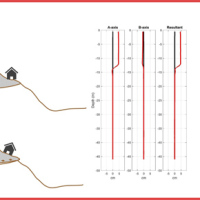 Our AIS (Automated Inclinometer System) allows for fully automatic inclinometer measurements in standard boreholes. The deep measurements have multiple applications, including (i) evaluating the rate of deep-seated ground deformation in landslide areas, (ii) evaluating the volume of deep-seated landslides, and (ii) assessing landslide hazards.
The AIS is composed of an electronic control manager, an inclinometer probe (with traditional ...
Our AIS (Automated Inclinometer System) allows for fully automatic inclinometer measurements in standard boreholes. The deep measurements have multiple applications, including (i) evaluating the rate of deep-seated ground deformation in landslide areas, (ii) evaluating the volume of deep-seated landslides, and (ii) assessing landslide hazards.
The AIS is composed of an electronic control manager, an inclinometer probe (with traditional ... ALMOND-F, an ALarm and MONitoring system for Debris-Flows
 ALMOND-F is an innovative unit for the microseismic detection of debris flows using a network of geophones.
The microseismic detection of debris flows is more complex than other types of monitoring. Use of the geophones requires: (1) the selection of the level of amplification of the signal, which depends on the distance from the stream; (2) the selection of the sampling frequency of the seismic signal, which must be sufficiently high; (3) ...
ALMOND-F is an innovative unit for the microseismic detection of debris flows using a network of geophones.
The microseismic detection of debris flows is more complex than other types of monitoring. Use of the geophones requires: (1) the selection of the level of amplification of the signal, which depends on the distance from the stream; (2) the selection of the sampling frequency of the seismic signal, which must be sufficiently high; (3) ... Detecting rainfall from the bottom up
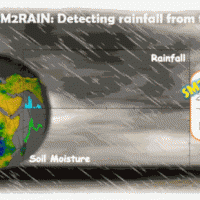 SM2RAIN is an innovative system for the estimation of the rainfall, based on measurements of the soil water content. SM2RAIN considers the soil as a natural rain gauge, and by measuring temporal variations of the soil water content, it estimates the rainfall falling on the soil, adopting a “bottom up” approach. Technically, SM2RAIN relies on the inversion of the soil water balance equation that computes the repartition of rainfall in ...
SM2RAIN is an innovative system for the estimation of the rainfall, based on measurements of the soil water content. SM2RAIN considers the soil as a natural rain gauge, and by measuring temporal variations of the soil water content, it estimates the rainfall falling on the soil, adopting a “bottom up” approach. Technically, SM2RAIN relies on the inversion of the soil water balance equation that computes the repartition of rainfall in ... Rainfall estimate from space
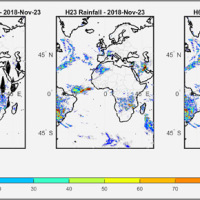 We have developed a new satellite rainfall product in near real-time. The product, called H64, is based on the integration of rainfall estimates obtained through two satellite sources. The developed algorithm combines estimates obtained by applying the SM2RAIN algorithm to satellite soil moisture data and those provided by a state-of-the-art product already operating on the full-disk area of the Meteosat satellites (60° West - 60° East, 60° ...
We have developed a new satellite rainfall product in near real-time. The product, called H64, is based on the integration of rainfall estimates obtained through two satellite sources. The developed algorithm combines estimates obtained by applying the SM2RAIN algorithm to satellite soil moisture data and those provided by a state-of-the-art product already operating on the full-disk area of the Meteosat satellites (60° West - 60° East, 60° ... MUltiHAzard framework for water related risks management
 The MUHA project is building upon the idea to address disaster management cycle consisting of preparedness-response-mitigation-rebuild components in the ADRION countries. It will connect the observed and modelled hazards and risks related to the integrated water cycle, by effectively join them with the existing and improved coping capacity developed by national, bilateral and EU Civil Protection ...
The MUHA project is building upon the idea to address disaster management cycle consisting of preparedness-response-mitigation-rebuild components in the ADRION countries. It will connect the observed and modelled hazards and risks related to the integrated water cycle, by effectively join them with the existing and improved coping capacity developed by national, bilateral and EU Civil Protection ... Progetto ADAPT
From population risk perception to social vulnerability in coastal areas subject to climate change: a proposal for risk management strategies in two Mediterranean regions
 Coastal areas are particularly sensitive to climate change. Because these areas have become particularly susceptible to extreme physical phenomena because of a significant increase in human pressure, climate change will cause heightened exposure and vulnerability of the population. The Authorities ought to make strong efforts to: i) take the necessary measures and actions to reduce the negative impacts of the natural phenomena on the coastal ...
Coastal areas are particularly sensitive to climate change. Because these areas have become particularly susceptible to extreme physical phenomena because of a significant increase in human pressure, climate change will cause heightened exposure and vulnerability of the population. The Authorities ought to make strong efforts to: i) take the necessary measures and actions to reduce the negative impacts of the natural phenomena on the coastal ... Towards geohazards resilient infrastructure under changing climates
 A trend of increasingly frequent intense rainfalls and changing rainfall patterns is causing a relevant number of landslides and floods affecting urban areas and engineering infrastructures such as roads, railways. Recently Transport networks across Europe experienced several failures the reasons of which are still poorly understood.. To improve the current situation, a step change in the way we design reliable and effective defence structures ...
A trend of increasingly frequent intense rainfalls and changing rainfall patterns is causing a relevant number of landslides and floods affecting urban areas and engineering infrastructures such as roads, railways. Recently Transport networks across Europe experienced several failures the reasons of which are still poorly understood.. To improve the current situation, a step change in the way we design reliable and effective defence structures ... Mediterranean Services Chain Based On Climate Predictions
 The project focuses on climate predictions from seasonal-to-decadal timescales for the Mediterranean region (here defined as the domain encompassing the Mediterranean basin and the surrounding areas), and their applications in different sectors. The IRPI contribution will cover this aspect of the project, with specific reference to the conditions and evolution of cryosphere resources (WP4, Task ...
The project focuses on climate predictions from seasonal-to-decadal timescales for the Mediterranean region (here defined as the domain encompassing the Mediterranean basin and the surrounding areas), and their applications in different sectors. The IRPI contribution will cover this aspect of the project, with specific reference to the conditions and evolution of cryosphere resources (WP4, Task ... Integrated approach for the development across Europe of user oriented climate indicators for GFCS high-priority sectors: agriculture, disaster risk reduction, energy, health, water and tourism
 Climate change strongly impacts the whole European territory. Drought severely affects agriculture; precipitation extremes are associated with flooding, severe damage to properties and lives; temperature extremes can increase mortality; the seasonality and availability of snow affects water resources and winter tourism; wind speed or sunshine hours affect the production of renewable energy. These relations can be studied through the computation ...
Climate change strongly impacts the whole European territory. Drought severely affects agriculture; precipitation extremes are associated with flooding, severe damage to properties and lives; temperature extremes can increase mortality; the seasonality and availability of snow affects water resources and winter tourism; wind speed or sunshine hours affect the production of renewable energy. These relations can be studied through the computation ... Documentation and analysis of flash floods
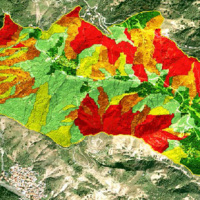
 Flash floods occur in small to medium size river basins, and are characterised by fast temporal evolution. Because of their intensity and short warning times, flash floods often cause not only major economic damage, but also loss of lives.
An integrated approach to documentation and analysis of flash floods has to include the following issues:
post-flood observations aimed at estimating peak discharge and reconstructing temporal ...
Flash floods occur in small to medium size river basins, and are characterised by fast temporal evolution. Because of their intensity and short warning times, flash floods often cause not only major economic damage, but also loss of lives.
An integrated approach to documentation and analysis of flash floods has to include the following issues:
post-flood observations aimed at estimating peak discharge and reconstructing temporal ... STSE Water Cycle Multi-mission Observation Strategy – Irrigation
 Irrigation is one of the greatest human intervention in the hydrological cycle. The knowledge of the distribution, the extent of irrigated areas and the amount of water used by irrigation is needed for different purposes: 1) modelling irrigation water requirements at the global scale, 2) assessing irrigated food production, 3) quantifying the impact of irrigation on climate, river discharge and groundwater depletion. Notwithstanding its ...
Irrigation is one of the greatest human intervention in the hydrological cycle. The knowledge of the distribution, the extent of irrigated areas and the amount of water used by irrigation is needed for different purposes: 1) modelling irrigation water requirements at the global scale, 2) assessing irrigated food production, 3) quantifying the impact of irrigation on climate, river discharge and groundwater depletion. Notwithstanding its ... Radar remote sensing techniques for the detection and measurements of ground surface deformations
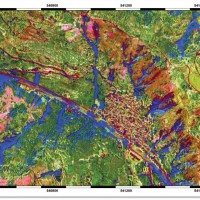
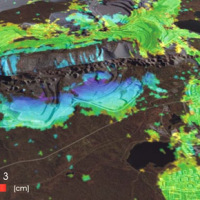 Space-borne radar interferometry or DInSAR (Differential Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar) is one of the latest techniques used for the detection and measurement of ground surface deformations caused by natural and / or man-made events. The DInSAR technique has been successfully used in the measurement of seismic deformations and of the effects of subsidence, unstable slopes and inflation of magma in volcanoes. The growth of space ...
Space-borne radar interferometry or DInSAR (Differential Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar) is one of the latest techniques used for the detection and measurement of ground surface deformations caused by natural and / or man-made events. The DInSAR technique has been successfully used in the measurement of seismic deformations and of the effects of subsidence, unstable slopes and inflation of magma in volcanoes. The growth of space ... India, Italy & UK join for study
E-TECH New technologies for support and prevention of emergencies
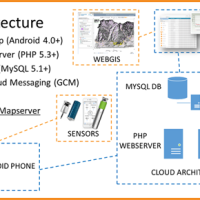 The management of natural hazards tends radically to distribute responsibilities at the local level, as the first civil protection actors. Prevention and preparedness are long-term goals, rooted in volunteer expertise, and awareness of local citizens, using solutions of "crowd-sourced mappers". The objective is designing mobile applications, sensors and dashboard for citizens and volunteers of civil protection, with pilot study cases selected ...
The management of natural hazards tends radically to distribute responsibilities at the local level, as the first civil protection actors. Prevention and preparedness are long-term goals, rooted in volunteer expertise, and awareness of local citizens, using solutions of "crowd-sourced mappers". The objective is designing mobile applications, sensors and dashboard for citizens and volunteers of civil protection, with pilot study cases selected ... Dikes and Debris Flows Monitoring by Novel Optical Fiber Sensors
 With more than 5 million people affected, more than 1000 killed, and with estimated total damages exceeding 4.5 billion Euros just in Europe and during the last decade, floods are among the most disruptive natural events threatening our Society. Due to increase in extreme weather events and rapid socio-economic developments in vulnerable locations, the risks connected to floods in general are growing rapidly, and the awareness of these risks ...
With more than 5 million people affected, more than 1000 killed, and with estimated total damages exceeding 4.5 billion Euros just in Europe and during the last decade, floods are among the most disruptive natural events threatening our Society. Due to increase in extreme weather events and rapid socio-economic developments in vulnerable locations, the risks connected to floods in general are growing rapidly, and the awareness of these risks ... Sentinel for Geohazards regional monitoring and forecasting
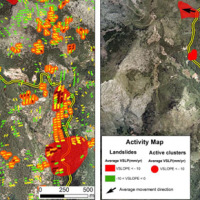 SAFETY aims at providing Civil Protection Authorities with the capability of periodically evaluating and assessing the potential impact of geohazards (volcanic activity, landslides and subsidence) on urban areas. The project improves the effort to detect and map geohazards, assess their activity and evaluate their impact on built-up areas and infrastructures ...
SAFETY aims at providing Civil Protection Authorities with the capability of periodically evaluating and assessing the potential impact of geohazards (volcanic activity, landslides and subsidence) on urban areas. The project improves the effort to detect and map geohazards, assess their activity and evaluate their impact on built-up areas and infrastructures ... Workshop to the Academy of Sciences, Prague
 Il sito web dell' "Institute of Rock Structure and Mechanics of the CAS (IRSM CAS)" ospita un resoconto del workshop (“Natural hazards around us – opinions of European experts on natural and social environment changes”) svoltosi a Praga il 3 dicembre 2015, citando Fausto Guzzetti e Paola Reichenbach, ricercatori presso l'IRPI CNR, quali principali relatori della giornata.
Vai alla pagina web ...
Il sito web dell' "Institute of Rock Structure and Mechanics of the CAS (IRSM CAS)" ospita un resoconto del workshop (“Natural hazards around us – opinions of European experts on natural and social environment changes”) svoltosi a Praga il 3 dicembre 2015, citando Fausto Guzzetti e Paola Reichenbach, ricercatori presso l'IRPI CNR, quali principali relatori della giornata.
Vai alla pagina web ... Installation AIS in the Breithorn area (Switzerland)
 Following the European project Lampre and according between CNR-IRPI and Swiss Federal Office of the Environment, the GeoHazard Monitoring Group (GMG) have installed an Automated Inclinometer System in the BreitHorn area (Kanton Wallis) at 2900 m altitude. The monitoring system, patented by CNR-IRPI allows realizing automatically high-precision inclinometer measurements to evaluate deep-seated ground deformations. More informations at the ...
Following the European project Lampre and according between CNR-IRPI and Swiss Federal Office of the Environment, the GeoHazard Monitoring Group (GMG) have installed an Automated Inclinometer System in the BreitHorn area (Kanton Wallis) at 2900 m altitude. The monitoring system, patented by CNR-IRPI allows realizing automatically high-precision inclinometer measurements to evaluate deep-seated ground deformations. More informations at the ... Randa landslide
La ricerca idrogeologica italiana per la gestione sostenibile delle acque sotterranee di Malta
 Dal sito del CNR una news riguardante l’Accordo di Cooperazione “Formulation of a framework to guide the development of a numerical groundwater model to estimate the sustainable yield of the mean sea level aquifer system” tra l'IRPI-CNR e il Sustainable Energy And Water Conservation Unit (SEWCU) del Ministry for Energy and Health (MEH) della Repubblica di ...
Dal sito del CNR una news riguardante l’Accordo di Cooperazione “Formulation of a framework to guide the development of a numerical groundwater model to estimate the sustainable yield of the mean sea level aquifer system” tra l'IRPI-CNR e il Sustainable Energy And Water Conservation Unit (SEWCU) del Ministry for Energy and Health (MEH) della Repubblica di ... STSE Water Cycle Multi-mission Observation Strategy for the Mediterranean
 Monitoring the water cycle from satellite observations is one of the major goals of the EO community and closing the water budget has been a long-standing objective of international programs. After years of hard work, calibrating satellite data, improving inversion techniques, and facilitating the coherency of retrievals, it is admitted that the water cycle budget can now be ...
Monitoring the water cycle from satellite observations is one of the major goals of the EO community and closing the water budget has been a long-standing objective of international programs. After years of hard work, calibrating satellite data, improving inversion techniques, and facilitating the coherency of retrievals, it is admitted that the water cycle budget can now be ... H-SAF AS: Integration of PR-OBS-5 and SM-OBS-1 products through SM2RAIN algorithm for improving rainfall estimate
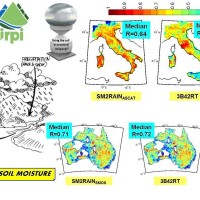 State-of-the-art satellite rainfall products are often the only way for measuring rainfall in remote areas of the world. However, these products may fail in properly reproducing the amount of precipitation reaching the ground, which is needed for hydrological applications. The integration of satellite soil moisture products is expected to significantly improve rainfall ...
State-of-the-art satellite rainfall products are often the only way for measuring rainfall in remote areas of the world. However, these products may fail in properly reproducing the amount of precipitation reaching the ground, which is needed for hydrological applications. The integration of satellite soil moisture products is expected to significantly improve rainfall ... SM2RAIN dataset
EUMETSAT Satellite Application Facility on Support to Operational Hydrology and Water Management
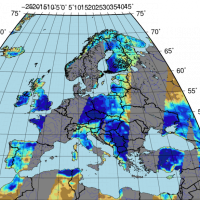 The H-SAF generates and archives high-quality data sets and products for operational hydrological applications starting from the acquisition and processing of data from Earth observation satellites in geostationary and polar orbits operated both by EUMETSAT and other satellite organization. The retrieval of products uses data from microwave and infrared instruments and aims at reaching the best possible accuracy compatible with satellite ...
The H-SAF generates and archives high-quality data sets and products for operational hydrological applications starting from the acquisition and processing of data from Earth observation satellites in geostationary and polar orbits operated both by EUMETSAT and other satellite organization. The retrieval of products uses data from microwave and infrared instruments and aims at reaching the best possible accuracy compatible with satellite ... Land cover change detection and monitoring methodologies based on the combined use of S1 and S2 for natural resources and hazard management
 ESA Sentinels missions will provide enhanced capabilities in the revisit frequency, and the coverage. Their complete exploitation is in the combination of the two to advantage of a further increased revisiting time and in the use of different wavelenght domains. This reflects in the capabilities to detect features of changes induced by different factors including natural hazards and crop ...
ESA Sentinels missions will provide enhanced capabilities in the revisit frequency, and the coverage. Their complete exploitation is in the combination of the two to advantage of a further increased revisiting time and in the use of different wavelenght domains. This reflects in the capabilities to detect features of changes induced by different factors including natural hazards and crop ... Automated Inclinometer System installed in the Portalet landslide
 Col du Pourtalet, El Portalet or Portalet d'Aneu is a mountain pass and border crossing in the Pyrenees, between France and Spain.
Installed in 2014, August as part of the European Project Lampre. The system allows to monitor in continuous (2÷4 meas/day) deep displacements on the landslide along 50 m borehole. In early July, the Geohazard Monitoring Group of CNR IRPI (http://gmg.irpi.cnr.it), has made a survey finalized to a ...
Col du Pourtalet, El Portalet or Portalet d'Aneu is a mountain pass and border crossing in the Pyrenees, between France and Spain.
Installed in 2014, August as part of the European Project Lampre. The system allows to monitor in continuous (2÷4 meas/day) deep displacements on the landslide along 50 m borehole. In early July, the Geohazard Monitoring Group of CNR IRPI (http://gmg.irpi.cnr.it), has made a survey finalized to a ... Connecting European Connectivity Research
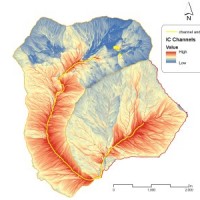 Water and sediment connectivity has emerged in recent years as a significant conceptual framework for understanding the transfer of surface water and sediment through landscapes. Connectivity can be seen both as a driver of hydrological and geomorphic processes within a catchment and as an emergent catchment property that is the result of processes acting at different ...
Water and sediment connectivity has emerged in recent years as a significant conceptual framework for understanding the transfer of surface water and sediment through landscapes. Connectivity can be seen both as a driver of hydrological and geomorphic processes within a catchment and as an emergent catchment property that is the result of processes acting at different ... RelationsHips between meteo-climAtic paraMeters and ground surface deforMation time sEries in mountain enviRonments
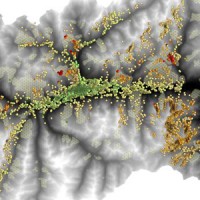 There is a systematic lack of information on the effects of the climate and environmental changes on the frequency and the intensity of landslides and their triggering phenomena (Huggel et al., 2012). The problem is particular severe in mountain area, where natural and human-driven climatic and environmental changes may alter significantly the frequency and the intensity of the slope processes, with largely unknown short and long-term effects ...
There is a systematic lack of information on the effects of the climate and environmental changes on the frequency and the intensity of landslides and their triggering phenomena (Huggel et al., 2012). The problem is particular severe in mountain area, where natural and human-driven climatic and environmental changes may alter significantly the frequency and the intensity of the slope processes, with largely unknown short and long-term effects ... Mobile Application for Emergency Response and Support
 The responsibilities within natural hazards involve citizens and volunteers as first actors of civil protection. The prevention implicates technical volunteers, but the priority implies now awareness of local citizens. The involvement of population creates context-specific strategies of territorial surveillance and management. MAppERS empowers “crowd-sourced mappers” through smart phone applications and sensors, with geo-tagged information, ...
The responsibilities within natural hazards involve citizens and volunteers as first actors of civil protection. The prevention implicates technical volunteers, but the priority implies now awareness of local citizens. The involvement of population creates context-specific strategies of territorial surveillance and management. MAppERS empowers “crowd-sourced mappers” through smart phone applications and sensors, with geo-tagged information, ... Landslide Modelling and tools for vulnerability assessment Preparedness and REcovery management
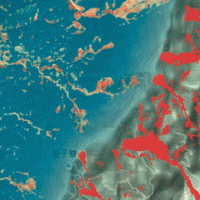 Il progetto FP7 LAMPRE - Landslide Modelling and tools for vulnerability assessment Preparedness and Recovery management svolge attività di ricerca innovative e di sviluppo tecnologico per migliorare le capacità del sistema Copernicus di far fronte a eventi di frana e alle loro conseguenze, in Europa e in altre parti del mondo. LAMPRE migliora il rischio di frana sforzi di mitigazione / preparazione e le attività di recupero e di ...
Il progetto FP7 LAMPRE - Landslide Modelling and tools for vulnerability assessment Preparedness and Recovery management svolge attività di ricerca innovative e di sviluppo tecnologico per migliorare le capacità del sistema Copernicus di far fronte a eventi di frana e alle loro conseguenze, in Europa e in altre parti del mondo. LAMPRE migliora il rischio di frana sforzi di mitigazione / preparazione e le attività di recupero e di ... Increasing Resilience through Earth Observation
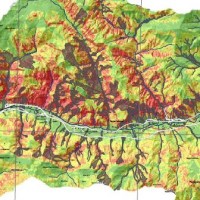 To significantly contribute to the operational capacities in the context of Global Monitoring for Environment and Security (GMES)/ Copernicus by developing customised mapping and geo-information products addressing risk, vulnerability and assets ready for deployment in the prevention and preparedness phases – complementary to the GMES/Copernicus Emergency Management Service. Solutions to be provided are based for the most part on Earth ...
To significantly contribute to the operational capacities in the context of Global Monitoring for Environment and Security (GMES)/ Copernicus by developing customised mapping and geo-information products addressing risk, vulnerability and assets ready for deployment in the prevention and preparedness phases – complementary to the GMES/Copernicus Emergency Management Service. Solutions to be provided are based for the most part on Earth ...