
The Copernicus Sentinel-3 Surface Topography Mission (STM) provides extremely valuable surface elevation information over inland waters, sea ice and land ice, thanks to its SAR altimeter which retrieves high-resolution along-track elevation measurements, and to its orbit that covers high-latitude polar regions.
To ensure that these measurements can be used with confidence, and to maximize the return on investment of the Copernicus Sentinel-3 ...
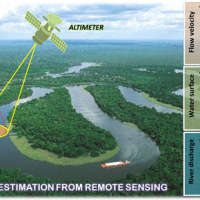
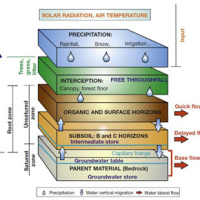
River discharge is defined as the amount of water flowing through a river over a specified period of time. Its estimate is crucial for all the operations of hydraulic structures design, the territorial planning and the flood risk assessment and management. River discharge at a specific river cross-section is not a direct measurement, but it is calculated by measuring other hydraulic quantities such as the flow velocity and the water depth, i.e. ...
The Mar Piccolo basin is an internal sea basin located along the Ionian coast (Southern Italy), and it is surrounded primarily by fractured carbonate karstic environment.
In primarily karstic environments, infiltration is greater than runoff; in the karstic coastal Apulian aquifers, the groundwater discharge to the sea is more than two-fold greater than the surface discharge, notwithstanding the high discharges by wells. In such ...

Not all that flows in creeks is water. Debris flows i.e., surges in which solid particles move together with little water, may occur in steep mountain streams, mainly as a consequence of intense rainfall. Debris flows have a high kinetic energy, and may cause major damage if they encroach buildings, roads and bridges. They are also a primary cause of landslide casualties. The video below shows an example of debris flows.
The low ...

Using long-term rainfall records obtained by the rain gauge network of the former Italian Hydrographic Service, in cooperation with colleagues in other CNR Institutes (ISAC and ISAFOM), we have studied the changes in the rainfall regimes in Calabria, Southern Italy.
Applying appropriate statistical methods, we checked the completeness of the historical records, verifying consistency and missing values in the records. We used the obtained ...
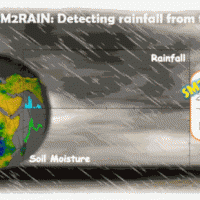
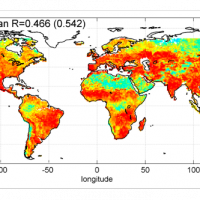
SM2RAIN is an innovative system for the estimation of the rainfall, based on measurements of the soil water content. SM2RAIN considers the soil as a natural rain gauge, and by measuring temporal variations of the soil water content, it estimates the rainfall falling on the soil, adopting a “bottom up” approach. Technically, SM2RAIN relies on the inversion of the soil water balance equation that computes the repartition of rainfall in ...
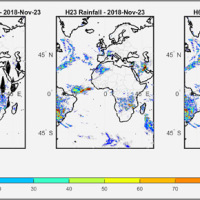
We have developed a new satellite rainfall product in near real-time. The product, called H64, is based on the integration of rainfall estimates obtained through two satellite sources. The developed algorithm combines estimates obtained by applying the SM2RAIN algorithm to satellite soil moisture data and those provided by a state-of-the-art product already operating on the full-disk area of the Meteosat satellites (60° West - 60° East, 60° ...
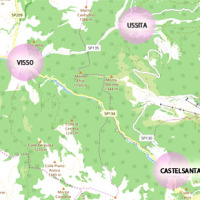
The seismic events that have affected central Italy since 24 August 2016 have caused extensive damage in the municipalities of Castelsantagelo sul Nera, Ussita and Visso (Marche Region). In order to proceed with the reconstruction, it is necessary to carry out interventions to reduce the hydraulic risk in urban ...
Water is at the centre of economic and social development; it is vital to maintain health, grow food, manage the environment, and create jobs. As well over half of the world’s potable water supply is extracted from rivers, either directly or from reservoirs, understanding the variability of the stored water on and below landmasses, i.e., total runoff, is of primary importance. In situ observations or land surface/hydrological models are ...

Although representing less than 1% of the total amount of water on Earth, the freshwater is essential for terrestrial life and human needs. Despite the existing in-situ gauging networks represent a tool for quantifying the instantaneous water volume in many river channels, we have surprisingly poor knowledge of the spatial and temporal dynamics of surface river discharge. Developing new procedures for river discharge estimation based on ...
L'IRPI è da molti anni impegnato nel monitoraggio di variabili idrologiche (umidità del suolo, pioggia, portata e velocità dei corsi d'acqua) che è risultato fondamentale per la rappresentazione del processo di formazione del deflusso e quindi per lo studio delle piene e delle ...
The area of interest specifically refers to the study of the following themes: extreme hydrological events and their interaction with slopes and watercourses; soil water erosion; debris flows; slope stability; triggering instability mechanisms; evolution of slope movements; monitoring systems for gravitational movements for the purpose of alerting for the mitigation of geo-hydrological risk. The activities proposed in the module are therefore ...

Rainfall-induced shallow landslides and floods are the most common and dangerous natural hazards, mainly due to their high temporal frequency, which causes fatalities and high economic damage worldwide. Climate changes will exacerbate this critical framework since an increase in extreme weather events is ...
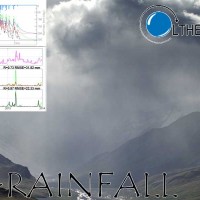
Accurate rainfall estimates are of paramount importance as rainfall plays a key-role in many fields as, to cite a few, natural hazard assessment (floods and landslides), drought management, weather forecasting, agriculture and diseases prevention. State-of-the-art rainfall products obtained by satellites are often the only way for measuring rainfall in remote areas of the ...

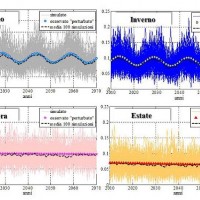
Climate change strongly impacts the whole European territory. Drought severely affects agriculture; precipitation extremes are associated with flooding, severe damage to properties and lives; temperature extremes can increase mortality; the seasonality and availability of snow affects water resources and winter tourism; wind speed or sunshine hours affect the production of renewable energy. These relations can be studied through the computation ...

Flash floods occur in small to medium size river basins, and are characterised by fast temporal evolution. Because of their intensity and short warning times, flash floods often cause not only major economic damage, but also loss of lives.
An integrated approach to documentation and analysis of flash floods has to include the following issues:
post-flood observations aimed at estimating peak discharge and reconstructing temporal ...
The improved understanding of the underlying physical processes of extreme events is closely linked to the development and verification of procedures to better control, analysis and validation of hydrological data for the description and visualization of meteorological events creating an operational "database of event" which enables to better identify under what conditions hazards ...

The dataset includes precipitation, temperature and discharge data recorded in the Missiaga catchment (Dolomites). The Missiaga catchment was monitored by CNR IRPI from 1983 to ...

With more than 5 million people affected, more than 1000 killed, and with estimated total damages exceeding 4.5 billion Euros just in Europe and during the last decade, floods are among the most disruptive natural events threatening our Society. Due to increase in extreme weather events and rapid socio-economic developments in vulnerable locations, the risks connected to floods in general are growing rapidly, and the awareness of these risks ...
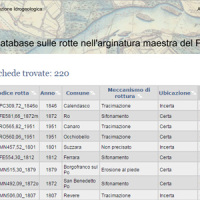
This is the web-based relational database on the main levee breaches of the Po River (Italy), which have occurred since the year 1800.
The database contains more than 200 fact sheets that show the information for each levee failure. For each fact sheet are attached documents and maps. The access is free of charge.
This database may provide a valid support in the design of defense interventions directed at the prevention and mitigation of ...

Monitoring the water cycle from satellite observations is one of the major goals of the EO community and closing the water budget has been a long-standing objective of international programs. After years of hard work, calibrating satellite data, improving inversion techniques, and facilitating the coherency of retrievals, it is admitted that the water cycle budget can now be ...
Quantitative information about precipitation is one vital input to meteorologists, hydrologic scientists, water resources managers, and environmental legislators. Yet, accurate measurement of precipitation over the relevant space and time scales remains a challenge. Soil moisture can be seen as the trace of the precipitation and, consequently, can be useful for providing a way to estimate rainfall accumulation or at least a new constrain to ...
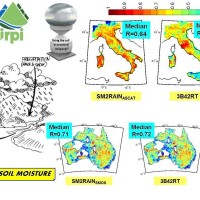
State-of-the-art satellite rainfall products are often the only way for measuring rainfall in remote areas of the world. However, these products may fail in properly reproducing the amount of precipitation reaching the ground, which is needed for hydrological applications. The integration of satellite soil moisture products is expected to significantly improve rainfall ...

The database includes annual maximum rainfall corresponding to durations of 1, 3, 6, 12, 24 hours and 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 days for approximately 800 raingauges in north-eastern Italy (Trentino, Alto Adige, Veneto and Friuli Venezia Giulia). The database contains data until 1997 for the Autonomous Province of Bozen-Bolzano, 1990 for the Autonomous Province of Trento, and 1996 for Veneto and Friuli Venezia ...
Recently, IRPI-CNR has developed an innovative approach for estimating rainfall from satellite soil moisture data, named SM2RAIN. The ESA funded project “Climate Change Initiative - Soil Moisture“ (CCI-SM) offers a valuable opportunity for testing SM2RAIN algorithm to a continuous, homogenous, long-term (>30 years) soil moisture time series. Indeed, SM2RAIN has the chance to be tested not only for rainfall estimation but also as a ...

The project aims at using Soil Moisture Active and Passive (SMAP) soil moisture (SM) products at different spatial resolution (3, 9, and 36 km) for hydrological applications in Europe (mainly in ...

The hydro-meteorological monitoring is the operational tool for the measures of atmospheric, hydrologic ad hydraulic variables characterizing the hydrological cycle and it represents the grounds of IRPI’s research activities finalized to forecast, prevention and mitigation of natural hazards. Indeed, an accurate knowledge of processes at basis of natural phenomenon cannot disregard the direct measure of hydrological quantities, considering ...
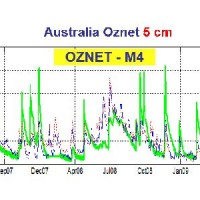
The service aims to assess the potential of different satellite products (from active and passive micro-waves, optical, SAR, spectroradiometers, radiometers sensors) in retrieving the main hydrological-hydraulic variables such as rainfall, soil moisture, water level, flow velocity and discharge. This is pursued through a comprehensive validation analysis by using in-situ observed or modelled data for several sited located ...
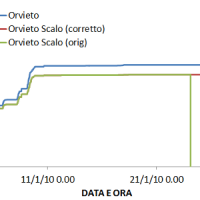
The analysis of hydro-meteorological data is required to verify the correct sensors functioning and possible presence of non-operational periods with missing data. When non-operational periods or malfunction occur, it could be possible to apply procedures for missing data reconstructions and wrong data ...

The service is based on a procedure consisting of four main steps: the analysis of hydro-meteorological data for the reconstruction of flood event in terms of precipitations and saturation conditions of the soils; assessment of the hydrological response of the basin; runoff estimation in each hydrometric site of interest; flooded areas delineation and comparison with in-situ ...
The service analyzes the climate change impact on the main hydro-meteorological variables involved in the hydrological cycle and, in particular, on extreme events of rainfall and discharge (droughts and floods). The service allows to evaluate the combined effects of natural and human processes related to climate change on surface runoff and groundwater, analyzing the possible consequences of such effects on the strategic water ...
The rainfall dataset provides rainfall estimates obtained through the application of an inversion algorithm to soil moisture data. The algorithm has been applied to ground and satellite data, obtained through various satellite ...
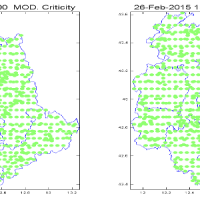
Real time evaluation of the rainfall and soil moisture conditions over the analysis grid point, and the combination with the available vulnerability and susceptibility information for the definition of the dynamic risk ...

Hydraulic hazard maps for return periods of 50, 100, 200 and 500 ...
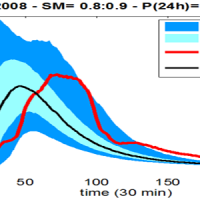
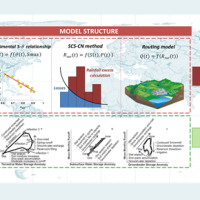
Semi-distributed continuous hydrological model (MISDc) for real-time soil moisture estimate and river discharge prediction in the Upper-Middle Tiber River basin; flood wave routing model (STAFOM-RCM) for stage hydrograph forecasting at some selected hydrometric stations in the Tiber River basin; Rainfall-runoff database coupled with the kinematic model KS for an expeditious estimate of probability flooding ...
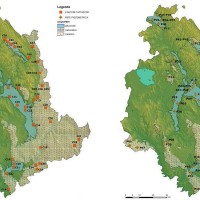
SECLI Project is aimed to assess the combined effects of processes related to natural and anthropogenic climate change on water resources, both surface and groundwater, in the Umbrian territory, identifying the possible consequences of such effects on drinking water policy, and on how these may affect the existing system of withdrawals and ...
The project activities were carried out in two phases:
delineation of flooding-prone areas for many river reaches selected in the secondary hydrographic network of Tiber River basin (2009-2011);
analysis of the severe flood event that affected the Paglia river basin on November ...
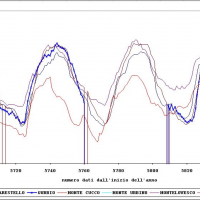
The activities of the project concerns the analysis and processing of hydro-meteorological data collected by the monitoring network of the Umbria Region for the period 1994-2014. In particular, the study regards the rainfall, temperature and water level time series. In addition, the discharge series corresponding to observed water levels are estimated for at hydrometric station through the rating curve estimated on the basis of flow velocity ...
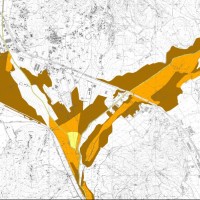
The activities of the project concern the delineation of hazard maps for return periods of 50, 100, 200 and 500 years for many reaches of interest identified in the secondary hydrographic network of Tiber ...
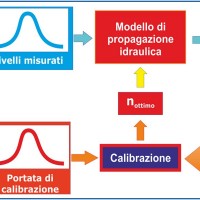
River discharge monitoring is fundamental for the study of the hydraulic regime of river flow and for the validation and calibration of rainfall-runoff models. The assessment of channel roughness coefficients associated with the measured discharges is fundamental for the calibration of flood routing models that can be used to address civil protection activities in real time. Unfortunately, the number of river flow monitoring stations in the ...
The main activities of the project, developed in the context of the program Nextdata funded by the Italian Ministry of Education, University and Research (MIUR), are:
collection, organization and analysis of the available hydro-meteorological and climate data for the characterization of the meteo-climate evolution in Apennine mountain areas;
extensive experimental campaigns for soil moisture monitoring in hillslope portions and ...
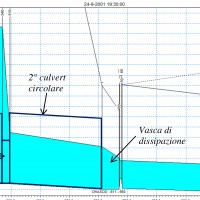
The artificial reservoirs are fundamental for water resources management, by regulating releases to meet the different users request (industrial, irrigation, hydropower, etc.), and for downstream territories floods defence through lamination of critical flood waves.
The main objective of the project concerns the review of hydrological-hydraulic studies carried out for the Montedoglio dam, on Tiber River, Casanuova dam, on Chiascio River, ...
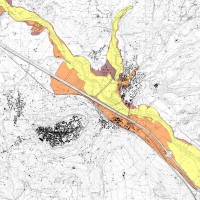
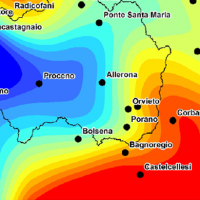
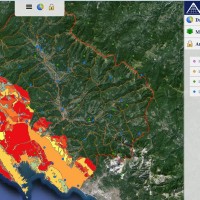
The Tiber River Basin Authority (ABT) and the Umbria Region (Service Water Resources and Hydraulic Risk), considering the verified underestimation of the flood-prone areas in the Paglia River basin provided by the Italian PAI (hydro-geological management plan) and the update of rating curves, decided to revise the hydrological study of the drainage basin in order to re-estimate the flood hazard maps for the Paglia River reach bounded upstream ...
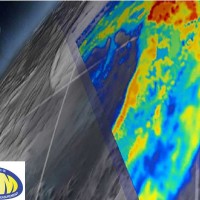
The proposal intends to contribute towards the establishment of a long-term partnership between the EUMETSAT Satellite Application Facility on support to Operational Hydrology and Water Management (H-SAF, or Hydrology SAF) and the NASA/JAXA Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) ...
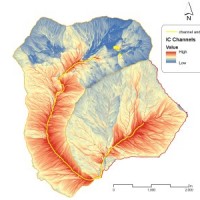
Water and sediment connectivity has emerged in recent years as a significant conceptual framework for understanding the transfer of surface water and sediment through landscapes. Connectivity can be seen both as a driver of hydrological and geomorphic processes within a catchment and as an emergent catchment property that is the result of processes acting at different ...

Nel 2014 ricorrono vent’anni dalla tragica alluvione che nel novembre 1994 colpì gran parte del territorio piemontese, con perdita di vite umane, di beni mobili ed immobili. L’alluvione 1994 costituì altresì un momento storico nel campo della pianificazione territoriale, prevenzione e gestione della pericolosità e rischio geologico-idraulico, che si tradusse in dettami normativi, per l’epoca avanzati e lungimiranti. Da quell’evento ...

Il progetto GeSeFlu nasce dalla necessità della Regione Lombardia mediante il Piano Operativo Regionale (Direttiva Comunitaria 2000/60/CE) di disporre di specifici Programmi di Gestione dei sedimenti per i sottobacini redatti in attuazione della Direttiva del Comitato Istituzionale dell’Autorità di Bacino del fiume Po (deliberazione n. 9 del 5 aprile ...
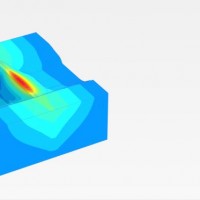
The project AIM-DAMS is aimed at developing a laboratory of integrated and advanced environmental monitoring for the control of the behavior of the earth-dams due to the different factors acting on the dams during their lifetime. Based on the integration of innovative and non-invasive sensors, as well as recent monitoring techniques and numerical modelling, the project is intended to fulfill the need of the dam management agencies of using ...
FLIRE is a demonstration project aiming to the development of an integrated Decision Support System (DSS) for both flash floods and forest fires risk assessment and management. The DSS tool will be designed by using state of art tools, technologies and methods and taking into account prevention, adaptation and interaction issues. The final model will be online available to key stakeholders and relevant authorities (local and national) for the ...
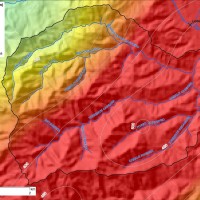
The occurrence of flash floods in mountainous catchments is often associated to relevant geomorphic effects, both in the channel network (channel changes and transport of large wood), and on the hillslopes (landslides and soil erosion). The concomitance of flash floods, channel changes and landslides enhances hazards and risk associated to individual ...
 The Copernicus Sentinel-3 Surface Topography Mission (STM) provides extremely valuable surface elevation information over inland waters, sea ice and land ice, thanks to its SAR altimeter which retrieves high-resolution along-track elevation measurements, and to its orbit that covers high-latitude polar regions.
To ensure that these measurements can be used with confidence, and to maximize the return on investment of the Copernicus Sentinel-3 ...
The Copernicus Sentinel-3 Surface Topography Mission (STM) provides extremely valuable surface elevation information over inland waters, sea ice and land ice, thanks to its SAR altimeter which retrieves high-resolution along-track elevation measurements, and to its orbit that covers high-latitude polar regions.
To ensure that these measurements can be used with confidence, and to maximize the return on investment of the Copernicus Sentinel-3 ...  River discharge is defined as the amount of water flowing through a river over a specified period of time. Its estimate is crucial for all the operations of hydraulic structures design, the territorial planning and the flood risk assessment and management. River discharge at a specific river cross-section is not a direct measurement, but it is calculated by measuring other hydraulic quantities such as the flow velocity and the water depth, i.e. ...
River discharge is defined as the amount of water flowing through a river over a specified period of time. Its estimate is crucial for all the operations of hydraulic structures design, the territorial planning and the flood risk assessment and management. River discharge at a specific river cross-section is not a direct measurement, but it is calculated by measuring other hydraulic quantities such as the flow velocity and the water depth, i.e. ...  The Mar Piccolo basin is an internal sea basin located along the Ionian coast (Southern Italy), and it is surrounded primarily by fractured carbonate karstic environment.
In primarily karstic environments, infiltration is greater than runoff; in the karstic coastal Apulian aquifers, the groundwater discharge to the sea is more than two-fold greater than the surface discharge, notwithstanding the high discharges by wells. In such ...
The Mar Piccolo basin is an internal sea basin located along the Ionian coast (Southern Italy), and it is surrounded primarily by fractured carbonate karstic environment.
In primarily karstic environments, infiltration is greater than runoff; in the karstic coastal Apulian aquifers, the groundwater discharge to the sea is more than two-fold greater than the surface discharge, notwithstanding the high discharges by wells. In such ...  Not all that flows in creeks is water. Debris flows i.e., surges in which solid particles move together with little water, may occur in steep mountain streams, mainly as a consequence of intense rainfall. Debris flows have a high kinetic energy, and may cause major damage if they encroach buildings, roads and bridges. They are also a primary cause of landslide casualties. The video below shows an example of debris flows.
The low ...
Not all that flows in creeks is water. Debris flows i.e., surges in which solid particles move together with little water, may occur in steep mountain streams, mainly as a consequence of intense rainfall. Debris flows have a high kinetic energy, and may cause major damage if they encroach buildings, roads and bridges. They are also a primary cause of landslide casualties. The video below shows an example of debris flows.
The low ...  Using long-term rainfall records obtained by the rain gauge network of the former Italian Hydrographic Service, in cooperation with colleagues in other CNR Institutes (ISAC and ISAFOM), we have studied the changes in the rainfall regimes in Calabria, Southern Italy.
Applying appropriate statistical methods, we checked the completeness of the historical records, verifying consistency and missing values in the records. We used the obtained ...
Using long-term rainfall records obtained by the rain gauge network of the former Italian Hydrographic Service, in cooperation with colleagues in other CNR Institutes (ISAC and ISAFOM), we have studied the changes in the rainfall regimes in Calabria, Southern Italy.
Applying appropriate statistical methods, we checked the completeness of the historical records, verifying consistency and missing values in the records. We used the obtained ...  SM2RAIN is an innovative system for the estimation of the rainfall, based on measurements of the soil water content. SM2RAIN considers the soil as a natural rain gauge, and by measuring temporal variations of the soil water content, it estimates the rainfall falling on the soil, adopting a “bottom up” approach. Technically, SM2RAIN relies on the inversion of the soil water balance equation that computes the repartition of rainfall in ...
SM2RAIN is an innovative system for the estimation of the rainfall, based on measurements of the soil water content. SM2RAIN considers the soil as a natural rain gauge, and by measuring temporal variations of the soil water content, it estimates the rainfall falling on the soil, adopting a “bottom up” approach. Technically, SM2RAIN relies on the inversion of the soil water balance equation that computes the repartition of rainfall in ...  We have developed a new satellite rainfall product in near real-time. The product, called H64, is based on the integration of rainfall estimates obtained through two satellite sources. The developed algorithm combines estimates obtained by applying the SM2RAIN algorithm to satellite soil moisture data and those provided by a state-of-the-art product already operating on the full-disk area of the Meteosat satellites (60° West - 60° East, 60° ...
We have developed a new satellite rainfall product in near real-time. The product, called H64, is based on the integration of rainfall estimates obtained through two satellite sources. The developed algorithm combines estimates obtained by applying the SM2RAIN algorithm to satellite soil moisture data and those provided by a state-of-the-art product already operating on the full-disk area of the Meteosat satellites (60° West - 60° East, 60° ...  The seismic events that have affected central Italy since 24 August 2016 have caused extensive damage in the municipalities of Castelsantagelo sul Nera, Ussita and Visso (Marche Region). In order to proceed with the reconstruction, it is necessary to carry out interventions to reduce the hydraulic risk in urban ...
The seismic events that have affected central Italy since 24 August 2016 have caused extensive damage in the municipalities of Castelsantagelo sul Nera, Ussita and Visso (Marche Region). In order to proceed with the reconstruction, it is necessary to carry out interventions to reduce the hydraulic risk in urban ...  Water is at the centre of economic and social development; it is vital to maintain health, grow food, manage the environment, and create jobs. As well over half of the world’s potable water supply is extracted from rivers, either directly or from reservoirs, understanding the variability of the stored water on and below landmasses, i.e., total runoff, is of primary importance. In situ observations or land surface/hydrological models are ...
Water is at the centre of economic and social development; it is vital to maintain health, grow food, manage the environment, and create jobs. As well over half of the world’s potable water supply is extracted from rivers, either directly or from reservoirs, understanding the variability of the stored water on and below landmasses, i.e., total runoff, is of primary importance. In situ observations or land surface/hydrological models are ...  Although representing less than 1% of the total amount of water on Earth, the freshwater is essential for terrestrial life and human needs. Despite the existing in-situ gauging networks represent a tool for quantifying the instantaneous water volume in many river channels, we have surprisingly poor knowledge of the spatial and temporal dynamics of surface river discharge. Developing new procedures for river discharge estimation based on ...
Although representing less than 1% of the total amount of water on Earth, the freshwater is essential for terrestrial life and human needs. Despite the existing in-situ gauging networks represent a tool for quantifying the instantaneous water volume in many river channels, we have surprisingly poor knowledge of the spatial and temporal dynamics of surface river discharge. Developing new procedures for river discharge estimation based on ...  The area of interest specifically refers to the study of the following themes: extreme hydrological events and their interaction with slopes and watercourses; soil water erosion; debris flows; slope stability; triggering instability mechanisms; evolution of slope movements; monitoring systems for gravitational movements for the purpose of alerting for the mitigation of geo-hydrological risk. The activities proposed in the module are therefore ...
The area of interest specifically refers to the study of the following themes: extreme hydrological events and their interaction with slopes and watercourses; soil water erosion; debris flows; slope stability; triggering instability mechanisms; evolution of slope movements; monitoring systems for gravitational movements for the purpose of alerting for the mitigation of geo-hydrological risk. The activities proposed in the module are therefore ...  Accurate rainfall estimates are of paramount importance as rainfall plays a key-role in many fields as, to cite a few, natural hazard assessment (floods and landslides), drought management, weather forecasting, agriculture and diseases prevention. State-of-the-art rainfall products obtained by satellites are often the only way for measuring rainfall in remote areas of the ...
Accurate rainfall estimates are of paramount importance as rainfall plays a key-role in many fields as, to cite a few, natural hazard assessment (floods and landslides), drought management, weather forecasting, agriculture and diseases prevention. State-of-the-art rainfall products obtained by satellites are often the only way for measuring rainfall in remote areas of the ...  Climate change strongly impacts the whole European territory. Drought severely affects agriculture; precipitation extremes are associated with flooding, severe damage to properties and lives; temperature extremes can increase mortality; the seasonality and availability of snow affects water resources and winter tourism; wind speed or sunshine hours affect the production of renewable energy. These relations can be studied through the computation ...
Climate change strongly impacts the whole European territory. Drought severely affects agriculture; precipitation extremes are associated with flooding, severe damage to properties and lives; temperature extremes can increase mortality; the seasonality and availability of snow affects water resources and winter tourism; wind speed or sunshine hours affect the production of renewable energy. These relations can be studied through the computation ...  Flash floods occur in small to medium size river basins, and are characterised by fast temporal evolution. Because of their intensity and short warning times, flash floods often cause not only major economic damage, but also loss of lives.
An integrated approach to documentation and analysis of flash floods has to include the following issues:
post-flood observations aimed at estimating peak discharge and reconstructing temporal ...
Flash floods occur in small to medium size river basins, and are characterised by fast temporal evolution. Because of their intensity and short warning times, flash floods often cause not only major economic damage, but also loss of lives.
An integrated approach to documentation and analysis of flash floods has to include the following issues:
post-flood observations aimed at estimating peak discharge and reconstructing temporal ...  The improved understanding of the underlying physical processes of extreme events is closely linked to the development and verification of procedures to better control, analysis and validation of hydrological data for the description and visualization of meteorological events creating an operational "database of event" which enables to better identify under what conditions hazards ...
The improved understanding of the underlying physical processes of extreme events is closely linked to the development and verification of procedures to better control, analysis and validation of hydrological data for the description and visualization of meteorological events creating an operational "database of event" which enables to better identify under what conditions hazards ...  With more than 5 million people affected, more than 1000 killed, and with estimated total damages exceeding 4.5 billion Euros just in Europe and during the last decade, floods are among the most disruptive natural events threatening our Society. Due to increase in extreme weather events and rapid socio-economic developments in vulnerable locations, the risks connected to floods in general are growing rapidly, and the awareness of these risks ...
With more than 5 million people affected, more than 1000 killed, and with estimated total damages exceeding 4.5 billion Euros just in Europe and during the last decade, floods are among the most disruptive natural events threatening our Society. Due to increase in extreme weather events and rapid socio-economic developments in vulnerable locations, the risks connected to floods in general are growing rapidly, and the awareness of these risks ...  Monitoring the water cycle from satellite observations is one of the major goals of the EO community and closing the water budget has been a long-standing objective of international programs. After years of hard work, calibrating satellite data, improving inversion techniques, and facilitating the coherency of retrievals, it is admitted that the water cycle budget can now be ...
Monitoring the water cycle from satellite observations is one of the major goals of the EO community and closing the water budget has been a long-standing objective of international programs. After years of hard work, calibrating satellite data, improving inversion techniques, and facilitating the coherency of retrievals, it is admitted that the water cycle budget can now be ...  Quantitative information about precipitation is one vital input to meteorologists, hydrologic scientists, water resources managers, and environmental legislators. Yet, accurate measurement of precipitation over the relevant space and time scales remains a challenge. Soil moisture can be seen as the trace of the precipitation and, consequently, can be useful for providing a way to estimate rainfall accumulation or at least a new constrain to ...
Quantitative information about precipitation is one vital input to meteorologists, hydrologic scientists, water resources managers, and environmental legislators. Yet, accurate measurement of precipitation over the relevant space and time scales remains a challenge. Soil moisture can be seen as the trace of the precipitation and, consequently, can be useful for providing a way to estimate rainfall accumulation or at least a new constrain to ...  State-of-the-art satellite rainfall products are often the only way for measuring rainfall in remote areas of the world. However, these products may fail in properly reproducing the amount of precipitation reaching the ground, which is needed for hydrological applications. The integration of satellite soil moisture products is expected to significantly improve rainfall ...
State-of-the-art satellite rainfall products are often the only way for measuring rainfall in remote areas of the world. However, these products may fail in properly reproducing the amount of precipitation reaching the ground, which is needed for hydrological applications. The integration of satellite soil moisture products is expected to significantly improve rainfall ...  The database includes annual maximum rainfall corresponding to durations of 1, 3, 6, 12, 24 hours and 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 days for approximately 800 raingauges in north-eastern Italy (Trentino, Alto Adige, Veneto and Friuli Venezia Giulia). The database contains data until 1997 for the Autonomous Province of Bozen-Bolzano, 1990 for the Autonomous Province of Trento, and 1996 for Veneto and Friuli Venezia ...
The database includes annual maximum rainfall corresponding to durations of 1, 3, 6, 12, 24 hours and 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 days for approximately 800 raingauges in north-eastern Italy (Trentino, Alto Adige, Veneto and Friuli Venezia Giulia). The database contains data until 1997 for the Autonomous Province of Bozen-Bolzano, 1990 for the Autonomous Province of Trento, and 1996 for Veneto and Friuli Venezia ...  Recently, IRPI-CNR has developed an innovative approach for estimating rainfall from satellite soil moisture data, named SM2RAIN. The ESA funded project “Climate Change Initiative - Soil Moisture“ (CCI-SM) offers a valuable opportunity for testing SM2RAIN algorithm to a continuous, homogenous, long-term (>30 years) soil moisture time series. Indeed, SM2RAIN has the chance to be tested not only for rainfall estimation but also as a ...
Recently, IRPI-CNR has developed an innovative approach for estimating rainfall from satellite soil moisture data, named SM2RAIN. The ESA funded project “Climate Change Initiative - Soil Moisture“ (CCI-SM) offers a valuable opportunity for testing SM2RAIN algorithm to a continuous, homogenous, long-term (>30 years) soil moisture time series. Indeed, SM2RAIN has the chance to be tested not only for rainfall estimation but also as a ...  The hydro-meteorological monitoring is the operational tool for the measures of atmospheric, hydrologic ad hydraulic variables characterizing the hydrological cycle and it represents the grounds of IRPI’s research activities finalized to forecast, prevention and mitigation of natural hazards. Indeed, an accurate knowledge of processes at basis of natural phenomenon cannot disregard the direct measure of hydrological quantities, considering ...
The hydro-meteorological monitoring is the operational tool for the measures of atmospheric, hydrologic ad hydraulic variables characterizing the hydrological cycle and it represents the grounds of IRPI’s research activities finalized to forecast, prevention and mitigation of natural hazards. Indeed, an accurate knowledge of processes at basis of natural phenomenon cannot disregard the direct measure of hydrological quantities, considering ...  The service aims to assess the potential of different satellite products (from active and passive micro-waves, optical, SAR, spectroradiometers, radiometers sensors) in retrieving the main hydrological-hydraulic variables such as rainfall, soil moisture, water level, flow velocity and discharge. This is pursued through a comprehensive validation analysis by using in-situ observed or modelled data for several sited located ...
The service aims to assess the potential of different satellite products (from active and passive micro-waves, optical, SAR, spectroradiometers, radiometers sensors) in retrieving the main hydrological-hydraulic variables such as rainfall, soil moisture, water level, flow velocity and discharge. This is pursued through a comprehensive validation analysis by using in-situ observed or modelled data for several sited located ...  The analysis of hydro-meteorological data is required to verify the correct sensors functioning and possible presence of non-operational periods with missing data. When non-operational periods or malfunction occur, it could be possible to apply procedures for missing data reconstructions and wrong data ...
The analysis of hydro-meteorological data is required to verify the correct sensors functioning and possible presence of non-operational periods with missing data. When non-operational periods or malfunction occur, it could be possible to apply procedures for missing data reconstructions and wrong data ...  The service is based on a procedure consisting of four main steps: the analysis of hydro-meteorological data for the reconstruction of flood event in terms of precipitations and saturation conditions of the soils; assessment of the hydrological response of the basin; runoff estimation in each hydrometric site of interest; flooded areas delineation and comparison with in-situ ...
The service is based on a procedure consisting of four main steps: the analysis of hydro-meteorological data for the reconstruction of flood event in terms of precipitations and saturation conditions of the soils; assessment of the hydrological response of the basin; runoff estimation in each hydrometric site of interest; flooded areas delineation and comparison with in-situ ...  The service analyzes the climate change impact on the main hydro-meteorological variables involved in the hydrological cycle and, in particular, on extreme events of rainfall and discharge (droughts and floods). The service allows to evaluate the combined effects of natural and human processes related to climate change on surface runoff and groundwater, analyzing the possible consequences of such effects on the strategic water ...
The service analyzes the climate change impact on the main hydro-meteorological variables involved in the hydrological cycle and, in particular, on extreme events of rainfall and discharge (droughts and floods). The service allows to evaluate the combined effects of natural and human processes related to climate change on surface runoff and groundwater, analyzing the possible consequences of such effects on the strategic water ...  Semi-distributed continuous hydrological model (MISDc) for real-time soil moisture estimate and river discharge prediction in the Upper-Middle Tiber River basin; flood wave routing model (STAFOM-RCM) for stage hydrograph forecasting at some selected hydrometric stations in the Tiber River basin; Rainfall-runoff database coupled with the kinematic model KS for an expeditious estimate of probability flooding ...
Semi-distributed continuous hydrological model (MISDc) for real-time soil moisture estimate and river discharge prediction in the Upper-Middle Tiber River basin; flood wave routing model (STAFOM-RCM) for stage hydrograph forecasting at some selected hydrometric stations in the Tiber River basin; Rainfall-runoff database coupled with the kinematic model KS for an expeditious estimate of probability flooding ...  SECLI Project is aimed to assess the combined effects of processes related to natural and anthropogenic climate change on water resources, both surface and groundwater, in the Umbrian territory, identifying the possible consequences of such effects on drinking water policy, and on how these may affect the existing system of withdrawals and ...
SECLI Project is aimed to assess the combined effects of processes related to natural and anthropogenic climate change on water resources, both surface and groundwater, in the Umbrian territory, identifying the possible consequences of such effects on drinking water policy, and on how these may affect the existing system of withdrawals and ...  The activities of the project concerns the analysis and processing of hydro-meteorological data collected by the monitoring network of the Umbria Region for the period 1994-2014. In particular, the study regards the rainfall, temperature and water level time series. In addition, the discharge series corresponding to observed water levels are estimated for at hydrometric station through the rating curve estimated on the basis of flow velocity ...
The activities of the project concerns the analysis and processing of hydro-meteorological data collected by the monitoring network of the Umbria Region for the period 1994-2014. In particular, the study regards the rainfall, temperature and water level time series. In addition, the discharge series corresponding to observed water levels are estimated for at hydrometric station through the rating curve estimated on the basis of flow velocity ...  River discharge monitoring is fundamental for the study of the hydraulic regime of river flow and for the validation and calibration of rainfall-runoff models. The assessment of channel roughness coefficients associated with the measured discharges is fundamental for the calibration of flood routing models that can be used to address civil protection activities in real time. Unfortunately, the number of river flow monitoring stations in the ...
River discharge monitoring is fundamental for the study of the hydraulic regime of river flow and for the validation and calibration of rainfall-runoff models. The assessment of channel roughness coefficients associated with the measured discharges is fundamental for the calibration of flood routing models that can be used to address civil protection activities in real time. Unfortunately, the number of river flow monitoring stations in the ...  The main activities of the project, developed in the context of the program Nextdata funded by the Italian Ministry of Education, University and Research (MIUR), are:
collection, organization and analysis of the available hydro-meteorological and climate data for the characterization of the meteo-climate evolution in Apennine mountain areas;
extensive experimental campaigns for soil moisture monitoring in hillslope portions and ...
The main activities of the project, developed in the context of the program Nextdata funded by the Italian Ministry of Education, University and Research (MIUR), are:
collection, organization and analysis of the available hydro-meteorological and climate data for the characterization of the meteo-climate evolution in Apennine mountain areas;
extensive experimental campaigns for soil moisture monitoring in hillslope portions and ...  The artificial reservoirs are fundamental for water resources management, by regulating releases to meet the different users request (industrial, irrigation, hydropower, etc.), and for downstream territories floods defence through lamination of critical flood waves.
The main objective of the project concerns the review of hydrological-hydraulic studies carried out for the Montedoglio dam, on Tiber River, Casanuova dam, on Chiascio River, ...
The artificial reservoirs are fundamental for water resources management, by regulating releases to meet the different users request (industrial, irrigation, hydropower, etc.), and for downstream territories floods defence through lamination of critical flood waves.
The main objective of the project concerns the review of hydrological-hydraulic studies carried out for the Montedoglio dam, on Tiber River, Casanuova dam, on Chiascio River, ...  The Tiber River Basin Authority (ABT) and the Umbria Region (Service Water Resources and Hydraulic Risk), considering the verified underestimation of the flood-prone areas in the Paglia River basin provided by the Italian PAI (hydro-geological management plan) and the update of rating curves, decided to revise the hydrological study of the drainage basin in order to re-estimate the flood hazard maps for the Paglia River reach bounded upstream ...
The Tiber River Basin Authority (ABT) and the Umbria Region (Service Water Resources and Hydraulic Risk), considering the verified underestimation of the flood-prone areas in the Paglia River basin provided by the Italian PAI (hydro-geological management plan) and the update of rating curves, decided to revise the hydrological study of the drainage basin in order to re-estimate the flood hazard maps for the Paglia River reach bounded upstream ...  Water and sediment connectivity has emerged in recent years as a significant conceptual framework for understanding the transfer of surface water and sediment through landscapes. Connectivity can be seen both as a driver of hydrological and geomorphic processes within a catchment and as an emergent catchment property that is the result of processes acting at different ...
Water and sediment connectivity has emerged in recent years as a significant conceptual framework for understanding the transfer of surface water and sediment through landscapes. Connectivity can be seen both as a driver of hydrological and geomorphic processes within a catchment and as an emergent catchment property that is the result of processes acting at different ...  Nel 2014 ricorrono vent’anni dalla tragica alluvione che nel novembre 1994 colpì gran parte del territorio piemontese, con perdita di vite umane, di beni mobili ed immobili. L’alluvione 1994 costituì altresì un momento storico nel campo della pianificazione territoriale, prevenzione e gestione della pericolosità e rischio geologico-idraulico, che si tradusse in dettami normativi, per l’epoca avanzati e lungimiranti. Da quell’evento ...
Nel 2014 ricorrono vent’anni dalla tragica alluvione che nel novembre 1994 colpì gran parte del territorio piemontese, con perdita di vite umane, di beni mobili ed immobili. L’alluvione 1994 costituì altresì un momento storico nel campo della pianificazione territoriale, prevenzione e gestione della pericolosità e rischio geologico-idraulico, che si tradusse in dettami normativi, per l’epoca avanzati e lungimiranti. Da quell’evento ...  The project AIM-DAMS is aimed at developing a laboratory of integrated and advanced environmental monitoring for the control of the behavior of the earth-dams due to the different factors acting on the dams during their lifetime. Based on the integration of innovative and non-invasive sensors, as well as recent monitoring techniques and numerical modelling, the project is intended to fulfill the need of the dam management agencies of using ...
The project AIM-DAMS is aimed at developing a laboratory of integrated and advanced environmental monitoring for the control of the behavior of the earth-dams due to the different factors acting on the dams during their lifetime. Based on the integration of innovative and non-invasive sensors, as well as recent monitoring techniques and numerical modelling, the project is intended to fulfill the need of the dam management agencies of using ...  FLIRE is a demonstration project aiming to the development of an integrated Decision Support System (DSS) for both flash floods and forest fires risk assessment and management. The DSS tool will be designed by using state of art tools, technologies and methods and taking into account prevention, adaptation and interaction issues. The final model will be online available to key stakeholders and relevant authorities (local and national) for the ...
FLIRE is a demonstration project aiming to the development of an integrated Decision Support System (DSS) for both flash floods and forest fires risk assessment and management. The DSS tool will be designed by using state of art tools, technologies and methods and taking into account prevention, adaptation and interaction issues. The final model will be online available to key stakeholders and relevant authorities (local and national) for the ... 














