News
Participation of IRPI in the “3rd European Regional Conference” of IAEG

The 3rd European Regional Conference of the IAEG https://euroengeo2020.org/, originally scheduled for 2020, just ended a few days ago. The conference, organized by the Greek National Group of the IAEG, was held in Athens on 6-10 October, 2021. The unifying theme of the event was: Leading to Innovative Engineering Geology Practices.
The Conference was run in a “hybrid” mode (face to face + online) and was attended by 244 researchers and professionals from all over the world (33 countries), out of which 55 participated on-line. The program included 6 Keynote lectures delivered in person. Janusz Wasowski, a senior scientist of the CNRI IRPI of Bari, presented a Keynote entitled “Recent advances in Remote Sensing for use in Engineering Geology”. Furthermore, the researchers of the CNRI IRPI of Turin contributed some papers presented orally on-line.
The Proceedings of the Conference (2 Volumes: full papers & extended abstracts) and the presentations will soon be available on the IAEG website. The publication of a Special Volume (thematic collection with Keynote lecture and selected papers) of the Quarterly Journal of Engineering Geology and Hydrology is also planned.
Special Issue “UAV Applications in Geology and Geomorphology” in Remote Sensing MDPI

The Special Issue of Remote Sensing on “UAV Applications in Geology and Geomorphology” (Deadline: 16 March 2022) – Gest Editors: Dr. Danilo Godone (CNR-IRPI), Dr. Cignetti Martina (CNR-IRPI), Dr. Mihai Ciprian Mărgărint (University of Iasi) is open for submission. This Special Issue of Remote Sensing aims to collects, high-quality, original research articles and technical notes on the application of the Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) in the environmental applications and in the earth sciences field, with particular interest in open-source approaches and the use of additional sensors mounted in the payload, functional to multi-sensor and multi-temporal investigations of the analysed phenomena.
Info: danilo.godone@irpi.cnr.it ; martina.cignetti@irpi.cnr.it
Link: https://www.mdpi.com/journal/remotesensing/special_issues/UAV_Geo
IRPI of Cosenza has participated to the event “2021 European Researchers’ Night”

CNR-IRPI of Cosenza is one of the partners of the project “SuperScienceMe 2021 – Research is your Re-generation”. The proposal is one of the 6 national projects selected and funded for the EC initiative “2021 European Researchers’ Night”. The aim of the 2021 initiative is the European Green Deal.
The partners of SuperscienceMe 2011 are the Universities of Calabria (Cosenza), Magna Graecia (Catanzaro) and Mediterranea (Reggio Calabria), the CNR Institutes of Calabria and Basilicata, and the Calabria and Basilicata Regions. The goal of the event “2021 European Researchers’ Night”, held on 24 September, mainly online, has been to encourage young people to acquire knowledge aiming to a change of their behaviours for inverting the climate and environmental challenges in opportunities.
Within the ambit of the “SuperScienceMe2021” project, IRPI has produced two brief videos, uploaded in the project web page www.superscienceme.it, and promoted a survey on the public perception of climate change and natural risks (mainly, floods and landslides). The survey is carried out by means of an online questionnaire and has the goal to propose strategies and actions to improve public knowledge and communication on these issues. It is possible to participate to the online questionnaire, present in the project web site, through the link www.superscienceme.it/questionario-cambiamenti-climatici-percezione-sociale .
Awarding of the Florisa Melone prize

On the occasion of the Hydrology Days 2021, organized by Società Idrologica Italiana, (SII) together with the University of Campania, the FLORISA MELONE AWARD was conferred on Dr. Elena Cristiano from the University of Cagliari and on Dr. Antonio Annis from the University for Foreigners of Perugia for the START-UP project – Multilayer Systems (Polder Roofs) applied to Urban Rainwater networks. The award, dedicated to the IRPI colleague Dr. Florisa Melone, a researcher of high moral and scientific stature, assigns financial support to research projects carried out by young researchers who are members of the SII with the aim of promoting research autonomy and stimulating new ideas in the hydrological field.
IRPI at the researchers’ night – Venetonight 2021

On September 24th, 2021 the European Researchers’ Night will take place and Giorgia Macchi, of CNR IRPI of Padova, institute will present an interactive laboratory “The movements of the mountains: everything there is to know about landslides (and more)!” to let the public understand what landslides are, how they are studied, why they are so dangerous and how to protect ourselves.
The sixth congress of the INTERNATIONAL SOCIETY FOR GEOMORPHOMETRY, held in Perugia from 13 to 15 September, is now over. One of the works presented by the IRPI researchers was awarded a “best paper” award

The sixth Geomorphometry conference, organized by the International Society For Geomorphometry together with the CNR IRPI and the Physics and Geology Department, was held at University of Perugia, September 13-15.
The conference was attended by more than 50 researchers from around the world, connected online from 11 different time zones.
The conference hosted high-profile names in international geomorphometry such as Michael Hutchinson, Ian Sylvester Evans, Peter Guth. The program included three keynote contributions and 44 presentations, based on short research articles presented at the congress after peer review by the congress scientific committee.
The contributions were voted by the participants of the congress. The “best student paper” award was assigned to the paper entitled “Estimating the spatial distribution of vegetation height and ground-level elevation in a mesotidal salt marsh from UAV LiDAR-derived point cloud”, presented by Daniele Pinton, University of Florida. The “best paper award” was shared between the papers “Reflections on adding the Z dimension to earth system analysis” presented by Michael Hutchinson , Australian National University, and “A data-driven method for assessing the probability for terrain grid cells of initiating rockfalls on a large area”, authored by researchers from CNRI IRPI, Perugia: M. Alvioli, M. Santangelo, F. Fiorucci, M. Cardinali, I. Marchesini, P. Reichenbach, M. Rossi, and presented by Federica Fiorucci. An extended version of the paper per was recently published in the journal Engineering Geology with the title “Rockfall susceptibility and network-ranked susceptibility along the Italian railway”.
Geomorphometry 2021
Brevetto CNR-IRPI “Sistema Perfezionato per il Monitoraggio di Ancoraggi Geotecnici”

La collaborazione pluriennale tra il CNR-IRPI, il gruppo di Geotecnica dell’Università di Padova e la società la Dalla Gassa srl, ideatrice degli ancoraggi compositi come sistemi per il rinforzo dei versanti in frana, ha portato allo registrazione di brevetto italiano riguardante l’integrazione di sensori distribuiti in fibra ottica, per la determinazione degli stati di sollecitazione degli ancoraggi (Data di deposito: 2019; concessione: 2021).
Referente: Luca Schenato
Si è concluso il workshop internazionale Resilient Infrastructures for Tomorrow’s Hazards a Venezia, premiati due ricercatori IRPI

Il 21 e il 22 luglio si è svolto in modalità mista, sia online sia in presenza nell’isola di S.Servolo (Venezia), il workshop Resilient Infrastructures for Tomorrow’s Hazards
nell’ambito del progetto Europeo di mobilità Marie Skłodowska Curie HERCULES (https://cordis.europa.eu/project/id/778360). Al workshop hanno partecipato ricercatori provenienti da Kazakistan, Iran, Austria, Cina e UK. A rappresentare l’Italia ricercatori IRPI della sedi di Padova e Perugia.
Il programma prevedeva 4 keynote e 26 brevi presentazioni per ciascun ricercatore che a partecipato al programma di mobilità. Le presentazioni sono state giudicate da un comitato composto dai leader di ciascun gruppo di ricerca e tra quelle selezionate per i premi di migliore presentazione vi sono quelle dei ricercatori IRPI Giulia Bossi, per l’intervento Modelling seepage in heterogenous soils with the Boolean Stochastic Generation Method e Giacomo Tedesco che presentava Monitoring and modelling of a road tunnel damaged by a large block slide.
IRPI organizza il workshop internazionale ‘Resilient Infrastructures for Tomorrow’s Hazards’ a Venezia

Special issue: GIS-Supported DEM Analysis for Characterization of Short to Long Term Landscape Dynamics

The availability of digital elevation models globally is providing increasing capabilities of scaling up geomorphological analyses through the use of geographic information systems (GIS).
We started a Special Issue on the International Journal of Geo-Information. The special issue is dedicated to current research in the characterization of short to long term landscape dynamics through GIS-supported analyses applied to digital elevation models. Contributions can explore methodological, conceptual, and technological aspects, as well as applications. Short-term landscape dynamics may include soil erosion, landslides, and river network dynamics. Long-term landscape dynamics may include the evaluation of erosion, denudation, uplift rates.
For a full description of the Special Issue, visit https://www.mdpi.com/journal/ijgi/special_issues/GIS-Supported_DEMLandscapeDynamics
The deadline for papers submission is 31/12/2021.
The Special Issue, in the Frontiers in Sensors magazine, is open

The goal of this Research Topic is to provide a platform for reporting the latest advances in the field of distributed sensors based on optical fiber technologies, both in form of original research articles that discuss the principles, performance, implementation, and/or application of these sensing systems, and to present review or perspective papers that draw a roadmap of this field.
Memorandum of understanding with the Department of Management of the University of Turin

Starting from 1 June 2021, CNR IRPI has signed a memorandum of understanding with the Department of Management (DM) of the University of Turin, in order to start research and training activities on areas of common interest. The DM deals with integrated management systems (economic-environmental) of the territory, sustainable tourism and Internet of Things (IoT) to support territorial management and monitoring. The protocol also provides for the possibility of collaboration in degree and doctorates theses as well as internships.
More info: danilo.godone@irpi.cnr.it
Atelier di formazione alla ricerca in alta quota – Edizione 2021

Nell’ambito del progetto GioMon, cofinanziato dalla Fondazione CRT, dal 6 al 10 settembre 2021 nel bacino glaciale della Bessanese (Balme, TO) si svolgerà un “Atelier di formazione alla ricerca in alta quota”. L’iniziativa è finalizzata all’introduzione di studenti universitari di atenei piemontesi ai metodi della ricerca scientifica ed alle loro dirette applicazioni in campo. Gli studenti saranno i veri protagonisti dell’Atelier: definiranno obiettivi e metodi del proprio progetto ricerca, raccoglieranno ed analizzeranno dati, e presenteranno infine i risultati del loro lavoro. Ricercatori del CNR-IRPI seguiranno tutto il percorso formativo degli studenti, stimolandoli e coinvolgendoli mediante l’applicazione di un approccio collaborativo e condiviso. La base logistica per le attività in campo sarà il Rifugio Gastaldi.
Per informazioni: marta.chiarle@irpi.cnr.it
Presentation by Luca Schenato at the ‘Belt and Road webinar series on Geotechnics, Energy and Environment’

On Friday 28th May, 9.00 a.m. Luca Schenato will give an invited talk about the “Development of innovative optical fiber sensors and systems for dikes and debris flows” in the framework of the Belt and Road webinar series on Geotechnics, Energy and Environment. The talk will illustrate some recent results about the development of fiber optic distributed and quasi-distributed pressure sensors with high sensitivity for the measurement of pressure on dikes and the results of some experiments aimed at validating the feasibility of the application of the distributed acoustic sensing for debris flow monitoring and characterization.

Innovative study of the embankments of the Adige river

The Padova section is working with the University of Padua in an innovative study for the geotechnical characterization of the embankments of the Adige river in Salorno (BZ). The study, coordinated by the Southern Mountain Basins Office of the Civil Protection Agency of Bolzano, involves taking soil samples with the “gel push sampler” technique. The boreholes will be then equipped with innovative geotechnical instrumentations. In particular, optical fibers will be installed for distributed temperature measurement, under the coordination of the Padova branch.
(Personnel involved: L. Schenato, G. Marcato – coordination; G. Tedesco – installation and measurement campaigns; for further information: luca.schenato@cnr.it).
link:
https://www.altoadige.it/cronaca/adige-indagini-geotecniche-sulla-stabilit%C3%A0-degli-argini-per-proteggere-l-a22-1.2912341
https://www.provincia.bz.it/news/it/news.asp?news_action=4&news_article_id=655807
LandAware MayDay round-the-clock conference

The MayDay round-the-clock conference of LandAware, the international network on Landslide Early Warning Systems, will be held online starting from 14:00 (CEST) on 19 May 2021. Stefano Luigi Gariano, researcher at IRPI in Perugia, is among the founding members of the network and among the organizers of the conference.
It will be a 24-hour event (it will finish at 14:00 CEST on 20 May 2021), an online, diversified and engaging conference that will include working groups meetings, networkwide activities and special events.
More information and the link for registration can be found at the following link: https://www.landaware.org/mayday-2021/
The IPROMO Summer School 2021 call for application is open!

The Summer School, chaired by Dr. Danilo Godone (CNR-IRPI), is organized by FAO-Mountain Partnership in cooperation with Turin and Tuscia University. This edition topic is “Post COVID-19 Recovery in Mountain Areas”. Due to the pandemic situation it will be held in online format.
The application deadline is 15 May 2021.
More info: danilo.godone@irpi.cnr.it
http://www.fao.org/mountain-partnership/our-work/capacitydevelopment/ipromo/course-2021/en/
Assegnata a Fausto Guzzetti la Sergey Soloviev Medal 2021

Oggi, il dottor Fausto Guzzetti, direttore delle attività tecnico scientifiche per la previsione e prevenzione dei rischi presso il Dipartimento nazionale di protezione civile, e già direttore del nostro Istituto, è stato insignito della “Sergey Soloviev Medal” 2021. Il premio è stato conferito per il suo fondamentale contributo scientifico nel campo dei rischi naturali e per i notevoli sforzi profusi nel raccordare la comunità scientifica e le autorità di protezione civile nelle tematiche riguardanti la previsione e la mitigazione del rischio geo-idrologico.
La cerimonia di premiazione si è tenuta nell’ambito della EGU General Assembly e la medal lecture dal titolo “Considerations on the prediction of hazards (mainly landslides) and their consequences” ha riguardato i molteplici aspetti che il dottor Guzzetti ha affrontato durante la sua carriera di ricercatore del CNR IRPI. Gli argomenti trattati durante la presentazione di oggi hanno spaziato tra vari quesiti di ricerca, andando dalle problematiche legate al riconoscimento e mappatura delle frane, alle difficoltà relative alla previsione spaziale e temporale di eventi di frana e ai possibili modelli attualmente disponibili per la valutazione degli impatti che questi fenomeni causano a strutture e infrastrutture, nonché alla popolazione.
“Ho trascorso una parte considerevole della mia carriera di ricerca occupandomi di rischi naturali, in particolare rischi geo-idrologici, e sono lieto che l’EGU abbia riconosciuto il mio lavoro, che è anche quello dei tanti colleghi con cui ho lavorato”, queste le parole di Guzzetti quando è stato raggiunto dalla inattesa quanto mai ben accolta notizia del riconoscimento offertogli.

Il prestigioso “Earth Observation Excellence Awards” al gruppo di idrologia del Cnr-Irpi

Il gruppo di idrologia dell’Istituto di ricerca per la protezione idrogeologica (Cnr-Irpi) di Perugia ha vinto il premio indetto dall’European Space Agency (ESA) e dall’European Geosciences Union (EGU) denominato “Earth Observation Excellence Awards”. Il premio è stato attribuito considerando le quattro seguenti categorie: eccellenza nella scienza, eccellenza nell’innovazione, impatto nel campo dell’osservazione della terra e potenzialità di fornire futuri contributi all’osservazione della Terra.
Il gruppo di Iidrologia, composto da Luca Brocca, Stefania Camici, Luca Ciabatta, Christian Massari e Angelica Tarpanelli, è stato premiato per la profonda esperienza nella modellazione idrologica e idraulica utilizzando sensori satellitari e in situ. In particolare, il gruppo ha condotto studi pionieristici sull’assimilazione di prodotti satellitari di umidità del suolo nella modellazione idrologica, e sull’uso dell’osservazione della Terra per la stima della portata fluviale e delle precipitazioni. I dati satellitari sono quindi utilizzati con successo per diverse applicazioni in idrologia quali la previsione delle piene e delle frane, il monitoraggio della siccità e la gestione delle risorse idriche.
Il direttore generale dell’ESA, Josef Aschbacher, il presidente dell’EGU, Alberto Montanari, si sono congratulati con i vincitori per questo straordinario riconoscimento e sono sicuri che continueranno ad essere pionieri dei risultati scientifici europei di osservazione della Terra in futuro.
“Siamo molto contenti di questo riconoscimento che premia l’importante lavoro del nostro gruppo nelle tematiche di osservazione della terra e rischi ambientali. Il raggiungimento di questo risultato è stato possibile grazie al lavoro sinergico dell’intero gruppo di Idrologia del Cnr-Irpi a cui estendiamo il nostro ringraziamento. Vogliamo infine ringraziare l’ESA e l’EGU per l’assegnazione del premio”, ha commentato Luca Brocca (Cnr-Irpi).
Il premio sarà presentato alla cerimonia virtuale di premiazione dell’Assemblea generale dell’EGU, che si terrà il 19 aprile alle 18:00 CET. I dettagli su come partecipare a questo evento saranno forniti in prossimità della data della cerimonia.

New receiver in the GNSS-CORS permanent station

Today, the CNR GMG GNSS-CORS (Global Navigation Satellite System- Continuously Operating Reference Station); already member of TOPCON NETGEO-TopNETlive GNSS Network (Code: TORC); was upgraded with the new multiconstellation TOPCON NET-G3 receiver, able to track NAVSTAR GPS; GLONASS; Galileo; BeiDou; SBAS and QZSS satellite network.
For more information: Marco Baldo (marco.baldo@irpi.cnr.it)

IRPI: new agreement with IREA

The Cooperation Agreement between the Institute for Electromagnetic Sensing of the Environment of the CNR, IREA, and the Research Institute for Geo-Hydrological Protection has been signed. In line with the programmatic guidelines of the National Research Council, the two Institutes intend to continue and strengthen the effective collaboration in the field of monitoring, forecasting and mitigation of geo-hydrological risks. Specific Executive Agreements will outline the individual actions or joint projects of the two Institutes.
Updated of the global satellite rainfall dataset

The global satellite rainfall dataset SM2RAIN-ASCAT has been updated until the end of 2020.
We are very happy to announce the new release of global #SM2RAIN-ASCAT satellite ️ rainfall product
14 years of daily rainfall at 10 km resolution!https://t.co/ou2VRA5rsC@eumetsat @CopernicusEU @CNRsocial_ @EO_OPEN_SCIENCE @EuroGeosciences @WMO pic.twitter.com/pqgyea3HXR— Hydrology IRPI-CNR (@Hydrology_IRPI) February 8, 2021
Special Issue: “Development and Use of Databases to Analyze Geo-Hydrological Hazards”

Guest Editors: Carmela Vennari (CNR-IRPI, Italy), Giuseppe Esposito (CNR-IRPI, Italy), Emanuela Toto (National Civil Protection Agency, Albania)
The journal Geosciences is currently running a special issue entitled “Development and Use of Databases to Analyze Geo-Hydrological Hazards”, which is accepting submissions until 30 September 2021.
This issue aims to gather high-quality, original research articles and technical notes on the development and use of databases to record and analyze geo-hydrological hazards, including information about landslides, floods, sinkholes, coastal processes, and the related triggering conditions, such as hydro-meteorological, seismic or human factors.
Special Issue “Geomorphometry 2020” in “Transactions in GIS”

General submission for the Special Issue “Geomorphometry 2020″ in TGIS is now open. The special issue “Geomorphometry 2020” in Transactions in GIS collects contributions stemming from the short papers submitted to the conference Geomorphometry 2020, but it is not limited to them. Authors of accepted abstracts for the conference were invited to submit papers for the special issue, according to the journal’s Author Guidelines. Submissions are now open for extra contributions, and all of them will go through standard peer review process of the Journal.
Submission Guidelines
Submissions to ScholarOne Manuscripts site:
https://mc.manuscriptcentral.com/tgis
Submission Deadline: April 1st, 2021
Expected Final Decision: August 1st, 2021
È stato nominato il nuovo Direttore IRPI

Nella giornata di ieri 19 gennaio 2021, il Direttore Generale del CNR, visto l’esito del Consiglio di Amministrazione del 20 novembre 2020 ha conferito l’incarico di Direttore dell’Istituto di Ricerca per la Protezione Idrogelogica al Dott. Tommaso Moramarco, già Dirigente di Ricerca presso il medesimo Istituto. Il nuovo direttore prenderà servizio a partire dall’1 febbraio 2021 e tale mandato durerà per i prossimi quattro anni. Tutto il personale dell’Istituto gli augura un proficuo lavoro.
Scheda personale – Dott. Tommaso Moramarco, Dirigente di Ricerca »
Innovative distributed temperature optical fiber sensing system

On last Dec. 22, 2020, within the framework of an upcoming monitoring project the IRPI personnal of the Padova branch (G. Tedesco, on the field, L. Schenato, from remote), with other collaborators from the University of Padova, have participated to the installation of an innovative distributed temperature optical fiber sensing system to investigated the hydraulic behavior of a dike affected by anomalous seepage piping.

The global threat of land subsidence: an anthropogenic hazard accompanying the depletion of groundwater resources. A new study published on “Science” Journal

The CNR-IRPI researcher Mauro Rossi participated to the realization of a new study published on “Science” Journal.
The article, titled “Mapping the global threat of land subsidence” realized within the “Land Subsidence International Initiative” of UNESCO and coordinated by Dr Gerardo Herrera-García, a researcher from the Geological Survey of Spain (IGME), analyses at a global scale, the land subsidence, an anthropogenic hazard accompanying the depletion of groundwater resources.
Even though land subsidence is a slow and gradual process, it can permanently reduce the storage capacity of aquifer systems, damage buildings and infrastructures, and increase the flooding risk in alluvial areas and coastal plains. Land subsidence greater than 25 cm/year is occurring in several countries including Indonesia, Iran and several cities in Mexico. In Jakarta, Indonesia, the subsidence impact is so severe that the government is planning to move the capital to the island of Borneo. Land subsidence is a serious threat even to many Italian coastal areas, in Emilia-Romagna, Veneto, Puglia, Toscana, Campania, Calabria, as claimed by Luigi Tosi (CNR-IGG) e Pietro Teatini (Università di Padova), co-authors of the study.
Potential subsidence areas threaten 1.2 billion inhabitants and 21% of the major cities worldwide, with 86% of the exposed population living in Asia. Even though further research is still needed to fully understand the global impact of land subsidence, this work estimates that the current economic exposure to potential subsidence amounts to US$8.17 trillion, or 12% of the global gross domestic product. Moreover, the research indicates that by 2040, an estimated 635 million inhabitants will be living in flood prone areas, where land subsidence could increase the flooding risk.
Citation: Gerardo Herrera-García, Pablo Ezquerro, Roberto Tomás, Marta Béjar-Pizarro, Juan López-Vinielles, Mauro Rossi, Rosa M. Mateos, Dora Carreón-Freyre, John Lambert, Pietro Teatini, Enrique Cabral-Cano, Gilles Erkens, Devin Galloway, Wei-Chia Hung, Najeebullah Kakar, Michelle Sneed, Luigi Tosi, Hanmei Wang, Shujun Ye (2021). Mapping the global threat of land subsidence. Science: Vol. 371, Issue 6524, pp. 34-36. DOI: 10.1126/science.abb8549.
Web links: https://science.sciencemag.org/content/371/6524/34
Agreement between CNR IRPI and FODAF

On 18 December 2020, the agreement between CNR IRPI and the Interregional Federation of the Orders of Agronomists and Forestry Doctors of Piedmont and Valle d’Aosta (Federazione Interregionale degli Ordini dei Dottori Agronomi e Dottori Forestali di Piemonte e Valle d’Aosta – FODAF) was signed. Its aim are the accomplishment of educational and experimental activities. The agreement provides, for the next two years, for the organization of training activities and lays the foundations for potential research collaborations in areas of common interest to the parties.
Info: Danilo Godone (danilo.godone@irpi.cnr.it)
Happy International Mountain Day!

The United Nations General Assembly designated 11 December “International Mountain Day”. As of 2003, it has been observed every year to create awareness about the importance of mountains to life, to highlight the opportunities and constraints in mountain development and to build alliances that will bring positive change to mountain peoples and environments around the world.

LandAware kick-off event

The kick-off event of LandAware network (www.landaware.org) will take place (online, using the Zoom platform) on Monday 14 December 2020, 13:30-15:30 CET.
The 2-hour event will include a presentation of the network, of its working groups, some invited lectures and a final interactive session. Being aware that the time of the event will not allow the easy participation of potentially interested people from all time-zones, the Landaware Executive Committee already decided that the event will be recorded and later posted online for watching on demand.
People interested in participating in the LandAware Kick-Off event, besides marking the date on their calendar, must register by filling the following form: https://forms.gle/chVsgEiUr69GBDWS7. The link to join the Zoom meeting will be sent by email to registered participants one day before the event.
IRPI at workshop INGV

IRPI presenting at INGV workshop “Fiber Optic Sensing in Geoscience”: On Dec. 10, Luca Schenato from the Padova IRPI’s branch will give a talk at the workshop “Fiber Optic Sensing in Geoscience” organized by the Istituto Nazionale di Geofisica e Vulcanologia. The workshop is organized in three main sessions dedicated to instrument technologies and applications of point and distributed fibre optic sensors in various fields, including seismology, volcanology, geodesy, hydrology, and geothermic. L. Schenato will give a talk entitled “Optical fiber Sensing in Geotechnical and Hydrological Applications.”
INMOSTRA: installation of an innovative optical fiber

On last Dec. 1, 2020, within the framework of the POR-FESR project “INMOSTRA: INgegnerizzazione di sensori in Fibra Ottica per il Monitoraggio dei rinforzi STrutturali su versAnti instabili” the IRPI personnal of the Padova branch (G. Tedesco, on the field, L. Schenato and G. Marcato, from remote) have participated to the installation of an innovative distributed strain and temperature optical fiber sensing system for soil nails with the other project partners from the University of Padova and Sirive Srl.
Link to project: https://www.irpi.cnr.it/en/project/inmostra/
CNR-IRPI @ AGU Fall Meeting 2020

On Dec 02, 2020, Luca Schenato from the IRPI’s Padova Branch was give a talk about the assessment of the feasibility of fiber-optic DTS for geophysical applications at the AGU 2020 Scientific workshop: Applications and Advances in Distributed Temperature Sensing (DTS) for Earth and Space Sciences organized by prof. Scott Tyler, University of Nevada
Web of Science: Luca Brocca named Highly Cited Researcher

Special Issue “Application of Remote Sensing in Hydrogeology: Landslides, Land Subsidence and Uplift”

The Special Issue of Remote Sensing journal on “Application of Remote Sensing in Hydrogeology: Landslides, Land Subsidence and Uplift” (deadline: 1 September 2021) – Guest Editors: Francesca Ardizzone (CNR-IRPI, Italy) – is still opened.
The goal of this Special Issue of Remote Sensing (Section Remote Sensing in Geology, Geomorphology, and Hydrology) is to gather original research or case studies exploiting remote sensing techniques for detecting, characterizing, and modelling landslides, land subsidence, and uplift due to groundwater level changes.
For information: francesca.ardizzone@irpi.cnr.it
Link: https://www.mdpi.com/journal/remotesensing/special_issues/Landslides_Land_Subsidence_Uplift
IPROMO 2020 Summer School – Mountains in a changing climate: Threats, challenges and opportunities

The 13th edition of the IPROMO (International Programme on Research and Training on Sustainable Management of Mountain Areas) Summer School was completed successfully. It was organized by Mountain Partnership Secretariat of the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO-MP), Università degli Studi di Torino and Università degli Studi della Tuscia. The whole Summer School was chaired, and organized, by Dr. Danilo Godone.
The 2020 Summer School, due to Covid-19 pandemic, took place online with lectures, quizzes and working group presentation. On the 6th of October, the lecture on “Climate Change and Natural Hazards” was held by Dr. Daniele Giordan and Dr. Niccolò Dematteis.
The Summer School was attended by 33 participants from 21 different countries all over the World.
Info: Danilo Godone (danilo.godone@irpi.cnr.it)
Link: http://www.fao.org/mountain-partnership/our-work/capacitydevelopment/ipromo/course-2020/en/
Special Issue on “Geo-Hydrological Risks Management” in Geosciences – MDPI

The Special Issue of Geosciences on “Geo-Hydrological Risks Management” (Deadline: 31 December 2020) – Guest Editors: Dr. Danilo Godone (CNR-IRPI); Dr. Louise Vick (The Arctic University of Norway), Prof. Changdong Li (China University of Geosciences) is open for submission. This Special Issue of Geosciences aims to gather, high-quality, original research articles and technical notes on the use of geosciences, applied to geo-hydrological risk management. The Special Issue will highlight case studies, best practices, and applied research.
Info: danilo.godone@irpi.cnr.it
Link: https://www.mdpi.com/journal/geosciences/special_issues/Geo-Hydrological_Risks
CNR IRPI joins the FAO – Mountain Partnership

Since 23 September 2020 CNR – IRPI is a member of the Mountain Partnership.
The Mountain Partnership is a, worldwide, voluntary alliance of governments, bodies and organizations working in mountains and acting for their sustainable development. Mountain Partnership encourages and facilitates, under the umbrella of FAO, initiatives and cooperation, at all levels, for joint projects and activities in the world’s mountain regions.
More info:
Focal Point – Danilo Godone (danilo.godone@irpi.cnr.it)
http://www.fao.org/mountain-partnership/en/
Luca Brocca Keynote Speaker at European Space Agency

Luca Brocca, Director of Research at the Research Institute for Geo-Hydrological Protection (CNR-IRPI), will be one of the keynote speaker at European Space Agency (ESA)’s Phi Week (https://phiweek.esa.int). At this link (https://youtu.be/M5twJ3dtkg4) you can see the preview of his talk which will be on 29 September at 16:30 CEST in live streaming. The DTE Hydrology project will be presented in which a high resolution (1 km) digital replica of the water cycle and its impacts will be developed for the River Po Basin, by exploiting advanced remote sensing techniques and modelling.
Pubblicato sulla rivista “Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences (NHESS)” un nuovo articolo che descrive una procedura automatica finalizzata all’individuazione di frane di evento

I ricercatori IRPI Giuseppe Esposito, Ivan Marchesini, Alessandro Cesare Mondini, Paola Reichenbach, Mauro Rossi hanno pubblicato un nuovo articolo sulla rivista “Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences (NHESS)”.
L’articolo, intitolato “A spaceborne SAR-based procedure to support the detection of landslides” descrive una procedura automatica finalizzata all’individuazione di frane di evento su aree di vaste dimensioni. La procedura è stata sviluppata dal CNR-IRPI di Perugia nell’ambito del progetto STRESS (Strategies, Tools and new data for REsilient Smart Societies), finanziato da FONDAZIONE CARIPLO e guidato da Simone Sterlacchini (CNR-IGAG, Milano).
Nello specifico, a partire da dati radar satellitari acquisiti dai satelliti Sentinel-1 dell’Agenzia Spaziale Europea, e mediante l’utilizzo di software Open Source, la procedura consente di monitorare aree di migliaia di chilometri quadrati, effettuando operazioni di change detection multitemporale volte ad individuare, su un prodotto raster preliminare, le variazioni di backscattering del segnale. La segmentazione di questo prodotto e l’analisi statistica dei pixel contenuti nei segmenti, consente di identificare le zone interessate da potenziali processi di instabilità indotti, per esempio, da piogge o terremoti. La cadenza temporale con cui vengono prodotte le mappe è connessa alla disponibilità delle immagini Sentinel-1.
La procedura può risultare particolarmente utile per la gestione delle emergenze da frana, rappresentando uno strumento di supporto alle decisioni, così come di supporto alla mappatura in campo delle frane. L’utilizzo di immagini radar consente, infatti, di avere informazioni anche in caso di copertura nuvolosa. Nell’articolo, oltre alla procedura, viene descritta una prima applicazione alle zone della Papua Nuova Guinea che nel 2018 sono state interessate da decine di frane sismoindotte, le quali hanno causato forti variazioni della copertura del suolo e quindi del backscattering del segnale radar.
Link articolo: https://nhess.copernicus.org/articles/20/2379/2020/
State-of-the-art review su rischi di salinizzazione delle risorse idriche sotterranee

Su una prestigiosa rivista americana (Journal of Water Resources Planning and Management) è stata pubblicata la “state-of-the art review” dal titolo Review of Utilization Management of Groundwater at Risk of Salinization curata dal Gruppo di Idrogeologia dell’IRPI di Bari (in particolare da Maurizio Polemio e Livia Emanuela Zuffianò) sulle modalità di gestione degli acquiferi costieri e/o a rischio di salinizzazione, problema molto sentito in Puglia, tenuto conto di tutte le esperienze ad oggi maturate a scala mondiale.
L’articolo è stato selezionato per entrare nella “Editor’s Choice Collection” per cui può essere scaricato liberamente per un mese, previa registrazione gratuita, alla pagina https://ascelibrary.org/journal/jwrmd5.
Per informazioni maurizio.polemio@irpi.cnr.it
Geomorphometry 2020. Conference Proceedings

La scienza dell’analisi quantitativa della superficie terrestre va sotto il nome di geomorfometria: essa comprende l’analisi geomorfologica, la morfometria del territorio e la produzione e l’uso di modelli digitali di elevazione. Il presente volume contiene i contributi inviati e accettati alla sesta edizione della Geomorphometry Conference, prevista per il 2020 a Perugia e rinviata al 2021 a causa della pandemia globale. La maggior parte dei contributi contiene materiale originale. I contributi sono stati raggruppati in sette tematiche: dati e metodi, georeferenziazione, processi glaciali, dati LIDAR e ad alta risoluzione, rischi naturali, erosione del suolo e processi fluviali. Una versione estesa di alcuni articoli apparirà in un numero speciale di una rivista.
Special Issue on “Climatic Trends and Impacts of Global Change in Europe and in the Mediterranean Basin” in Water (Open Access Journal by MDPI)

The Special Issue of Water on “Climatic Trends and Impacts of Global Change in Europe and in the Mediterranean Basin” (deadline: 31 may 2021) – Guest Editors: Roberto Coscarelli of CNR-IRPI and Tommaso Caloiero of CNR-ISAFOM – is now opened.
The overall goal of this Special Issue of Water is to focus research and analyses on these areas, starting from high-quality databases of climatic variables. Interdisciplinary original research articles highlighting new ideas, approaches, and innovations in the spatial and temporal analysis of the main climatological variables (rainfall, temperature, wind, etc.) and the analysis of future scenarios using GCM projections are welcome.
For information: roberto.coscarelli@irpi.cnr.it
Link: https://www.mdpi.com/journal/water/special_issues/Climate_Impacts_Mediterranean
Attached: promotional leaflet of the Special Issue
Seminario Cetemps con Luca Brocca

Nell’ambito dei Webinar organizzati da CETEMPS (Center of Excellence Telesensing of Environment and Model Prediction of Severe events), il nostro collega Luca Brocca – ricercatore presso il CNR-IRPI di Perugia – ha tenuto, nella giornata di ieri 28 maggio 2020, un seminario dal titolo “Umidità del suolo, una variabile chiave per le previsioni idrologiche: Piene, Pioggia, Frane e Siccità”. Altri link, lavori e riferimenti a questa tematica sono disponibili in questo sito.
Gli eventi di dissesto idrogeologico verificatisi dal 26 marzo al 1 aprile 2020 in Calabria

A seguito dell’evento meteorologico che ha colpito alcuni settori della Calabria nel periodo 26 marzo 2020-1 aprile 2020, è stato elaborato un rapporto di evento basato sull’analisi della rassegna stampa giornalmente effettuata presso l’IRPI di Cosenza. Sebbene nel periodo dell’evento l’attenzione della stampa locale e nazionale fosse particolarmente focalizzata sulla pandemia in corso, è stato possibile raccogliere notizie stampa, corredate da immagini che hanno consentito di ricostruire il quadro dell’evento.
L’evento è iniziato con mareggiate e danni causati dal vento sul settore jonico reggino-catanzarese. In seguito, piogge intense hanno determinato allagamenti in aree urbane. I danni si sono estesi poi sia alla provincia cosentina, determinando fenomeni franosi, che al crotonese, colpito da mareggiate e al versante occidentale della provincia di Catanzaro, interessato da allagamenti in aree urbane. Infine i danni si sono estesi alla provincia di Vibo Valentia, causando numerosi allagamenti e smottamenti.
New precipitation product from the SMOS+Rainfall project

A new rainfall product has been released within the ESA SMOS+Rainfall project funded by the European Space Agency and led by CNR-IRPI. The product integrates latest Global Precipitation Measurement (NASA-GPM) mission rainfall estimates with satellite soil moisture-based rainfall derived from the Advanced Scatterometer (ASCAT), the Soil Moisture and Ocean Salinity (SMOS) and the Soil Moisture Active and Passive (SMAP) missions. 25 km per 25 km rainfall estimates are distributed over Europe, United States, India, Australia, Africa and South America and are potentially available with a time delay of three days. Further information on the project (with the possibility to download and test the products of the project) can be found at www.esasmosrainfall.org.
Updates on the 2020 Geomorphometry conference

CNR IRPI and the Department of Physics and Geology of UniPG will host next June 22-26 the sixth edition of the Geomorphometry conference. Recent updates are as follows:
The DEADLINE for sending an abstract to Geomorphometry 2020 is postponed to February 29: http://geomorphometry2020.org/submission-of-short-papers
PROCEEDINGS of the conference will be published in a SPECIAL ISSUE of “Transactions in GIS” (Wiley): https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/journal/14679671
The list of KEYNOTE SPEAKERS is updated with the “Lifetime Achievement Award” winner named after Richard Pike: http://geomorphometry2020.org/keynote-speakers
The list of WORKSHOPS offered by the conference is now available: http://geomorphometry2020.org/scientific-program/workshops
The International Association of Geomorphologists offers a GRANT for a young (not Italy-based) geomorphologist: http://geomorphometry2020.org/grant
A new Alpine geo-lithological map (Alpine-Geo-LiM) and global carbon cycle implications

Published, on GSA (Geological Society of America) Bulletin, a paper – curated by Marco Donnini, Ivan Marchesini and Azzurra Zucchini – that re-evaluates the contribution, in the consumption of atmospheric CO2, of the chemical weathering of arenaceous and conglomerate sedimentary rocks and of igneous rocks. Although to a modest extent, this result has implications for the calculation of the atmospheric CO2 balance both at local and at global scale.
To carry out the estimate we produced a new geo-lithological map of the Alpine region (Alpine-Geo-LiM), derived in the framework of a scientific collaboration between the CNR-IRPI of Perugia and the Department of Physics and Geology of the University of Perugia. The map was used, together with the chemical compositions of the main Alpine river waters (i) to study the relationship between the alkalinity of the Alpine rivers and the lithologies of the corresponding river basins and (ii) to quantify the atmospheric CO2 consumed by the chemical dissolution of carbonate and silicate rocks.
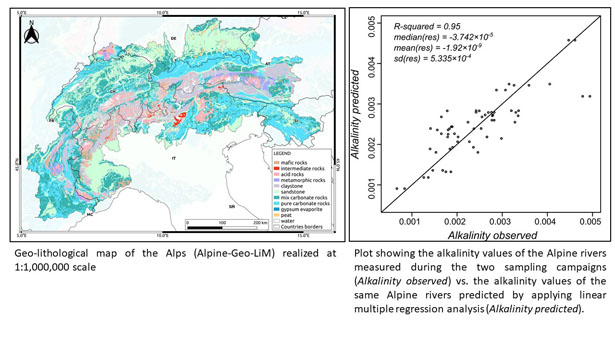
The results of the study confirm that carbonate rocks are highly prone to consume atmospheric CO2. Furthermore, the results show that sandstones (which could have a non-negligible carbonate component) play an important role in the atmospheric CO2 consumption. Another result is that in multi-lithological basins containing lithologies more prone to consume atmospheric CO2, the contribution of igneous rocks to atmospheric CO2 consumption is negligible.
Alpine-Geo-LiM presents several innovations if compared to the lithological maps available in the literature. A first novelty is due to the attention paid to discriminate metamorphic rocks, that have been classified according to the chemical composition of the protoliths. The second novelty is that the procedures used for the definition of the map are made available on the Web to allow the replicability and reproducibility of the product.
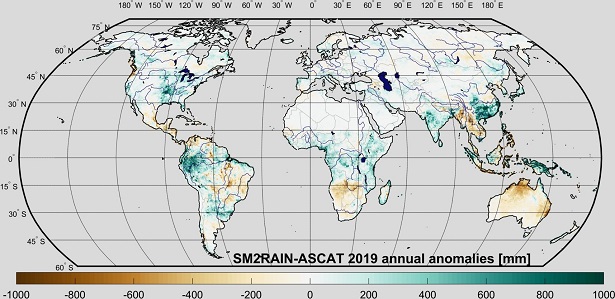
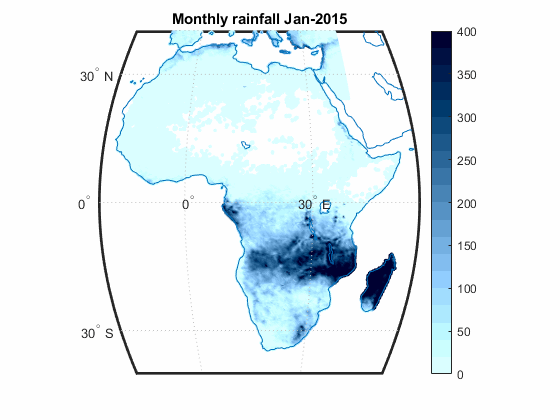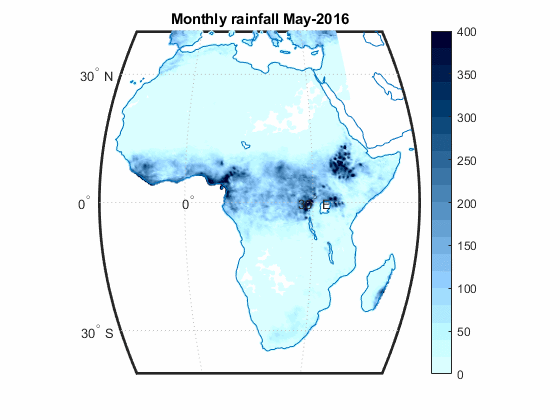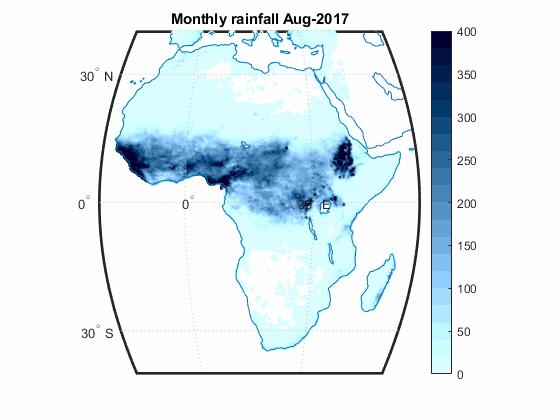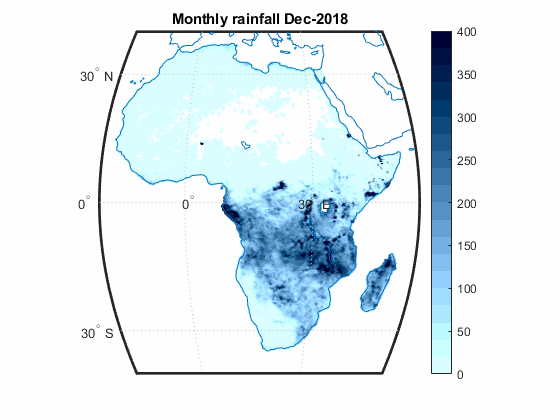
The updated version of the global SM2RAIN-ASCAT rainfall, has been released

The Hydrology group, of the IRPI CNR of Perugia, announce the release of the updated version of the global SM2RAIN-ASCAT rainfall dataset, now available in the time interval from 2007 to 2019.
The link to the dataset is here: https://zenodo.org/record/3635932.
The map shows the global annual rainfall anomalies for 2019 with respect to the period 2007-2018.