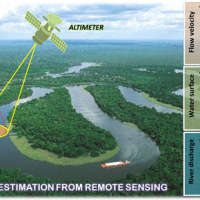
River discharge is defined as the amount of water flowing through a river over a specified period of time. Its estimate is crucial for all the operations of hydraulic structures design, the territorial planning and the flood risk assessment and management. River discharge at a specific river cross-section is not a direct measurement, but it is calculated by measuring other hydraulic quantities such as the flow velocity and the water depth, i.e. ...

The characterization of an impact crater requires an understanding of the impact phenomena, considering the properties of the materials involved in the impact. The size and energy of the projectile control the width and depth of the crater. Related to impact craters is the formation of mass concentrations, or mascons, which produce intense positive gravity anomalies. One of the largest mascons is in the Isidis Planitia, Mars.
Using the ...
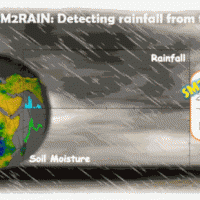
SM2RAIN is an innovative system for the estimation of the rainfall, based on measurements of the soil water content. SM2RAIN considers the soil as a natural rain gauge, and by measuring temporal variations of the soil water content, it estimates the rainfall falling on the soil, adopting a “bottom up” approach. Technically, SM2RAIN relies on the inversion of the soil water balance equation that computes the repartition of rainfall in ...
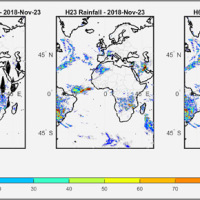
We have developed a new satellite rainfall product in near real-time. The product, called H64, is based on the integration of rainfall estimates obtained through two satellite sources. The developed algorithm combines estimates obtained by applying the SM2RAIN algorithm to satellite soil moisture data and those provided by a state-of-the-art product already operating on the full-disk area of the Meteosat satellites (60° West - 60° East, 60° ...

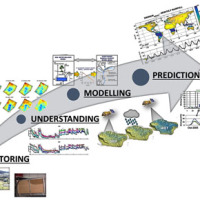
The OT4CLIMA project moves from the awareness that the impacts of climate change on the environment need to be better observed, understood, and modelled, especially at the local and regional scale, in order to put in place appropriate and effective risk mitigation ...

Although representing less than 1% of the total amount of water on Earth, the freshwater is essential for terrestrial life and human needs. Despite the existing in-situ gauging networks represent a tool for quantifying the instantaneous water volume in many river channels, we have surprisingly poor knowledge of the spatial and temporal dynamics of surface river discharge. Developing new procedures for river discharge estimation based on ...
L'IRPI è da molti anni impegnato nel monitoraggio di variabili idrologiche (umidità del suolo, pioggia, portata e velocità dei corsi d'acqua) che è risultato fondamentale per la rappresentazione del processo di formazione del deflusso e quindi per lo studio delle piene e delle ...

The urbanisation of seismically active areas, coupled with the ongoing change in climate patterns, require a shift in the approaches to land/infrastructure instability hazard assessment and risk reduction. This is particularly relevant in seismically active regions where the recurrent damage from landsliding, subsidence and ground deformations can be widespread. Geotechnical investigations and in situ monitoring of land prone to instability are ...

Rainfall-induced shallow landslides and floods are the most common and dangerous natural hazards, mainly due to their high temporal frequency, which causes fatalities and high economic damage worldwide. Climate changes will exacerbate this critical framework since an increase in extreme weather events is ...
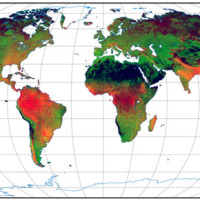
Accurate rainfall estimates are of paramount importance as rainfall plays a key-role in many fields as, to cite a few, natural hazard assessment (floods and landslides), drought management, weather forecasting, agriculture and diseases prevention. State-of-the-art rainfall products obtained by satellites are often the only way for measuring rainfall in remote areas of the ...
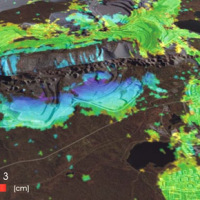
Space-borne radar interferometry or DInSAR (Differential Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar) is one of the latest techniques used for the detection and measurement of ground surface deformations caused by natural and / or man-made events. The DInSAR technique has been successfully used in the measurement of seismic deformations and of the effects of subsidence, unstable slopes and inflation of magma in volcanoes. The growth of space ...
EPSILON Italia, the leader of the partnership proposing the project, is a SME, located in Calabria, specializing in the delivery of advanced services for the protection and management of natural resources, with a high standard of quality and technological content. The SME is also actively involved in the development and implementation of new technologies and in R&D activities conducted both in their own and in partnership with universities ...
The 3DA software is a new procedure that allows retrieving in near-real-time 3D surface deformation models starting from data acquired via robotized total stations or others system that acquire the surface displacements. The measurements are first pre-processed and then implemented on 3D maps that include vector arrows representative of the intensities and of the real directions of motion in a given system of coordinates. The 3D surface ...

Monitoring the water cycle from satellite observations is one of the major goals of the EO community and closing the water budget has been a long-standing objective of international programs. After years of hard work, calibrating satellite data, improving inversion techniques, and facilitating the coherency of retrievals, it is admitted that the water cycle budget can now be ...
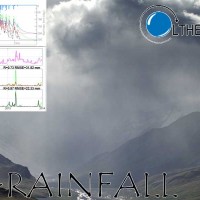
Quantitative information about precipitation is one vital input to meteorologists, hydrologic scientists, water resources managers, and environmental legislators. Yet, accurate measurement of precipitation over the relevant space and time scales remains a challenge. Soil moisture can be seen as the trace of the precipitation and, consequently, can be useful for providing a way to estimate rainfall accumulation or at least a new constrain to ...
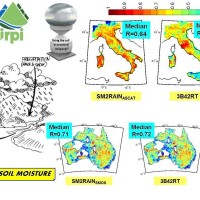
State-of-the-art satellite rainfall products are often the only way for measuring rainfall in remote areas of the world. However, these products may fail in properly reproducing the amount of precipitation reaching the ground, which is needed for hydrological applications. The integration of satellite soil moisture products is expected to significantly improve rainfall ...
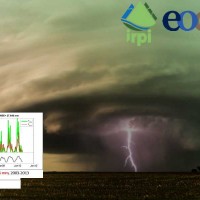
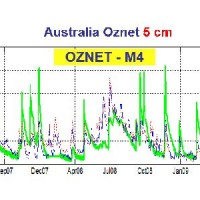
Recently, IRPI-CNR has developed an innovative approach for estimating rainfall from satellite soil moisture data, named SM2RAIN. The ESA funded project “Climate Change Initiative - Soil Moisture“ (CCI-SM) offers a valuable opportunity for testing SM2RAIN algorithm to a continuous, homogenous, long-term (>30 years) soil moisture time series. Indeed, SM2RAIN has the chance to be tested not only for rainfall estimation but also as a ...

The project aims at using Soil Moisture Active and Passive (SMAP) soil moisture (SM) products at different spatial resolution (3, 9, and 36 km) for hydrological applications in Europe (mainly in ...
The service aims to assess the potential of different satellite products (from active and passive micro-waves, optical, SAR, spectroradiometers, radiometers sensors) in retrieving the main hydrological-hydraulic variables such as rainfall, soil moisture, water level, flow velocity and discharge. This is pursued through a comprehensive validation analysis by using in-situ observed or modelled data for several sited located ...
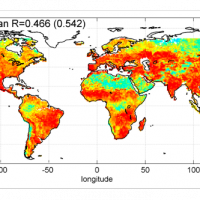
The rainfall dataset provides rainfall estimates obtained through the application of an inversion algorithm to soil moisture data. The algorithm has been applied to ground and satellite data, obtained through various satellite ...
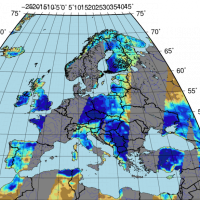
The H-SAF generates and archives high-quality data sets and products for operational hydrological applications starting from the acquisition and processing of data from Earth observation satellites in geostationary and polar orbits operated both by EUMETSAT and other satellite organization. The retrieval of products uses data from microwave and infrared instruments and aims at reaching the best possible accuracy compatible with satellite ...
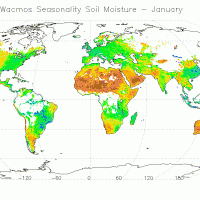
The CCI Programme wants to contribute to the data bases collecting ECVs required by GCOS (Global Climate Observing System) and other international parties. In particular, the Soil Moisture CCI will analyse the needs of the climate research community in terms of soil moisture data, adapt soil moisture satellite measurements for their use by the climate research community and create a long-term consistent soil moisture time series, based on ...

The environment monitoring has several purposes, including the prevention of geo-hydrogeological risks, forest fires, or prevention and suppression of illegal activities. The SMAT-F2 main objective is to define, design and develop an advanced monitoring system of the territory based on innovative unmanned air systems, coordinated by a supervision and coordination station (SSC). The first phase of the project, called SMAT-F1, finished at ...
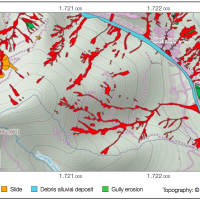
An Event Landslide Inventory Map (ELIM) shows the location and extent of landslides caused by a specific natural trigger, such as an intense rainfall event, a period of prolonged rainfall, a rapid snowmelt event, or an earthquake. The methods and tools developed by CNR-IRPI allow preparation of an ELIM anywhere recent landslides have left discernible ...
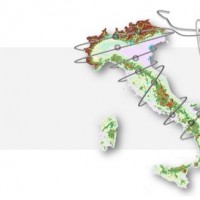
Le frane sono eventi del tutto naturali nell’evoluzione di un territorio, in particolare in Italia. Esse pongono un problema e diventano un pericolo allorché interagiscono con l’uomo e l’ambiente antropico. I movimenti franosi presentano una grande varietà fenomenologia. Le notevoli differenze nella tipologia, dimensione, e velocità di spostamento delle frane, rendono difficile e complessa la definizione della loro pericolosità, per ...

ESA Sentinels missions will provide enhanced capabilities in the revisit frequency, and the coverage. Their complete exploitation is in the combination of the two to advantage of a further increased revisiting time and in the use of different wavelenght domains. This reflects in the capabilities to detect features of changes induced by different factors including natural hazards and crop ...
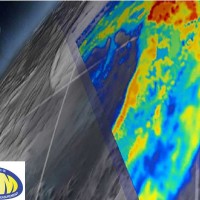
The proposal intends to contribute towards the establishment of a long-term partnership between the EUMETSAT Satellite Application Facility on support to Operational Hydrology and Water Management (H-SAF, or Hydrology SAF) and the NASA/JAXA Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) ...
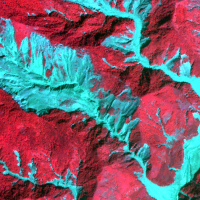
Earthquakes and strong rainfall precipitations, cause worldwide landslide. Inventories of the ground effects of an event must be prepared in a few days or less for the residual risk management. Satellite images and image analysis techniques have started to back up traditional mapping methods. Purpose of this project is to increase the automatization of image ...
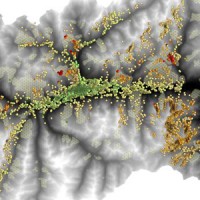
There is a systematic lack of information on the effects of the climate and environmental changes on the frequency and the intensity of landslides and their triggering phenomena (Huggel et al., 2012). The problem is particular severe in mountain area, where natural and human-driven climatic and environmental changes may alter significantly the frequency and the intensity of the slope processes, with largely unknown short and long-term effects ...
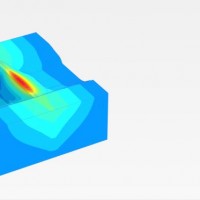
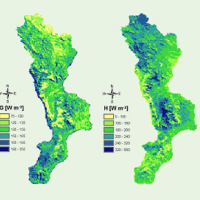
The project AIM-DAMS is aimed at developing a laboratory of integrated and advanced environmental monitoring for the control of the behavior of the earth-dams due to the different factors acting on the dams during their lifetime. Based on the integration of innovative and non-invasive sensors, as well as recent monitoring techniques and numerical modelling, the project is intended to fulfill the need of the dam management agencies of using ...

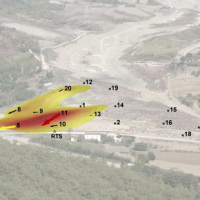
The Planpincieux Glacier is one of the glaciers that characterize the Italian side of the massif of the Grandes Jorasses. It is considered a temperate glacier and its front is currently located near a morphological step that determines a strong propensity to the activation of frequent ice falls in particular during the summer. These phenomena are typical of this glacier, but its particular asset may cause, as already occurred in the past, to ...
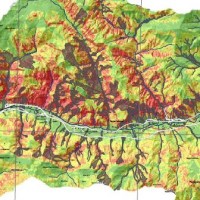
To significantly contribute to the operational capacities in the context of Global Monitoring for Environment and Security (GMES)/ Copernicus by developing customised mapping and geo-information products addressing risk, vulnerability and assets ready for deployment in the prevention and preparedness phases – complementary to the GMES/Copernicus Emergency Management Service. Solutions to be provided are based for the most part on Earth ...
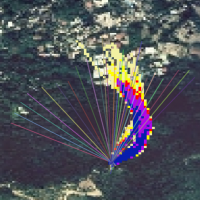
Taiwan, an active orogenic belt with subtropical climate is characterized by a high uplift rate and several major typhoons each year. Italy is on one of the most seismically active regions in Europe because of the thrust of African plate on Eurasian continental one. Both experience numerous landslides along with earthquakes and intense rainfalls, causing heavy damages and casualties. The purpose of this project was to share scientific knowledge ...

Sinkholes are in Apulia among the main geohazards, and are at the origin of severe interactions with the anthropogenic environment, and heavy losses to society. Since several years the territory of Marina di Lesina is diffusely affected by development of sinkholes (that have caused an emergency state to be declared), mostly concentrated near the Acquarotta Channel, linking the Lesina Lake to the Adriatic ...

Sinkholes occur as sudden collapses of the ground, related to natural cavities produced by karst processes in soluble rocks, or to man-made cavities deriving from different types of human activities in different historical ages. Sinkholes are widespread all over the world, and the related hazard is extremely high, with very severe damage to built-up areas and human infrastructures, and heavy losses to the ...

Fennoscandia bears witness of the Pleistocene glaciation in the form of a series of large geological faults. Pärvie which is the longest runs for 150 km. No information is available on its state of activity and no surface deformations data have ever been collected. The length of the fault and its location, make the traditional monitoring techniques unfeasible and ...
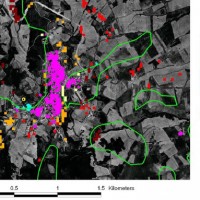
The focus on landslides results from the recognition that in many European countries slope instabilities affect urbanized areas and are a major threat to populations.
Through the integration of remotely sensed data with ground data we identify significant surface changes which are taking place on landslide susceptible slopes and this is used as input to the assessment of ...
 River discharge is defined as the amount of water flowing through a river over a specified period of time. Its estimate is crucial for all the operations of hydraulic structures design, the territorial planning and the flood risk assessment and management. River discharge at a specific river cross-section is not a direct measurement, but it is calculated by measuring other hydraulic quantities such as the flow velocity and the water depth, i.e. ...
River discharge is defined as the amount of water flowing through a river over a specified period of time. Its estimate is crucial for all the operations of hydraulic structures design, the territorial planning and the flood risk assessment and management. River discharge at a specific river cross-section is not a direct measurement, but it is calculated by measuring other hydraulic quantities such as the flow velocity and the water depth, i.e. ...  SM2RAIN is an innovative system for the estimation of the rainfall, based on measurements of the soil water content. SM2RAIN considers the soil as a natural rain gauge, and by measuring temporal variations of the soil water content, it estimates the rainfall falling on the soil, adopting a “bottom up” approach. Technically, SM2RAIN relies on the inversion of the soil water balance equation that computes the repartition of rainfall in ...
SM2RAIN is an innovative system for the estimation of the rainfall, based on measurements of the soil water content. SM2RAIN considers the soil as a natural rain gauge, and by measuring temporal variations of the soil water content, it estimates the rainfall falling on the soil, adopting a “bottom up” approach. Technically, SM2RAIN relies on the inversion of the soil water balance equation that computes the repartition of rainfall in ...  We have developed a new satellite rainfall product in near real-time. The product, called H64, is based on the integration of rainfall estimates obtained through two satellite sources. The developed algorithm combines estimates obtained by applying the SM2RAIN algorithm to satellite soil moisture data and those provided by a state-of-the-art product already operating on the full-disk area of the Meteosat satellites (60° West - 60° East, 60° ...
We have developed a new satellite rainfall product in near real-time. The product, called H64, is based on the integration of rainfall estimates obtained through two satellite sources. The developed algorithm combines estimates obtained by applying the SM2RAIN algorithm to satellite soil moisture data and those provided by a state-of-the-art product already operating on the full-disk area of the Meteosat satellites (60° West - 60° East, 60° ...  Although representing less than 1% of the total amount of water on Earth, the freshwater is essential for terrestrial life and human needs. Despite the existing in-situ gauging networks represent a tool for quantifying the instantaneous water volume in many river channels, we have surprisingly poor knowledge of the spatial and temporal dynamics of surface river discharge. Developing new procedures for river discharge estimation based on ...
Although representing less than 1% of the total amount of water on Earth, the freshwater is essential for terrestrial life and human needs. Despite the existing in-situ gauging networks represent a tool for quantifying the instantaneous water volume in many river channels, we have surprisingly poor knowledge of the spatial and temporal dynamics of surface river discharge. Developing new procedures for river discharge estimation based on ...  Accurate rainfall estimates are of paramount importance as rainfall plays a key-role in many fields as, to cite a few, natural hazard assessment (floods and landslides), drought management, weather forecasting, agriculture and diseases prevention. State-of-the-art rainfall products obtained by satellites are often the only way for measuring rainfall in remote areas of the ...
Accurate rainfall estimates are of paramount importance as rainfall plays a key-role in many fields as, to cite a few, natural hazard assessment (floods and landslides), drought management, weather forecasting, agriculture and diseases prevention. State-of-the-art rainfall products obtained by satellites are often the only way for measuring rainfall in remote areas of the ...  Space-borne radar interferometry or DInSAR (Differential Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar) is one of the latest techniques used for the detection and measurement of ground surface deformations caused by natural and / or man-made events. The DInSAR technique has been successfully used in the measurement of seismic deformations and of the effects of subsidence, unstable slopes and inflation of magma in volcanoes. The growth of space ...
Space-borne radar interferometry or DInSAR (Differential Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar) is one of the latest techniques used for the detection and measurement of ground surface deformations caused by natural and / or man-made events. The DInSAR technique has been successfully used in the measurement of seismic deformations and of the effects of subsidence, unstable slopes and inflation of magma in volcanoes. The growth of space ...  EPSILON Italia, the leader of the partnership proposing the project, is a SME, located in Calabria, specializing in the delivery of advanced services for the protection and management of natural resources, with a high standard of quality and technological content. The SME is also actively involved in the development and implementation of new technologies and in R&D activities conducted both in their own and in partnership with universities ...
EPSILON Italia, the leader of the partnership proposing the project, is a SME, located in Calabria, specializing in the delivery of advanced services for the protection and management of natural resources, with a high standard of quality and technological content. The SME is also actively involved in the development and implementation of new technologies and in R&D activities conducted both in their own and in partnership with universities ...  Monitoring the water cycle from satellite observations is one of the major goals of the EO community and closing the water budget has been a long-standing objective of international programs. After years of hard work, calibrating satellite data, improving inversion techniques, and facilitating the coherency of retrievals, it is admitted that the water cycle budget can now be ...
Monitoring the water cycle from satellite observations is one of the major goals of the EO community and closing the water budget has been a long-standing objective of international programs. After years of hard work, calibrating satellite data, improving inversion techniques, and facilitating the coherency of retrievals, it is admitted that the water cycle budget can now be ...  Quantitative information about precipitation is one vital input to meteorologists, hydrologic scientists, water resources managers, and environmental legislators. Yet, accurate measurement of precipitation over the relevant space and time scales remains a challenge. Soil moisture can be seen as the trace of the precipitation and, consequently, can be useful for providing a way to estimate rainfall accumulation or at least a new constrain to ...
Quantitative information about precipitation is one vital input to meteorologists, hydrologic scientists, water resources managers, and environmental legislators. Yet, accurate measurement of precipitation over the relevant space and time scales remains a challenge. Soil moisture can be seen as the trace of the precipitation and, consequently, can be useful for providing a way to estimate rainfall accumulation or at least a new constrain to ...  State-of-the-art satellite rainfall products are often the only way for measuring rainfall in remote areas of the world. However, these products may fail in properly reproducing the amount of precipitation reaching the ground, which is needed for hydrological applications. The integration of satellite soil moisture products is expected to significantly improve rainfall ...
State-of-the-art satellite rainfall products are often the only way for measuring rainfall in remote areas of the world. However, these products may fail in properly reproducing the amount of precipitation reaching the ground, which is needed for hydrological applications. The integration of satellite soil moisture products is expected to significantly improve rainfall ...  Recently, IRPI-CNR has developed an innovative approach for estimating rainfall from satellite soil moisture data, named SM2RAIN. The ESA funded project “Climate Change Initiative - Soil Moisture“ (CCI-SM) offers a valuable opportunity for testing SM2RAIN algorithm to a continuous, homogenous, long-term (>30 years) soil moisture time series. Indeed, SM2RAIN has the chance to be tested not only for rainfall estimation but also as a ...
Recently, IRPI-CNR has developed an innovative approach for estimating rainfall from satellite soil moisture data, named SM2RAIN. The ESA funded project “Climate Change Initiative - Soil Moisture“ (CCI-SM) offers a valuable opportunity for testing SM2RAIN algorithm to a continuous, homogenous, long-term (>30 years) soil moisture time series. Indeed, SM2RAIN has the chance to be tested not only for rainfall estimation but also as a ...  The service aims to assess the potential of different satellite products (from active and passive micro-waves, optical, SAR, spectroradiometers, radiometers sensors) in retrieving the main hydrological-hydraulic variables such as rainfall, soil moisture, water level, flow velocity and discharge. This is pursued through a comprehensive validation analysis by using in-situ observed or modelled data for several sited located ...
The service aims to assess the potential of different satellite products (from active and passive micro-waves, optical, SAR, spectroradiometers, radiometers sensors) in retrieving the main hydrological-hydraulic variables such as rainfall, soil moisture, water level, flow velocity and discharge. This is pursued through a comprehensive validation analysis by using in-situ observed or modelled data for several sited located ...  The H-SAF generates and archives high-quality data sets and products for operational hydrological applications starting from the acquisition and processing of data from Earth observation satellites in geostationary and polar orbits operated both by EUMETSAT and other satellite organization. The retrieval of products uses data from microwave and infrared instruments and aims at reaching the best possible accuracy compatible with satellite ...
The H-SAF generates and archives high-quality data sets and products for operational hydrological applications starting from the acquisition and processing of data from Earth observation satellites in geostationary and polar orbits operated both by EUMETSAT and other satellite organization. The retrieval of products uses data from microwave and infrared instruments and aims at reaching the best possible accuracy compatible with satellite ...  The CCI Programme wants to contribute to the data bases collecting ECVs required by GCOS (Global Climate Observing System) and other international parties. In particular, the Soil Moisture CCI will analyse the needs of the climate research community in terms of soil moisture data, adapt soil moisture satellite measurements for their use by the climate research community and create a long-term consistent soil moisture time series, based on ...
The CCI Programme wants to contribute to the data bases collecting ECVs required by GCOS (Global Climate Observing System) and other international parties. In particular, the Soil Moisture CCI will analyse the needs of the climate research community in terms of soil moisture data, adapt soil moisture satellite measurements for their use by the climate research community and create a long-term consistent soil moisture time series, based on ...  The environment monitoring has several purposes, including the prevention of geo-hydrogeological risks, forest fires, or prevention and suppression of illegal activities. The SMAT-F2 main objective is to define, design and develop an advanced monitoring system of the territory based on innovative unmanned air systems, coordinated by a supervision and coordination station (SSC). The first phase of the project, called SMAT-F1, finished at ...
The environment monitoring has several purposes, including the prevention of geo-hydrogeological risks, forest fires, or prevention and suppression of illegal activities. The SMAT-F2 main objective is to define, design and develop an advanced monitoring system of the territory based on innovative unmanned air systems, coordinated by a supervision and coordination station (SSC). The first phase of the project, called SMAT-F1, finished at ...  ESA Sentinels missions will provide enhanced capabilities in the revisit frequency, and the coverage. Their complete exploitation is in the combination of the two to advantage of a further increased revisiting time and in the use of different wavelenght domains. This reflects in the capabilities to detect features of changes induced by different factors including natural hazards and crop ...
ESA Sentinels missions will provide enhanced capabilities in the revisit frequency, and the coverage. Their complete exploitation is in the combination of the two to advantage of a further increased revisiting time and in the use of different wavelenght domains. This reflects in the capabilities to detect features of changes induced by different factors including natural hazards and crop ...  There is a systematic lack of information on the effects of the climate and environmental changes on the frequency and the intensity of landslides and their triggering phenomena (Huggel et al., 2012). The problem is particular severe in mountain area, where natural and human-driven climatic and environmental changes may alter significantly the frequency and the intensity of the slope processes, with largely unknown short and long-term effects ...
There is a systematic lack of information on the effects of the climate and environmental changes on the frequency and the intensity of landslides and their triggering phenomena (Huggel et al., 2012). The problem is particular severe in mountain area, where natural and human-driven climatic and environmental changes may alter significantly the frequency and the intensity of the slope processes, with largely unknown short and long-term effects ...  The project AIM-DAMS is aimed at developing a laboratory of integrated and advanced environmental monitoring for the control of the behavior of the earth-dams due to the different factors acting on the dams during their lifetime. Based on the integration of innovative and non-invasive sensors, as well as recent monitoring techniques and numerical modelling, the project is intended to fulfill the need of the dam management agencies of using ...
The project AIM-DAMS is aimed at developing a laboratory of integrated and advanced environmental monitoring for the control of the behavior of the earth-dams due to the different factors acting on the dams during their lifetime. Based on the integration of innovative and non-invasive sensors, as well as recent monitoring techniques and numerical modelling, the project is intended to fulfill the need of the dam management agencies of using ...  The Planpincieux Glacier is one of the glaciers that characterize the Italian side of the massif of the Grandes Jorasses. It is considered a temperate glacier and its front is currently located near a morphological step that determines a strong propensity to the activation of frequent ice falls in particular during the summer. These phenomena are typical of this glacier, but its particular asset may cause, as already occurred in the past, to ...
The Planpincieux Glacier is one of the glaciers that characterize the Italian side of the massif of the Grandes Jorasses. It is considered a temperate glacier and its front is currently located near a morphological step that determines a strong propensity to the activation of frequent ice falls in particular during the summer. These phenomena are typical of this glacier, but its particular asset may cause, as already occurred in the past, to ...  To significantly contribute to the operational capacities in the context of Global Monitoring for Environment and Security (GMES)/ Copernicus by developing customised mapping and geo-information products addressing risk, vulnerability and assets ready for deployment in the prevention and preparedness phases – complementary to the GMES/Copernicus Emergency Management Service. Solutions to be provided are based for the most part on Earth ...
To significantly contribute to the operational capacities in the context of Global Monitoring for Environment and Security (GMES)/ Copernicus by developing customised mapping and geo-information products addressing risk, vulnerability and assets ready for deployment in the prevention and preparedness phases – complementary to the GMES/Copernicus Emergency Management Service. Solutions to be provided are based for the most part on Earth ...  Sinkholes are in Apulia among the main geohazards, and are at the origin of severe interactions with the anthropogenic environment, and heavy losses to society. Since several years the territory of Marina di Lesina is diffusely affected by development of sinkholes (that have caused an emergency state to be declared), mostly concentrated near the Acquarotta Channel, linking the Lesina Lake to the Adriatic ...
Sinkholes are in Apulia among the main geohazards, and are at the origin of severe interactions with the anthropogenic environment, and heavy losses to society. Since several years the territory of Marina di Lesina is diffusely affected by development of sinkholes (that have caused an emergency state to be declared), mostly concentrated near the Acquarotta Channel, linking the Lesina Lake to the Adriatic ...  Sinkholes occur as sudden collapses of the ground, related to natural cavities produced by karst processes in soluble rocks, or to man-made cavities deriving from different types of human activities in different historical ages. Sinkholes are widespread all over the world, and the related hazard is extremely high, with very severe damage to built-up areas and human infrastructures, and heavy losses to the ...
Sinkholes occur as sudden collapses of the ground, related to natural cavities produced by karst processes in soluble rocks, or to man-made cavities deriving from different types of human activities in different historical ages. Sinkholes are widespread all over the world, and the related hazard is extremely high, with very severe damage to built-up areas and human infrastructures, and heavy losses to the ...  Fennoscandia bears witness of the Pleistocene glaciation in the form of a series of large geological faults. Pärvie which is the longest runs for 150 km. No information is available on its state of activity and no surface deformations data have ever been collected. The length of the fault and its location, make the traditional monitoring techniques unfeasible and ...
Fennoscandia bears witness of the Pleistocene glaciation in the form of a series of large geological faults. Pärvie which is the longest runs for 150 km. No information is available on its state of activity and no surface deformations data have ever been collected. The length of the fault and its location, make the traditional monitoring techniques unfeasible and ... 















