The coloured circles represent the total number of activities (project, products and services, outreach, collaborations) that we have in the corresponding geographical zone
Map data: © OpenStreetMap contributors
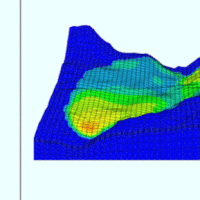
When soil behaviour is studied, whether landslide soils are concern, levee materials or foundations, the problem regarding how much and how reliable information about the soil properties we have available has to be addressed.
Understanding “what’s beneath” the visible surface is fundamental, yet complicated. Drillings are performed to analyse the stratigraphy of soils (the order and the thickness of the different soil levels) and ...

Not all that flows in creeks is water. Debris flows i.e., surges in which solid particles move together with little water, may occur in steep mountain streams, mainly as a consequence of intense rainfall. Debris flows have a high kinetic energy, and may cause major damage if they encroach buildings, roads and bridges. They are also a primary cause of landslide casualties. The video below shows an example of debris flows.
The low ...

ALMOND-F is an innovative unit for the microseismic detection of debris flows using a network of geophones.
The microseismic detection of debris flows is more complex than other types of monitoring. Use of the geophones requires: (1) the selection of the level of amplification of the signal, which depends on the distance from the stream; (2) the selection of the sampling frequency of the seismic signal, which must be sufficiently high; (3) ...
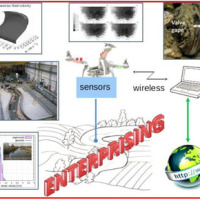
The development of an innovative system for monitoring river flows during extreme events and the impact of hydrodynamic pressures on ecosystems are two important challenges identified by the World Meteorological Organization for flood event control and by the European Commission for the European Biodiversity Strategy for the protection of ecosystems and ...

Climate change in the Greater Alpine Region is seriously affecting glacial and periglacial areas, especially for the presence of snow, glaciers and permafrost (cryosphere), with relevant consequences on slope stability. Cryosphere degradation, changes of the precipitation and temperature patterns and of the hydrological regimes, are some of the main terrestrial indicators of climatic change. Moreover, the increasing number of tourists and human ...

Critical and depositional friction angles are characteristic for the deposition of a granular mass; the wrong angle adoption determines the ineffectiveness of a containment basin. The term is used with different meanings and measured by various procedures. The numerical simulation is a useful tool for the hazard assessment, but the definition of friction needed parameters requires insights on their ...
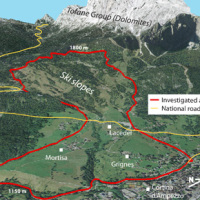
The study of the dynamics of large landslide is a heuristic process based on the integration of multiple investigation techniques: geological and geomorphological analysis, monitoring systems (traditional and innovative) and numerical models. Risk mitigation may require major interventions that call for detailed studies on the specific ...

Usually the video cameras installed within a debris-flow monitoring site have the role of recording videos to better understand the behavior of the event for an improved interpretation of its dynamic. The use of such cameras for Image Velocimetry purpose is still nowadays a ...

The aim of the geomorphometric analysis is to derive indices capable of characterizing the spatial variability of specific hydro-geomorphological processes (e.g., sediment connectivity, erosion and deposit). The growing availability of high-resolution topographic data has increased the interest in geomorphometry and its applications. Debris-flow monitoring in instrumented areas and flash-flood documentation are invaluable ways to gather field ...

The database includes annual maximum rainfall corresponding to durations of 1, 3, 6, 12, 24 hours and 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 days for approximately 800 raingauges in north-eastern Italy (Trentino, Alto Adige, Veneto and Friuli Venezia Giulia). The database contains data until 1997 for the Autonomous Province of Bozen-Bolzano, 1990 for the Autonomous Province of Trento, and 1996 for Veneto and Friuli Venezia ...
Le frane sono eventi del tutto naturali nell’evoluzione di un territorio, in particolare in Italia. Esse pongono un problema e diventano un pericolo allorché interagiscono con l’uomo e l’ambiente antropico. I movimenti franosi presentano una grande varietà fenomenologia. Le notevoli differenze nella tipologia, dimensione, e velocità di spostamento delle frane, rendono difficile e complessa la definizione della loro pericolosità, per ...

Il video youtube, a cura della 'Ripartizione Opere Idrauliche' della Provincia Autonoma di Bolzano, presenta una colata detritica registrata da una videocamera della stazione di monitoraggio del bacino del Rio Gadria (Vinschgau - Val Venosta) il 18 luglio 2013. Il CNR IRPI collabora dal 2010, anno di installazione della stazione, con la Ripartizione Opere Idrauliche, la Libera Università di Bolzano e l’Università di Padova alle attività di ...

Monitoring of debris flows in instrumented areas is carried out since many years in different Countries worldwide. It is still missing, however, an adequate standardization of methodologies, instrumentations and procedures. The instrumented areas are also employed for testing warning systems. Even though these latter have been more and more employed, a systematic experimentation of these systems has not yet been carried ...
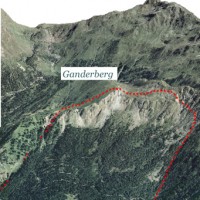
A Deep-seated Gravitational Slope Deformation (DGSD) affects the south-west flank of mount Ganderberg (Moso in Passiria – BZ). The continuous displacements of the landslide induce secondary hazardous phenomena. A 800.000 m3 rock slab shows signs of incipient movement; a detachment could create a natural barrier on the river ...

Sediment transport in small mountain catchments (drainage area < 10-20 km2) is a fundamental process for the equilibrium and the dynamics of the whole channel network. At the same time, sediment transport can create high-risk conditions due to the occurrence of extreme phenomena such as debris flow, hyperconcentrated flow, and flood with intense bedload, usually triggered by intense and short duration rainfall. In order to properly manage ...

Decision matrices may contribute to mountain watershed management by defining coherent event scenarios that take into account the type of flow processes (e.g., water floods with bedload, debris flows), their geomorphic effects, and the interactions with hydraulic control ...

Debris-flow monitoring in instrumented areas is an invaluable way to gather field data that may improve the understanding of these hazardous phenomena, as well as for the development of warning systems. The number of monitoring sites and the amount of recorded data on debris flows, however, still remain limited if compared to landslides and fluvial sediment transport. This motivated the Autonomous Province of Bozen-Bolzano to implement a new ...

The accurate representation of the channel network is fundamental in cartography. The increasing availability of high-resolution, LiDAR-derived DTMs provides an excellent topographic basis for the representation of the channel network, but requires innovative techniques for managing and processing ...
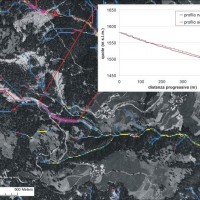
The assessment debris-flow hazard is of utmost importance in the management of alpine catchments. The analysis of morphometric variables of drainage basins and channels can contribute to preliminary assessment of debris-flow hazard at regional ...

The study of the evolution of the watercourses is traditionally based on the use of historical maps and aerial photographs for the comprehension of the planimetric changes and on the use of topographical sections in order to have also the measure of the altimetric change occurred in the considered time interval.
Through this approach it is possible, for the Po basin, to have the first indications of the main watercourses evolution starting ...
 Not all that flows in creeks is water. Debris flows i.e., surges in which solid particles move together with little water, may occur in steep mountain streams, mainly as a consequence of intense rainfall. Debris flows have a high kinetic energy, and may cause major damage if they encroach buildings, roads and bridges. They are also a primary cause of landslide casualties. The video below shows an example of debris flows.
The low ...
Not all that flows in creeks is water. Debris flows i.e., surges in which solid particles move together with little water, may occur in steep mountain streams, mainly as a consequence of intense rainfall. Debris flows have a high kinetic energy, and may cause major damage if they encroach buildings, roads and bridges. They are also a primary cause of landslide casualties. The video below shows an example of debris flows.
The low ...  ALMOND-F is an innovative unit for the microseismic detection of debris flows using a network of geophones.
The microseismic detection of debris flows is more complex than other types of monitoring. Use of the geophones requires: (1) the selection of the level of amplification of the signal, which depends on the distance from the stream; (2) the selection of the sampling frequency of the seismic signal, which must be sufficiently high; (3) ...
ALMOND-F is an innovative unit for the microseismic detection of debris flows using a network of geophones.
The microseismic detection of debris flows is more complex than other types of monitoring. Use of the geophones requires: (1) the selection of the level of amplification of the signal, which depends on the distance from the stream; (2) the selection of the sampling frequency of the seismic signal, which must be sufficiently high; (3) ...  The development of an innovative system for monitoring river flows during extreme events and the impact of hydrodynamic pressures on ecosystems are two important challenges identified by the World Meteorological Organization for flood event control and by the European Commission for the European Biodiversity Strategy for the protection of ecosystems and ...
The development of an innovative system for monitoring river flows during extreme events and the impact of hydrodynamic pressures on ecosystems are two important challenges identified by the World Meteorological Organization for flood event control and by the European Commission for the European Biodiversity Strategy for the protection of ecosystems and ...  The database includes annual maximum rainfall corresponding to durations of 1, 3, 6, 12, 24 hours and 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 days for approximately 800 raingauges in north-eastern Italy (Trentino, Alto Adige, Veneto and Friuli Venezia Giulia). The database contains data until 1997 for the Autonomous Province of Bozen-Bolzano, 1990 for the Autonomous Province of Trento, and 1996 for Veneto and Friuli Venezia ...
The database includes annual maximum rainfall corresponding to durations of 1, 3, 6, 12, 24 hours and 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 days for approximately 800 raingauges in north-eastern Italy (Trentino, Alto Adige, Veneto and Friuli Venezia Giulia). The database contains data until 1997 for the Autonomous Province of Bozen-Bolzano, 1990 for the Autonomous Province of Trento, and 1996 for Veneto and Friuli Venezia ...  Il video youtube, a cura della 'Ripartizione Opere Idrauliche' della Provincia Autonoma di Bolzano, presenta una colata detritica registrata da una videocamera della stazione di monitoraggio del bacino del Rio Gadria (Vinschgau - Val Venosta) il 18 luglio 2013. Il CNR IRPI collabora dal 2010, anno di installazione della stazione, con la Ripartizione Opere Idrauliche, la Libera Università di Bolzano e l’Università di Padova alle attività di ...
Il video youtube, a cura della 'Ripartizione Opere Idrauliche' della Provincia Autonoma di Bolzano, presenta una colata detritica registrata da una videocamera della stazione di monitoraggio del bacino del Rio Gadria (Vinschgau - Val Venosta) il 18 luglio 2013. Il CNR IRPI collabora dal 2010, anno di installazione della stazione, con la Ripartizione Opere Idrauliche, la Libera Università di Bolzano e l’Università di Padova alle attività di ...  A Deep-seated Gravitational Slope Deformation (DGSD) affects the south-west flank of mount Ganderberg (Moso in Passiria – BZ). The continuous displacements of the landslide induce secondary hazardous phenomena. A 800.000 m3 rock slab shows signs of incipient movement; a detachment could create a natural barrier on the river ...
A Deep-seated Gravitational Slope Deformation (DGSD) affects the south-west flank of mount Ganderberg (Moso in Passiria – BZ). The continuous displacements of the landslide induce secondary hazardous phenomena. A 800.000 m3 rock slab shows signs of incipient movement; a detachment could create a natural barrier on the river ...  The accurate representation of the channel network is fundamental in cartography. The increasing availability of high-resolution, LiDAR-derived DTMs provides an excellent topographic basis for the representation of the channel network, but requires innovative techniques for managing and processing ...
The accurate representation of the channel network is fundamental in cartography. The increasing availability of high-resolution, LiDAR-derived DTMs provides an excellent topographic basis for the representation of the channel network, but requires innovative techniques for managing and processing ... 














