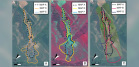
M. Czarnogórska, M. Graniczny, S. Uoecinowicz, R. Nutricato, S. Triggiani, D. O. Nitti, F. Bovenga, J. Wasowski, 2012, Ground deformations along SW coast of the Gulf of Gdansk analysed using satellite radar interferometry,
Przeglad Geologiczny 60 (2012): 206–2011.,
Abstract
The paper presents results of SPINUA (Stable Point Interferometry over
Unurbanised Areas) Persistent Scatterers Interferometry (PSI) ...
The paper presents results of SPINUA (Stable Point Interferometry over
Unurbanised Areas) Persistent Scatterers Interferometry (PSI) processing chain to study
Earth surface deformations along the SW coast of the Gulf of Gdañsk, along the SE part of
the Baltic Sea. As the input for SPINUA techniques 40 descending ERS-1/2 SLC (Frame =
251, Track = 36) images from the period 1995-2001 has been used. The area of interest
(AOI) includes few cities and several towns, villages and harbors. The low lying coastal
areas of the SW part of the Gulf of Gdañsk are at risk of floods and marine erosion. The PSI
results, however, did not reveal the presence of a regional scale, spatially consistent pattern
of displacements. It is likely that any crustal deformations in the AOI simply do not exceed ±2
mm/year, which is the velocity threshold we assumed to distinguish between moving and non-moving persistent scatterers (PS). Importantly,
for the most part the urban areas of the main cities (Gdañsk, Gdynia and Sopot) results show ground stability. Nevertheless, significant
downward movements up to several mm/year, are locally noticed in the Vistula river delta - alluvial plain system located in the
coastal zone east of Gdañsk as well as in the inland area west of the Gdañsk city. Indeed, the highest subsidence rates (-12 mm/year)
was observed in the Gdañsk petroleum refinery constructed on alluvial sediments. Thus the anthropogenic loading and consolidation
of the recent deposits can locally be an important factor causing ground subsidence.
Dijkstra T.A., Chandler J.H., Wackrow R., Meng X.M., Ma D.T., Gibson A., Whitworth M., Foster C., Lee K., Hobbs P.R.N., Reeves H.J., Wasowski J., 2012, Geomorphic controls and debris flows – the 2010 Zhouqu disaster, China,
11th International and 2nd North American Symposium on Landslides, Banff (Canada), 3-8 June, 2012, pp. 287–293, 2012,
Muscillo S., Del Gaudio V., Wasowski J., 2012, Caratterizzazione della risposta sismica in aree di pendio soggette a frane_ nuovi sviluppi ed applicazioni dell’analisi di rumore ambientale,
31° Convegno Nazionale G.N.G.T.S., Potenza, 20-22 Novembre 2012, pp. 191–199, 2012,
Del Gaudio V., Wasowski J., 2012, Application of ambient noise analysis for investigating site amplification properties of slopes susceptible to seismically induced failures.,
11th International and 2nd North American Symposium on Landslides, Banff (Canada), 3-8 June, 2012, pp. 537–543, 2012,
Ruggero Matteucci, Guido Gosso, Silvia Peppoloni, Sandra Piacente, Janusz Wasowski, 2012, A Hippocratic Oath for geologists?,
Annals of geophysics (Online) 55 (2012). doi_10.4401/ag-5650,
DOI: 10.4401%2Fag-5650
Abstract
We argue here that the introduction of an ethical code of conduct that
follows the example ...
We argue here that the introduction of an ethical code of conduct that
follows the example of the Hippocratic Oath of physicians will help
geologists to acquire binding awareness of their professional and social
responsibilities. The ethical behavior and obligations of modern
geologists involve, but are not limited to, the following issues_ correct
land/environment use and management; respect of truth and science;
and protection of the Earth systems, on both the local and global scales,
and therefore, of our well-being. We believe that for geoligists, the
explicit acceptance of an ethical code will help to promote_ (i) an
awareness of their social role, expertise and sense of belonging to a
professional community; (ii) an understanding of the expectations of
citizens and society; and (iii) cultural growth, with better use of
research and implementation of scientific and professional skills. All
this should enhance the public recognition of the social mission of
geologists, which is essential for the well-being of society. Therefore,
we suggest that like in the majority of medical schools, ethical training
should be a part of the university curriculum for students in geology.
M. Angeli*, P. Gasparetto**. F. Marabini *** A. Mertzanis****, F. Pontoni, 2012, The Adriatic Sea Evolution,
ITALY-CHINA - AN ANCIENT CULTURAL HERITAGE AND THE CHALLENGE FOR FUTURE DEVELOPMENT, Bologna (Italy), 22-24 October 2012,
M.G.Angeli*, P.Gasparetto**, F.Marabini***, A.Mertzanis**** & F.Pontoni*****, 2012, The Adriatic Coastal Zone geomorphology,
Atti del Convegno_ Italy-China: An ancient cultural heritage and the challenge for future development, Bologna 22 - 23 Ottobre 2012, Bologna, 22-24 ottobre 2012,
Abstract
Since the beginning of this century, everywhere in the world, the coastal areas have, been ...
Since the beginning of this century, everywhere in the world, the coastal areas have, been affected by a widespread regression, which reached the critical stage after 1950. This situation is in contrast with the general trend of accretion that has affected the coastal zone in the past century. The 8000 kms of Italian coast show a large variety of shoreline. Today about forty- five percent of the Italian coast is threatened by a progressive and general degradation which mainly is manifested as beach erosion. This phenomenon seemed to worsen in the '50s after a long period of general beach stability (fig. 1). If one considers the intense interventions of man on its coasts for touristic purposes, by demolishing the dunes to create beach areas, summer residential and marine areas; the diminished fluvial sediment load to the sea by haphazard removal of riverbed material; the creased subsidence caused by groundwater, gas and oil extractions in areas too dose to the sea; one obtains a picture which easily explains the rapid instability of this coastal environment. This situation is present not only along the Italian coast but, in a greater or lesser degree, includes the coastlines of many other countries. This increased economic development, without worrying about what would be the future impact on the environment, tends to worsen the already precarious situation even more. From the end of the fifties, up to the present day, the coastal area -was used as an inexhaustible and indestructible property on which it would be possible to burden an infinite "number of works without this feeling the least bit. An improper exploitation (by 'robbery') was used in this fragile region, without taking into account the consequences, instead of managing it as a precious commodity which must last in time to permit better economic management.
Aristeidis Mertzanis1, Francesco Marabini2, Maceo Giovanni Angeli3, Adrian Stanica4,
Adriana Galvani5, Paolo Gasparetto6 and Fabrizio Pontoni7, 2012, SEDIMENT TRANSFER AND GEOMORPHOLOGICAL EVOLUTION IN RIVER SYSTEMS & COASTAL ZONES IN ITALY, ROMANIA AND GREECE,
ITALY-CHINA - AN ANCIENT CULTURAL HERITAGE AND THE CHALLENGE FOR FUTURE DEVELOPMENT, Bologna (Italy), 22-24 October 2012,
Abstract
In many Mediterranean coastal areas, have been observed that human activities-engineering works, such as large ...
In many Mediterranean coastal areas, have been observed that human activities-engineering works, such as large dams and reservoirs construction (hydroelectric power dams, irrigation dams and water supply dams), channelization (drainage pits and drainage dams, deepening and creation of canals), arrangement and redirection of the main beds of rivers and torrents, construction of jetties in the coastal zone and anti-erosion works (water breakers, large concrete rocks, etc.), motorway and railway line in operation or under construction, as well as other human interventions and activities (sand extraction from river beds, intensification and development of agriculture projects
and industrialization, infrastructure works, embankments, exsiccation, deforestation, etc.), may seriously affect the sediment transfer and the environmental balance of inland and coastal environments (wetlands, lagoons, Deltas, estuaries and coastal areas). This work deals with the comparative account and evaluation of the impact to the environment and especially the changes to the sediment transfer and geomorphological evolution in river systems & coastal zones in Italy (northern Adriatic coastal zone), Romania (Danube river Delta) and Greece (Nestos and Spercheios river Delta, Western Peloponnesian coastal zone) caused by the human activity.
F.Marabini *, A. Galvani **, M. Angeli ***.,P.Gasparetto ****. F. Pontoni *****, 2012, Environmental Protection and Economic Development,
ITALY-CHINA - AN ANCIENT CULTURAL HERITAGE AND THE CHALLENGE FOR FUTURE DEVELOPMENT, Bologna (Italy), 22-24 October 2012,
Abstract
The huge territorial-economic-demographic dimensions of China would be an exemplary field in order to study ...
The huge territorial-economic-demographic dimensions of China would be an exemplary field in order to study the global issues of sustainable development and the the future of our world. Because China has to face the most extraordinary problems of the world , more than all other countries, studying their solutions would provide suggestions for our country and we will help it with our proposals. China should balance habited and lands, fertile and arid soils, to face climate change, pollution, spreading urbanisation, strong differences of urbanisation between coasts and inland, impacts on coastal zones. Furthermore ot seems necessary to manage greater revenue, new wellness and new leisure exigenses. The natural and antropic evolution of Italy and China territories share a long term historical record, since the two countries where cradle for highly-civilized populations, that produced documental material during the last two millennia, at least. They also share the presence in their territories of intensively industrialized and populated areas along the major rivers , the deltaic zones and the coastal zones. These deltaic apparatus and the adjacent coastal areas are characterized by a geomorphological trend controlled by natural (climate and environment) and antropic (deforestation and industrialization) changes. The increasing urbanisation of coastal cities leads to the modification of anemological patterns of the local circulation because of the formation of the urban heat island. This phenomenon is mainly produced by alteration of the land coverage usage in terms of both optical and conductive properties of new materials deployed ( buildings, flooring , etc.) and by production of heat generated by anthropogenic activities. The increased energetic of the planetary boundary layer over the urban canopy can strongly alter the local winds and, consequently, the precitative patterns as well as the recirculation of pollutants and their deposition pathways causing impacts on the human health and marine environment. The rate of these changes has not been constant during the last millennia, being mainly controlled by antropogenic variables at regional and global scales. We propose to compare and to define ,in the selected chinese and italian coastal zones, the effect of the the global and regional changes in the past times. On the basis of these studies we can understand the future evolutional trend of the selected areas. Our work will focus the comparison of the italian plain industrialization history, wich date back to the beginning of the last century, and the effects of the newly booming chinese economy which is in a huge expanding phase. We will also compare those recent changes to that occurred in the past , i.e., the beginning of intensive agricolture and farming, the alternating periods of wet and dry climate which induced important changes in the characteristics and rate of sediment supply in both natural systems. We also propose to recover and organize already collected geological, geophisical and environmental data in key selected location in chinese and italian coastal zones. A particular attention to the collection, elaboration and comparison of the geomorphological and cartographic data of the studied areas. The study of the variations of the bathymetry in shallow water to understand when the situation evolves to a dangerous state for the coastal equilibrium. The comparison of these data with the bathymetric data of the past times provides indications about the evolutional trend of the studied areas. The study of the surficial sediment distribution, with special attention to grain size parameters to provide sediments maps following both the Shepard and Nota classifications to evidence the variations of the energetic level in the coastal zone. The goal of the project is to give significantly contribute to enhancement of management plans of protected areas from floodplains, wetlands and coastal areas, by comprehensive consideration of geological diversity. Benefiting from the high italian experience, a geoturism strategy will be promoted in order to ensure long term development of the protected area through sustainable and quality tourism and to attenuate disparities between protected areas from the italian and the chinese seas. Finally_ researches from a comparative point of view of the national and the local legislations on environmental protection. Comparison between Italy and China with regard to the rules for the environmental protection. All the results of the studied chinese and italian selected areas will be used to try to answer to the following questions_ 1) are there differences in the geomorphological and sedimentological records of corresponding sectors of the selected natural systems at different times scale from the past times up to the present time? 2) Are these differences mainly controlled by local factors, such a different industrialization history, or by global forcing (global changes) ? 3) What is the environmental present-day status of these delicate environments under different anthropogenic pressures? 4) At the light of the italian experience , could we forecast the effect of intensive use of the territory under similar conditions in the present day China for the next future ? 5) Could we offer some warnings ? This is only a first attempt to face the same economical and environmental problems interesting the italian and chinese coastal zones.
A.Mondini, F.Bucci, J.Wasowski, 2012, Report Attività Progetto anno 2012,
2012,
Abstract
Le attività svolte nel corso del 2012 per il progetto bilaterale CNR / NSC 2012/2013 ...
Le attività svolte nel corso del 2012 per il progetto bilaterale CNR / NSC 2012/2013 possono essere condensate in tre macro gruppi_ (I) Attività scientifica svolta dal Team, derivante anche da altri progetti, ma che riguarda l'argomento trattato all'interno del bilaterale e che viene resa disponibile al progetto perchè venga divulgata durante I workshop, (ii) organizzazione di workshop tematici per la divulgazione dei risultati ottenuti, (iii) organizzazione di attività di collaborazioni scientifiche e di formazione attraverso lo scambio di ricercatori. Tutte le attività si sono in parte sovrapposte a quelle svolte per il progetto bilaterale 2010/2011 che è terminato con il workshop di fine Giugno 2012 tenutosi a Caramanico Terme, Provincia di Pescara e a l'Aquila.
Mondini, 2012, Remote sensing data and methodologies for semi-automatic event landslide mapping,
2012,
Ciampalini A., Del Ventisette C., Moretti S., Manunta M., Calò F., Paglia L., Ardizzone F., Guzzetti F., Rossi M, Bellotti F., Colombo D., Strozzi T., Wegmuller U., Mora O., Sanches F., 2012, DORIS downstream service_ a support to civil defence autorithies in landslides and subsidence risk management,
EGU 2012, 2012,
Ardizzone F., Bonano, M., Giocoli, A., Lanari R., Marsella,M., Pepe A., Perrone A., Piscitelli S., Scifoni S., Scutti M., Solaro G., 2012, Analysis of ground deformation using SBAS-DInSAR technique applied to COSMO-SkyMed images, the test case of Roma urban area,
SAR Image Analysis, Modeling, and Techniques XII. SPIE, Remote Sensing., pp. Art. N 85360D, Edimburgo,United Kingdom, 24-27 settmbre 2012,
Abstract
Differential Synthetic Aperture Radar Interferometry (DInSAR) represents a well-established remote sensing technique for the investigation ...
Differential Synthetic Aperture Radar Interferometry (DInSAR) represents a well-established remote sensing technique for the investigation of ground deformation phenomena. Among the DInSAR techniques, the Small BAseline Subset (SBAS) approach exploits ground surface at two mapping scales, low and high resolution, and allows the detection and monitoring of local deformation processes that may affect single buildings or man-made structures in urban areas. This work investigates the capability improvement of the SBAS-DInSAR technique to analyse deformation processes in urban areas by exploiting SAR data acquired by the Cosmo-SkyMed (CSM) constellation in comparison with the results obtained from data of first generation ERS/ENVISAT radar systems of he European Space Agency. In particular, we extracted mean deformation velocity maps as seen by the three different radar systems and, for each coherent pixel, we retrieved the corresponding displacement time series. Our analysis was focused on the Torrino area where independent studies had already revealed significant deformation signals testified by the serious damages on many buildings in the area. Moreover, in order to understand the causes of the CSM observed displacement rates, reaching few cm per year, we also performed a comparative analysis between DInSAR products and independent information derived from electrical resistivity tomography data and geological maps.
Ivan Marchesini, Michele Santangelo, 2012, ortofrane.sh,
2012,
Abstract
Script che integra comandi di GRASS GIS e bash per aiutare a ortorettificare foto aeree. ...
Script che integra comandi di GRASS GIS e bash per aiutare a ortorettificare foto aeree. Utilizzato per migliorare la qualità e l'efficienza del riporto della fotointerpretazione sulle carte topografiche di base.
Minelli A, Marchesini I, De Rosa P, Casagrande L, Cenci M, 2012, Geographical analysis and numerical quantification of visual impact for aerogenerators and photovoltaic panels using Open Source GIS,
OGRS 2012 (Open Source Geospatial Research & Education Symposium), Yverdon Les Bains (CH), 24-26 ottobre 2012,
Michele Santangelo, Ivan Marchesini, Mauro Cardinali, 2012, Carta dei domini giaciturali, Collazzone (PG),
2012,
Abstract
Carta tematica generata a partire dalla carta delle tracce della stratificazione, applicando i software geobed.py ...
Carta tematica generata a partire dalla carta delle tracce della stratificazione, applicando i software geobed.py e r.surf.ba.py. I risultati sono descitti nei lavori Marchesini et al., 2013 (A GIS Method for Obtaining Geologic Bedding Attitude; http_//link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007%2F978-3-642-31325-7_32 ) e Santangelo et al., 2014 (A method for the assessment of the influence of bedding on landslide abundance and types; http_//link.springer.com/article/10.1007%2Fs10346-014-0485-x)
A. Tarpanelli, L. Brocca, F. Melone, T. Moramarco, T. Lacava, W. Wagner, 2012, Utilizzo di dati satellitari per applicazioni idrologiche nel bacino dell’Alto-Medio Tevere,
XXXIII CONVEGNO NAZIONALE DI IDRAULICA E COSTRUZIONI IDRAULICHE, Brescia, 10-14 Settembre 2012,
Abstract
La memoria presenta un'analisi delle potenzialità di sensori satellitari a bassa
risoluzione spaziale per la stima ...
La memoria presenta un'analisi delle potenzialità di sensori satellitari a bassa
risoluzione spaziale per la stima di variabili idrologiche, quali la portata e il
contenuto d'acqua, e per la calibrazione della modellistica idraulica attraverso la
simulazione delle aree allagate. Per quanto riguarda la portata, si è ottenuta una
buona correlazione tra i dati elaborati del radiometro MODIS e la velocità media
per due sezioni del Fiume Tevere che ha permesso quindi di valutare la potenzialità
di tali dati anche per la determinazione della scala di deflusso. L'assimilazione dei
dati di contenuto d'acqua stimati dallo scatterometro a microonde ASCAT nella
modellistica idrologica ha fornito un effettivo miglioramento per la previsione delle
portate. Infine, l'uso di immagini SAR si è rivelato un grande supporto per la
calibrazione della scabrezza nel modello idraulico applicato per un piccolo bacino
dell'Alto Medio Tevere. I risultati sono, quindi, promettenti per l'effettivo utilizzo dei
dati satellitari in condizioni operative.
G. Corato F.Melone T.Moramarco Singh V.P., 2012, Uncertainty analysis of flow velocity estimation by a simplified entropy model,
Hydrological processes (Print) (2012). doi_10.1002/hyp.9590,
DOI: 10.1002%2Fhyp.9590
Abstract
The velocity field in a river flow cross-sectional area can be determined by applying entropy ...
The velocity field in a river flow cross-sectional area can be determined by applying entropy as done in 1978 by Chiu, who developed a two-dimensional model of flow velocity based on the knowledge of maximum velocity, umax, and the dimensionless entropic parameter, characteristic of the river site. This is appealing in the context of discharge monitoring, particularly for high floods, considering that umax occurs in the upper portion of flow area and can be easily sampled, unlike velocity in the lower portion of flow area. The simplified form of Chiu's entropy-based velocity model, proposed in 2004 by Moramarco et al., has been found to be reasonably accurate for determining mean flow velocity along each vertical sampled in the flow area, but no uncertainty analysis has been reported for this simplified entropy-based velocity model. This study, therefore, performed uncertainty analysis of the simplified model following a procedure proposed by Misirli et al. in 2003. The flow velocity measurements at the Rosciano River section along the Chiascio River, central Italy, carried out for a period spanning 20 years were used for this purpose. Results showed that the simplified entropy velocity model was able to provide satisfactory estimates of velocity profiles in the whole flow area and the 95% confidence bands for the computed estimated mean vertical velocity were quite representative of observed values. In addition, using these 95% confidence bands, it was possible to have an indication of the uncertainty in the determination of mean cross-sectional flow velocity as well.
Silvia Barbetta, Luca Brocca, Florisa Melone, Tommaso Moramarco, 2012, Real-time flood forecasting by relating local stage and remote discharge,
, 2012,
Abstract
A real-time Flood Forecasting and Warning System (FFWS) is the main nonstructural
measure for reducing risk ...
A real-time Flood Forecasting and Warning System (FFWS) is the main nonstructural
measure for reducing risk in flood-prone areas. A model able to provide
reliable stage and discharge forecasts is one of the fundamental FFWS components.
In this context, a simple model for real-time flood forecasting is proposed for river
reaches where significant lateral inflow contributions occur. The model, based on the
real-time Rating Curve Model, allows predicting the discharge hydrograph at a river
site where only the stage is monitored when the flow is known at an upstream
section. The model performance was found satisfactory for two river reaches of the
Tiber river basin, central Italy, characterized by different intermediate drainage areas.
Finally, the forecast uncertainty estimate is addressed through 95% confidence
interval based on the statistical properties of the forecast lateral inflow.
A. Tarpanelli, L. Brocca, F. Melone and T. Moramarco, 2012, Hydraulic modelling calibration in small rivers by using coarse resolution synthetic aperture radar imagery,
Hydrological processes (Online) (2012). doi_10.1002/hyp.9550,
DOI: 10.1002%2Fhyp.9550
Abstract
This study investigates the potential of the low-resolution images (150m) derived by the Advanced SyntheticAperture ...
This study investigates the potential of the low-resolution images (150m) derived by the Advanced SyntheticAperture Radar onboard
the ENVISAT satellite to calibrate a hydraulicmodel coupled with a semidistributed hydrologicmodel applied to a subcatchment of the
upper-middle TiberRiver,Genna basin (<100 km²), in central Italy,wherein a flood event occurred on 28 November 2010 causing high
damages. Specifically for thisflood event, anAdvanced SyntheticAperture Radar image is available for the peak region of the discharge
hydrograph. Different image processing techniques are used for the assessment of the flooded areas by using both a single image and a
change detection image based on an additional (dry) reference image. The satellite-derived flooded areas are adopted for the calibration
of the channel and floodplain Manning's roughness coefficients of a 'quasi-two-dimensional' hydraulic model applied to the study
basin, which allows to distinguish the main channel from the floodplain. The inflows for the hydraulic model corresponding to each
tributary of the main channel are determined by a semidistributed hydrologic model calibrated by using a set of historical flood events.
The hydraulic model calibration is also carried out by using the same set of historical flood events. For the event of November
2010, the modelled discharge and water level hydrographs obtained with the two sets of Manning roughness (via satellite and
historical calibration) are compared with in situ observations at the outlet of the basin.
This application on a small catchment contributes to strengthen the value of remote sensing data confirming the potential of
synthetic aperture radar imagery to reduce uncertainties in hydraulic modelling calibration.
A. Tarpanelli, M. Franchini, L. Brocca, S. Camici, F. Melone, T. Moramarco, 2012, A simple approach for stochastic generation of spatial rainfall patterns,
Journal of hydrology (Amst.) 472-473 (2012): 63–76. doi_10.1016/j.jhydrol.2012.09.010,
DOI: 10.1016%2Fj.jhydrol.2012.09.010
Abstract
Rainfall scenarios are of considerable interest for design flood and flood risk analysis. To this ...
Rainfall scenarios are of considerable interest for design flood and flood risk analysis. To this end, the stochastic
generation of continuous rainfall sequences is often coupled with the continuous hydrological
modelling. In this context, the spatial and the temporal rainfall variability represents a significant issue,
especially for basins in which the rainfall field cannot be approximated through the use of a single
station. Therefore, methodologies for the spatially and temporally correlated rainfall generation are welcome.
An example of such a methodology is the well-established Spatial-Temporal Neyman-Scott Rectangular
Pulse (STNSRP), a modification of the single-site Neyman-Scott Rectangular Pulse (NSRP)
approach, designed to incorporate specific features to reproduce the rainfall spatial cross-correlation.
In order to provide a simple alternative to the STNSRP, a new method of generating synthetic rainfall
time series with pre-set spatial-temporal correlation is proposed herein. This approach relies on the single-
site NSRP model, which is used to generate synthetic hourly independent rainfall time series at each
rain gauge station with the required temporal autocorrelation (and several other appropriately selected
statistics). The rank correlation method of Iman and Conover (IC) is then applied to these synthetic rainfall
time series in order to introduce the same spatial cross-correlation that exists between the observed
time series. This combination of the NSRP model with the IC method consents the reproduction of the
observed spatial-temporal variability of a rainfall field.
In order to verify the proposed procedure, four sub-basins of the Upper Tiber River basin are investigated
whose basin areas range from 165 km² to 2040 km². Results show that the procedure is able to preserve
both the rainfall temporal autocorrelation at single site and the rainfall spatial cross-correlation at
basin scale, and its performance is comparable with that of the STNSRP model for rainfall field generation.
Given its simple formal structure (based on well established methods_ i.e. NSRP and IC), we believe that
the proposed approach can be conveniently utilized to generate spatially and temporally correlated rainfall
scenarios.
A.A. PASQUA; O. PETRUCCI, 2012, The impact of two damaging hydrogeological events in Calabria (southern Italy).,
Geophysical research abstracts 14 (2012).,
Abstract
Basing on the analysis of a detailed historical database concerning the impact of bad weather ...
Basing on the analysis of a detailed historical database concerning the impact of bad weather periods in Calabria (southern Italy), two cases, occurred in October 1951 and October 1953, have been selected. The choice of these events firstly depends on their high socio-economic impact_ they caused severe economic damage and, during both the events, about 100 people were killed. Secondly it depends on the extremely high rainfall values recorded in both cases_ during 1951 event, as example, in 13 rain gauges of the hit area, the daily rainfall reached the highest value ever recorded.
After the delimitation of the geographic areas hit, the events are described in terms of types of damaging phenomena occurred (floods, landslides, wind storms). Basing on the available historical data, the amount of direct, indirect and intangible damage is also assessed.
Then, the amount of rainfall recorded in the raingauges of the affected areas is analyzed. Rainfall values are compared to the whole historical rainfall series, in order to select similar rainfall events and to compare the different damaging effects reported in the historical database. This comparison is focused on the analysis of the actual role played by the rainfall in causing the huge damage occurred in the studied cases, which could even be related to the past anthropogenic configuration of the hit areas. Finally, an actualization of the scenario of these events -in the current territory configuration- is attempted, aiming to assess the possible impact of similar rainfall scenarios in the future.
PETRUCCI O; PASQUA A.A., 2012, The impact of damaging hydro geological events on people in a Mediterranean region,
Geophysical research abstracts 14 (2012): 2726–2726.,
Abstract
Bad weather periods are a source of multiple hazards, because they can trigger several types ...
Bad weather periods are a source of multiple hazards, because they can trigger several types of damaging
phenomena which may cause different types of impacts on several natural and manmade elements in a wide
range of circumstances. The whole of all the phenomena triggered by bad weather periods have been defined as
Damaging Hydro Geological Events (DHE).
Phenomena which occur during DHEs can be roughly sorted in some main groups_ landslides, floods, erosion
processes and sea storms. Each type of phenomenon is characterized by a proper dynamic and, according to the
social and economic framework in which it develops, can cause different impacts.
Despite during bad weather periods all these phenomena occur at the same time (or in a short while), often
strongly amplifying damage and hinting emergency management actions, the studies available in literature tend
to analyse each type of phenomenon (and its impact) separately, thus supplying a fragmentary framework of the
effects.
In the present work, basing on a dataset concerning effects of DHEs in Calabria (southern Italy), a classification
of the effects on people affected by the different types of triggered phenomena is attempted. The results is a
classification of main circumstances during which the different types of phenomenon triggered can hit people.
This kind of result can be useful in education programs for people living in risk prone areas, in order promote
more conscious behaviours during DHEs and to avoid unnecessary risk-taking behaviour.
Llasat, M.C., Llasat-Botija, M., Petrucci, O., Pasqua, A.A., Rosselló, J., Grimalt., M., Vinet, F., Boisier, L., 2012, The HYMEX database on societal impact of floods,
6th HyMeX Workshop, Primostern Croatia, 7-10 may 2012,
PETRUCCI O., 2012, Impact of extreme events on people along the road network of a Mediterranean region,
6th HyMeX Workshop, Primostern Croatia, 7-10 may 2012,
Petrucci O., Pasqua A.A., 2012, Impact of extreme events on people along the road network of a Mediterranean region,
6th HyMeX Workshop, Primostern Croatia, 7-10 may 2012,
Petrucci O., Pasqua A.A., 2012, Il dissesto idrogeologico in Calabria_ dati disponibili e loro possibili applicazioni,
Geologia dell'ambiente 2 (2012): 57–61.,
Abstract
Vengono presentati i risultati di un'attività di ricerca avviata nel 2000 e volta a ricostruire ...
Vengono presentati i risultati di un'attività di ricerca avviata nel 2000 e volta a ricostruire la serie storica dei fenomeni di dissesto idrogeologico verificatisi negli ultimi secoli in Calabria. Si descrivono le principali applicazioni effettuate sulla base dei dati disponibili e le loro possibili utilizzazioni future
Petrucci O., Pasqua A.A., 2012, From past to present_ the effects of historical damaging hydrogeological events in the current urban setting,
EGU Plinius Topical Conference Series on Mediterranean Storms 14 (2012): 25.,
Llasat M.C. (1), Llasat-Botija M.(1), Petrucci O., Pasqua A.A., Rossello J. (2), Vinet F. (3), Boisier, L. (3), 2012, Floods in north-western of Mediterranean region_ perception, vulnerability and societal impact,
Evènements extrêmes fluviaux et maritimes, Paris, 1-2 February 2012,
Petrucci O.
Pasqua A.A, 2012, Effects of Landslides and floods on people_ a classification of damage scenarios obtained from the analysis of past events,
Rendiconti online Società Geologica Italiana (2012): 423–423.,
Petrucci O., Vranken L., 2012, Determination of natural and socio-economic factors affecting landslide damage_ an econometric approach using empirical evidence from the Calabria Region (Southern Italy),
Geophysical research abstracts (Online) 14 (2012): 3158.,
Petrucci O. (1), Llasat-Botija M. (2), Pasqua A.A. (1), Rosselló J. (3), Vinet F. (4), Boisier L. (4), Llasat M.C. (2), 2012, Building the HYMEX database on societal impact of floods_ first results and difficulties related to the concept of “event severity”,
EGU 2012 Leonardo_ Hydrology and society, Torino, November 14-16,
O. Payrastre, E. Gaume, P. Javelle, B. Janet, P. Fourmigué, Ph. Lefort, A. Martin, B. Boudevillain, P. Brunet, G. Delrieu, L. Marchi, Y. Aubert, E. Dautrey, L. Durand, M. Lang, L. Boissier, J. Douvinet, C. Martin, I. Ruin, TTO2-D Team HyMeX, 2012, Analyse hydrologique de la catastrophe du 15 juin 2010 dans la région de Draguignan (Var, France),
Congrès SHF : «Evènements extrêmes fluviaux et maritimes», Paris, 1-2/02/2012,
Abstract
Suite à la crue exceptionnelle qui s'est produite le 15 juin 2010 dans la région ...
Suite à la crue exceptionnelle qui s'est produite le 15 juin 2010 dans la région de Draguignan (Var), plusieurs équipes
de chercheurs et d'ingénieurs sont intervenues sur le terrain afin de documenter et de caractériser cet événement, en
proposant notamment des estimations des débits de pointe sur le cours principal de l'Argens ainsi que l'ensemble des
affluents touchés. Des informations sur la chronologie des crues ont également été obtenues auprès de témoins
oculaires. Un travail de coordination et d'échanges entre ces équipes a été organisé par le SCHAPI et la DREAL
PACA, et a permis de confronter et de mettre en cohérence les résultats obtenus, et d'engager une discussion sur les
périodes de retour de la crue. Cette comparaison a révélé que malgré les différentes sources possibles d'erreurs
d'estimation, les valeurs de débits proposées par les différentes équipes restaient globalement assez proches. Cette
première étape a permis de cartographier les débits sur la base d'une quarantaine d'estimations au total. La
répartition spatiale obtenue apparaît, de premier abord, cohérente avec l'estimation des cumuls pluviométriques
fournie par les lames d'eau radar. L'analyse hydrologique de l'événement a été complétée en comparant les débits
estimés à des hydrogrammes simulés à l'aide d'un modèle pluie-débit simple. Ces résultats mettent en évidence une
grande disparité des comportements hydrologiques des affluents de l'Argens. La Nartuby se distingue notablement avec
une réponse hydrologique très progressive et atténuée ce qui peut être attribué à l'effet du karst très présent sur ce
bassin. Enfin, le travail sur les périodes de retour a permis d'identifier les secteurs pour lesquels la crue a dépassé un
niveau centennal.
M. Polemio, T. Lonigro, 2012, Variabilità climatica e ricorrenza degli eventi catastrofici idrogeologici (ECI) in Puglia,
Engineering, hydro, environmental geology (2012): 190–191. doi_10.1474/EHEGeology.2012-14.B.l47,
DOI: 10.1474%2FEHEGeology.2012-14.B.l47
Davide Scrocca (1), Barbara Inversi (1, 6), Giordano Montegrossi (2), Lorenzo Petracchini (1, 7), Michele Livani (1, 6), Mauro Brilli (1), Francesca Giustini (1), Marco Brandano (1, 6), Riccardo Recanati (1), Gianluca Gola (2), Maurizio Polemio (3), Roberto De Franco (4), Grazia Caielli (4), Bruno Testa (4), Alessandro Romi (5), Claudio Chiarabba (8), Mario Anselmi (8), Marta Pischiutta (8), Antonio Rovelli (8), Fedora Quattrocchi (8), 2012, Studio Tecnico di Fattibilità – Impianto Geotermico Sito di Guardia dei Lombardi,
2012,
Polemio M., Limoni P. P, L. E. Zuffianò, F. Santaloia, 2012, Santa Cesarea Coastal Thermal Springs (Southern Italy),
22nd Salt Water Intrusion Meeting_ Salt Water Intrusion in Aquifers_ Challenges and Perspectives, Giugno 2012,
M. Iorio, P. P. Bruno, N. Cardellicchio, A. Caputi, G. Cavuoto, S. Chiesa, A. Corniello, E. Cuoco, R. de Franco, U. del Vecchio, V. di Fiore, M. Di Leo, D. Ducci, A. D'Oriano, M. Fedi, L. Ferranti, G. Florio, A. Giocoli, A. Manzella, A. Minissale, D. Montanari, M. Mussi, N. Pelosi, E. Petruccione, M. Polemio, E. Rizzo, C. Romano, G. Romano, A. Rovelli, S. Tamburrino, D. Tarallo, D. Tedesco, P. Tiano, 2012, Mondragone progetto geotermico_ Rapporto di Fattibilità Tecnica. Rapporto progetto VIGOR MISE,
2012,
M. Polemio, 2012, Modelling and optimization of the management systems of groundwater in the presence of marine intrusion_ the case of Salento (Apulia, Italy),
22° Salt Water Intrusion Meeting (SWIM22), Buzios, Brasile, 17-22 giugno 2012,
M. Polemio, A. Romanazzi, 2012, La gestione degli acquiferi carsici costieri_ il caso del Salento (Puglia),
Engineering, hydro, environmental geology (2012). doi_10.1474/EHEGeology.2012-14.B.l48,
DOI: 10.1474%2FEHEGeology.2012-14.B.l48
Petrucci O., Dragone V., Polemio M., 2012, Flood damage, protection works and population amount_ a 150-year case history concerning the Sibari coastal plain (southern Italy),
Hydrology and Society-Connections between Hydrology and_ Population dynamics, Policy making and Power Generation, Torino, 14-16/11/2012,
Petrucci O. (1), Dragone V. (2), Polemio M. (2), 2012, Flood damage, protection works and population amount_ a 150-year case history concerning the Sibari coastal plain (southern Italy),
EGU Leonardo 2012, Hydrology And Society, Torino, November 14-16,
PARISE M. & CANNON S.H., 2012, Wildfire impacts on the processes that generate debris flows in burned watersheds,
Natural hazards (Dordr.) 61 (2012): 217–227. doi_10.1007/s11069-011-9769-9,
DOI: 10.1007%2Fs11069-011-9769-9
Abstract
Every year, and in many countries worldwide, wildfires cause significant damage and economic losses due ...
Every year, and in many countries worldwide, wildfires cause significant damage and economic losses due to both the direct effects of the fires and the subsequent accelerated runoff, erosion, and debris flow. Wildfires can have profound effects on the hydrologic response of watersheds by changing the infiltration characteristics and erodibility of the soil, which leads to decreased rainfall infiltration, significantly increased overland flow and runoff in channels, and movement of soil. Debris-flow activity is among the most destructive consequences of these changes, often causing extensive damage to human infrastructure. Data from the Mediterranean area and Western United States of America help identify the primary processes that result in debris flows in recently burned areas. Two primary processes for the initiation of fire-related debris flows have been so far identified_ (1) runoff-dominated erosion by surface overland flow; and (2) infiltration-triggered failure and mobilization of a discrete landslide mass. The first process is frequently documented immediately post-fire and leads to the generation of debris flows through progressive bulking of storm runoff with sediment eroded from the hillslopes and channels. As sediment is incorporated into water, runoff can convert to debris flow. The conversion to debris flow may be observed at a position within a drainage network that appears to be controlled by threshold values of upslope contributing area and its gradient. At these locations, sufficient eroded material has been incorporated, relative to the volume of contributing surface runoff, to generate debris flows. Debris flows have also been generated from burned basins in response to increased runoff by water cascading over a steep, bedrock cliff, and incorporating material from readily erodible colluvium or channel bed. Post-fire debris flows have also been generated by infiltration-triggered landslide failures which then mobilize into debris flows. However, only 12% of documented cases exhibited this process. When they do occur, the landslide failures range in thickness from a few tens of centimeters to more than 6 m, and generally involve the soil and colluvium mantled hillslopes. Surficial landslide failures in burned areas most frequently occur in
response to prolonged periods of storm rainfall, or prolonged rainfall in combination with rapid snowmelt or rain-on-snow events.
Parise M., 2012, Underground aqueducts_ a first preliminary bibliography around the world,
3rd IWA Specialized Conference on "Water and Wastewater Technologies in Ancient Civilizations", pp. 65–72, Istanbul (Turkey), 22-24 March 2012,
MARTIMUCCI V., PARISE M., ANTONICELLI A., ANTONUCCI M.P., CARBONARA M., CHIECO M. & PACE F., 2012, The regional registers of natural and artificial caves of Apulia (southern Italy): recent developments from a joint project Regione Puglia – Federazione Speleologica Pugliese,
Geologia dell'Ambiente 3 (2012): 70–72.,
MARTIMUCCI V., PARISE M., ANTONICELLI A., ANTONUCCI M.P., CARBONARA M., CHIECO M. & PACE F., 2012, The regional registers of natural and artificial caves of Apulia (southern Italy): recent developments from a joint project Regione Puglia – Federazione Speleologica Pugliese,
7th International Symposium ProGEO on the Conservation of the Geological Heritage, pp. 35–35, Bari, 24-28 September 2012,
DEL PRETE S. & PARISE M., 2012, The influence of geological and morphological factors in the realization of artificial caves,
The Rupestrian Settlements in the Circum-Mediterranean area, pp. 19–30, 2012,
PEPE M. & PARISE M., 2012, Structural control in sinkhole development and speleogenesis_ a case study from the High Murge karst landscape (Apulia, Italy),
Geophysical research abstracts 14 (2012): 340–340.,
FIORE A. & PARISE M., 2012, Sprofondamenti connessi a cavità di origine antropica in Puglia,
Geologia dell'Ambiente 2 (2012): 41–45.,
Pepe M., Parise M., 2012, Some considerations on depressions, dolines, and similar karst landforms,
20th International Karstological School "Karst Forms and Processes", pp. 70–71, Postojna (Slovenia), 18-21 June 2012,
FESTA V., FIORE A., PARISE M. & SINISCALCHI A., 2012, Sinkhole evolution in the Apulian karst of southern Italy_ a case study, with some considerations on sinkhole hazards.,
Journal of caves and karst studies 74 (2012): 137–147. doi_10.4311/2011JCKS0211,
DOI: 10.4311%2F2011JCKS0211