Rossi M., Witt A., Malamud B.D., Guzzetti F., Peruccacci S., 2010, Examination of historical landslide time series_ a test case from the Emilia-Romagna region, northern Italy.,
AGU Fall metting, San Francisco, 2010,
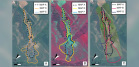
Reichenbach P., Mondini A.C., Ardizzone F., Cardinali M., Fiorucci F., Guzzetti F., Rossi M., 2010, Semi-automatic mapping of rainfall-induced landslides using VHR optical imagery_ the Messina, Sicily, 1 October 2009 landslide event.,
2010 AGU Fall Meeting, San Francisco, 2010,
Guzzetti F., Rossi M., Peruccacci S., Brunetti M.T., Marchesini I., Ardizzone F., Balducci V., Bianchi C., Cardinali M., Fiorucci F., Mondini A.C., Reichenbach P., Salvati P., Tonelli G., Dello Buono D., Izzi F., Amato L., La Scaleia G., Maio D., Pagliara, 2010, A national early warning system for rainfall-induced landslides in Italy.,
2010 AGU Fall meeting, San Francisco, 2010,
Guzzetti F., 2010, Landslide hazard, vulnerability and risk assessment_ methods, limits and challenges.,
2010 AGU Fall Meeting, San Francisco, 2010,
Rizzo E., Valeria G., Votta M., Lapenna V., Moramarco T., Aricò C., Camici S., Morbidelli R., Sinagra M., Tucciarelli T., 2010, Experimental analysis of the levees safety based on geophysical monitoring.,
Vienna, 2010,
Tarpanelli, A., Franchini, M., Camici, S., Brocca, L., Melone, F., Moramarco, T., 2010, A simple approach for stochastic generation of spatial rainfall patterns.,
2010,
Calamita, G., Perrone, A., Satriani, A., Brocca, L., Moramarco, T., 2010, Soil moisture – resistivity relation at the plot and catchment scale.,
2010,
Brocca, L., Penna, D., Barbetta, S., Melone, F., Moramarco, T., Gobbi, A., 2010, Use of soil moisture and water table data for rainfall-runoff modelling in alpine catchments.,
2010,
Brocca, L., Melone, F., Moramarco, T., Heitz, S., Matgen, P., Pfister, L., 2010, On the monitoring of antecedent wetness conditions across different scales.,
2010,
Brocca, L., Melone, F., Moramarco, T., Wagner, W., Hasenauer, S., Berni, N., 2010, Use of ASCAT derived soil moisture product for real-time flood forecasting in the Upper Tiber river.,
2010,
Calamita, G., Perrone, A., Rizzo, E., Lapenna, E., Brocca, L., Melone, F., Moramarco, T., Tullo, T., 2010, Application of electromagnetic induction and resistivity methods for soil moisture estimation at the hillslope scale.,
Int. Conf. EGU Leonardo Topical Conference Series on the hydrological cycle 2010, Luxembourg, 2010,
Ponziani. F., Berni, N., Pandolfo, C., Stelluti, M., Brocca, L., 2010, An integrated approach for the real-time monitoring of a high risk landslide by a regional civil protection office.,
Int. Conf. EGU Leonardo Topical Conference Series on the hydrological cycle 2010, Luxembourg, 2010,
Berni, N., Pandolfo, C., Ponziani. F., Stelluti, M., Viterbo, A., Brocca, L., 2010, Upper-Medium Tiber river flood management during January 2010 event at Umbria Region operational forecasting system.,
Int. Conf. EGU Leonardo Topical Conference Series on the hydrological cycle 2010, Luxembourg, 2010,
Brocca, L., Faruolo, M., Coviello, I., Lacava, T., Melone, F., Moramarco, T., Pergola, N., Tramutoli, V., 2010, Soil moisture variations estimation through robust satellite technique on different satellite sensors_ an intecomparison and validation study across Europe.,
Luxembourg, 2010,
De Rosnay, P., Muñoz Sabater, J., Balsamo, G., Drusch, M., Scipal, K., Isaksen, L., Grippa, M., Albergel, C., Brocca, L., Merlin, O., Roulin, E., 2010, Use of satellite data for land surface analysis at ECMWF.,
Int. Conf. Earth Observation for Land-Atmosphere Interaction Science, ESA-ESRIN, Frascati, 2010,
Guzzetti F., 2010, Pericolosità, vulnerabilità e rischio da frana in Italia.,
Frane e Dissesto Idrogeologico_ Consuntivo, Roma, 2010,
Tonelli G., Marchesini I., Rossi M., Guzzetti F., 2010, PostgreSQL in ausilio alla previsione di pericolosità da frana ai fini di Protezione Civile.,
PgDay2010@Roma, Roma, 10/12/2010,
ANGELI M.G., GASPARETTO P., MARABINI F. & PONTONI F., 2010, An examples of large coastal landslide affecting an inhabited area in the Marche Region (Italy).,
China-Italy bilateral symposium on the coastal zone and continental shelf evolutional trend, Qing Dao, 2010,
ANGELI M.G., GASPARETTO P., MARABINI F. & PONTONI F., 2010, Shear strength regain tests of clayey soils.,
4th International Conference on Geotechnical Engineering and Soil Mechanics, Theran, 2010,
ANGELI M.G., GASPARETTO P. & PONTONI F., 2010, Shear Strength Regain of Clayey Landslides and Remedial Works.,
International Symposium on Geomechanics and Geotechnics_ From Micro to Macro, Shanghai, 10-12 Ottobre 2010,
Abstract
The shear strength regain effect takes place whenever an intermittent landslide on clayey materials occurs. ...
The shear strength regain effect takes place whenever an intermittent landslide on clayey materials occurs. During the rest period, the clay material nearby the sliding surface regains part of its shear strength. The new strength level can overcome the residual shear strength by more than 20%. The more is the rest period, the more is the shear strength regain. A new movement will take place only if the hydraulic conditions will be able to exceed the new level of shear strength. The paper examines closely the shear strength regain phenomenon, analysing the results derived from several dedicated ring shear tests on clayey landslide materials, and deals with some case studies which, taking into account the positive effect of the shear strength regain, provide us a new approach to bet-ter design the remedial works on clayey landslide.
ANGELI M.G., GALVANI A., GASPARETTO P., MARABINI F., MERTZANIS A. & PONTONI F., 2010, Coastal zone evolution of the Marche region (Adriatic Sea Italy).,
China-Italy bilateral symposium on the coastal zone and continental shelf evolutional trend, Bologna, 2010,
Brocca, L., Camici, S., Tarpanelli, A., Melone, F., Moramarco, T., 2010, Analysis of climate change effects on floods frequency through a continuous hydrological modelling.,
Conf. NATO advanced research workshop, Climate change and its effect on water resources - issues of national and global security., Izmir, Turchia, 2010,
Aricò C., Moramarco T., Morbidelli R., Rizzo E., Sinagra M., Tucciarelli T., 2010, Il metodo MAST,
XXXII Convegno di Idraulica e Costruzioni Idrauliche, Palermo, 2010,
Corato G., Melone F., Moramarco T., 2010, Relazione tra le caratteristiche geometriche ed idrauliche di un sito fluviale ed il parametro entropico per la stima della velocità media in canali.,
XXXII Convegno di Idraulica e Costruzioni Idrauliche, Palermo, 2010,
Corato G., Moramarco T., Tucciarelli T., 2010, Integrazione di metodologie dirette ed indirette per la stima degli idrogrammi di piena in alvei naturali,
XXXII Convegno di Idraulica e Costruzioni Idrauliche, Palermo, 2010,
Brocca L., Corato G, Corradini C., Melone F., Moramarco, T., 2010, Stima della velocità media in canali naturali attraverso il monitoraggio della velocità massima superficiale.,
XXXII Convegno di Idraulica e Costruzioni Idrauliche, Palermo, 2010,
Aricò C., Sinagra M., Tarpanelli A., Moramarco T., Tucciarelli T., 2010, Utilizzo di un modello diffusivo 2D di acque basse per la simulazione in tempo reale di scenari di inondazione.,
XXXII Convegno di Idraulica e Costruzioni Idrauliche, Palermo, 2010,
Brocca L., Melone F., Moramarco, T., 2010, Modellistica afflussi-deflussi di tipo continuo per la previsione delle piene su bacini dell’alto medio Tevere.,
XXXII Convegno di Idraulica e Costruzioni Idrauliche, Palermo, 2010,
Aricò C., Camici S., Moramarco T., Sinagra M., Tucciarelli T., Rizzo E., Gaimpaolo V., Morbidelli R., 2010, Analisi del moto di filtrazione in rilevati arginali mediante tomografia di resistività elettrica.,
XXXII Convegno di Idraulica e Costruzioni Idrauliche, Palermo, 2010,
Tarpanelli A., Camici S., Brocca L., Franchini M., Melone F., Moramarco, T., 2010, Un metodo semplice per la generazione di serie sintetiche di pioggia con correlazione spaziale e temporale.,
XXXII Convegno di Idraulica e Costruzioni Idrauliche, Palermo, 2010,
Barbetta S., Franchini M., Melone F., Moramarco T., 2010, Modello per la stima della scala di deflusso in siti fluviali con sole registrazioni di livello,
XXXII Convegno di Idraulica e Costruzioni Idrauliche, Palermo, 2010,
Nativi S., Mazzetti P., Guzzetti F., Oggioni A., Pirrone N., Santoleri R., Tartarig G., Viola A., Santoro M., 2010, The GIIDA project_ a spatial information infrastructure for environmental data sharing.,
International Symposium on Geo-information for Disaster Management (Gi4DM), Torino, 2010,
Marchesini I., Balducci V., Tonelli G., Rossi M., Guzzetti F., 2010, Geospatial information on landslides and floods in Italy.,
International Symposium on Geo-information for Disaster Management (Gi4DM), Torino, February 02 to 04,
Abstract
We describe a system for the dissemination of geographical and thematic information on landslides and ...
We describe a system for the dissemination of geographical and thematic information on landslides and floods in Italy. In the
framework of the Integrated Management of the Environmental Data project - GIIDA - of the Italian National Research Council
(CNR), the research Institute for Geo-Hydrological Hazard Assessment (IRPI) has designed and implemented a new Spatial Data
Infrastructure (SDI). The SDI is compliant to Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC) specifications for the publication, access, and
discovery of dedicated services, including WMS, WFS, WCS and CSW services. The CNR IRPI spatial data infrastructure (SDI) fully
exploits Open Source Software (OSS). Adoption of an OSS approach for the design and the implementation of the new SDI proved
valid, and economically convenient. As part of the GIIDA project, the national landslide warning system for the possible occurrence of
rainfall-induced landslides in Italy was integrated in the new SDI. The integration proved successful, and was facilitated by the fact that
the warning system operates on data and geographical information stored in a PostgreSQL + PostGIS database.
Parise M., Perrone A., Violante C., Stewart J.P., Simonelli A., Guzzetti F., 2010, Activity of the Italian National Research Council in the aftermath of the 6 April 2009 Abruzzo earthquake_ the Sinizzo Lake case study.,
2° Workshop Internazionale I Sinkholes - Gli sprofondamenti catastrofici nellambiente naturale ed in quello antropizzato., Roma, 2010,
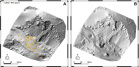
Santangelo M.; Cardinali M.; Rossi M.; Mondini A.C.; Guzzetti F., 2010, Remote landslide mapping using a laser rangefinder binocular and GPS.,
Natural hazards and earth system sciences (Print) 10 (2010): 2539–2546. doi_10.5194/nhess-10-2539-2010,
DOI: 10.5194%2Fnhess-10-2539-2010
Abstract
We tested a high-quality laser rangefinder binocular coupled with a GPS receiver connected to a ...
We tested a high-quality laser rangefinder binocular coupled with a GPS receiver connected to a Tablet PC running dedicated software to help recognize and map in the field recent rainfall-induced landslides. The system was tested in the period between March and April 2010, in the Monte Castello di Vibio area, Umbria, Central Italy. To test the equipment, we measured thirteen slope failures that were mapped previously during a visual reconnaissance field campaign conducted in February and March 2010. For reference, four slope failures were also mapped by walking the GPS receiver along the landslide perimeter. Comparison of the different mappings revealed that the geographical information obtained remotely for each landslide by the rangefinder binocular and GPS was comparable to the information obtained by walking the GPS around the landslide perimeter, and was superior to the information obtained through the visual reconnaissance mapping. Although our tests were not exhaustive, we maintain that the system is effective to map recent rainfall induced landslides in the field, and we foresee the possibility of using the same (or similar) system to map landslides, and other geomorphological features, in other areas.
BORSELLI L., TORRI D., 2010, Soil roughness, slope and surface storage relationship for impervious areas.,
Journal of hydrology (Amst.) 393 (2010): 389–400.,
Katz O.; Reichenbach P.; Guzzetti F., 2010, Rock fall hazard along the railway corridor to Jerusalem, Israel, in the Soreq and Refaim valleys.,
Natural hazards (Dordr.) (2010).,
Perumal M., Moramarco T., Sahoo B., Barbetta S., 2010, On the practical applicability of the VPMS routing method for rating curve development at ungauged river sites.,
Water resources research 46 (2010). doi_10.1029/2009WR008103,
DOI: 10.1029%2F2009WR008103
Abstract
This paper presents a novel approach for enhancing the accuracy of the variable
parameter Muskingum stage ...
This paper presents a novel approach for enhancing the accuracy of the variable
parameter Muskingum stage hydrograph routing method proposed by Perumal et al.
(2007) for rating curve development at ungauged river sites having irregular cross sections.
The approach has been well tested for the reproduction of stage and discharge hydrographs
and for rating curve development at an ungauged section of the Tiber River in central Italy
considering two different natural channel reaches.
Brocca L.1; Melone F.1; Moramarco T.1; Morbidelli R.2, 2010, Spatial-temporal variability of soil moisture and its estimation across scales,
Water resources research 46 (2010). doi_10.1029/2009WR008016,
DOI: 10.1029%2F2009WR008016
Abstract
The soil moisture is a quantity of paramount importance in the study of hydrologic phenomena ...
The soil moisture is a quantity of paramount importance in the study of hydrologic phenomena and soil-atmosphere interaction. Because of its high spatial and temporal variability, the soil moisture monitoring scheme was investigated here both for soil moisture retrieval by remote sensing and in view of the use of soil moisture data in rainfall-runoff modeling. To this end, by using a portable Time Domain Reflectometer, a sequence of 35 measurement days were carried out within a single year in seven fields located inside the Vallaccia catchment, central Italy, with area of 60 km(2). Every sampling day, soil moisture measurements were collected at each field over a regular grid with an extension of 2000 m(2). The optimization of the monitoring scheme, with the aim of an accurate mean soil moisture estimation at the field and catchment scale, was addressed by the statistical and the temporal stability. At the field scale, the number of required samples (NRS) to estimate the field-mean soil moisture within an accuracy of 2%, necessary for the validation of remotely sensed soil moisture, ranged between 4 and 15 for almost dry conditions (the worst case); at the catchment scale, this number increased to nearly 40 and it refers to almost wet conditions. On the other hand, to estimate the mean soil moisture temporal pattern, useful for rainfall-runoff modeling, the NRS was found to be lower. In fact, at the catchment scale only 10 measurements collected in the most "representative" field, previously determined through the temporal stability analysis, can reproduce the catchment-mean soil moisture with a determination coefficient, R(2), higher than 0.96 and a root-mean-square error, RMSE, equal to 2.38%. For the "nonrepresentative" fields the accuracy in terms of RMSE decreased, but similar R(2) coefficients were found. This insight can be exploited for the sampling in a generic field when it is sufficient to know an index of soil moisture temporal pattern to be incorporated in conceptual rainfall-runoff models. The obtained results can address the soil moisture monitoring network design from which a reliable soil moisture temporal pattern at the catchment scale can be derived.
Moramarco T., Singh V.P., 2010, Formulation of the entropy parameter based on hydraulic and geometric characteristics of river cross section.,
Journal of hydrologic engineering 15 (2010): 852–858.,
Brocca L., Melone F., Moramarco T., Wagner W., Hasenauer S., 2010, ASCAT Soil Wetness Index validation through in-situ and modeled soil moisture data in central Italy.,
Remote sensing of environment 114 (2010): 2745–2755.,
Brunetti M.T.; Peruccacci S.; Rossi M.; Luciani S.; Valigi D.; Guzzetti F., 2010, Rainfall thresholds for the possible occurrence of landslides in Italy.,
Natural hazards and earth system sciences (Print) 10 (2010): 447–458.,
Salvati P.; Bianchi C.; Rossi M.; Guzzetti F., 2010, Societal landslide and flood risk in Italy.,
Natural hazards and earth system sciences (Print) 10 (2010): 465–483.,
Rossi F.; Witt A.; Guzzetti F.; Malamud B.D.; Peruccacci S., 2010, Analysis of historical landslide time series in the Emilia-Romagna Region, Northern Italy.,
Earth surface processes and landforms (Print) 35 (2010): 1123–1137.,
Witt A., Malamud B.D., Rossi M., Guzzetti F., Peruccacci S., 2010, Temporal correlation and clustering of landslides.,
Earth surface processes and landforms (Print) 35 (2010): 1138–1156.,
Rossi M.; Guzzetti F.; Reichenbach P.; Mondini A.; Peruccacci S., 2010, Optimal landslide susceptibility zonation based on multiple forecasts.,
Geomorphology (Amst.) 114 (2010): 129–142. doi_10.1016/j.geomorph.2009.06.020,
DOI: 10.1016%2Fj.geomorph.2009.06.020
Abstract
Environmental and multi-temporal landslide information for an area in Umbria, Italy, was exploited to produce ...
Environmental and multi-temporal landslide information for an area in Umbria, Italy, was exploited to produce four single and two combined landslide susceptibility zonations. The 78.9 km2 study area was partitioned in 894 slope units, and the single susceptibility zonations were obtained through linear discriminant analysis (LDA), quadratic discriminant analysis (QDA), logistic regression (LR), and by training a neural network (NN). The presence or absence of landslides in the slope units in the period from pre-1941 to 1996 (training set) was used as the dependent variable for the terrain classification. Next, adopting a regression approach, two "optimal" combinations of the four single zonations were prepared. The single and the combined zonations were tested against landslides in the 9-year period from 1997 to 2005 (validation set). Different metrics were used to evaluate the quality of the susceptibility zonations, including degree of model fit, uncertainty in the probability estimates, and model prediction skills. These metrics showed that the degree of model fit was not a good indicator of the model forecasting skills. Zonations obtained through classical multivariate classification techniques (LDA, QDA and LR) produced superior predictions when compared to the NN model, that over fitted the landslide information in the training set. LDA and LR produced less uncertain zonations than QDA and NN. The combined models resulted in a reduced number of errors and in less uncertain predictions; an important result that suggests that the ombination of landslide susceptibility zonations can provide "optimal" susceptibility assessments.
Casadei S, Bellezza M, Casagrande L, Pierleoni A, Marchesini I, 2009, Tecnologie libere ed open source per la consultazione e l’elaborazione di dati territoriali ed idrometeorologici in applicazioni web-based,
Geo media 4 (2009).,
Abstract
L'articolo presenta un sistema di supporto alle decisioni dei tecnici addetti alla gestione delle concessioni ...
L'articolo presenta un sistema di supporto alle decisioni dei tecnici addetti alla gestione delle concessioni idriche
sul fiume Tevere, in grado di facilitare il raggiungimento del consenso tra tutti i partecipanti al processo decisionale,
predisponendo la valutazione delle richieste, in funzione dei molteplici fattori correlati. Un approccio con tecnologie
GIS Open Source in grado di acquisire dati da varie fonti e predisporre i risultati su una piattaforma web facilmente
consultabile da tutti.
Marchesini I, Cencetti C, Rosa P, 2009, A preliminary method for the evaluation of the landslides volume at a regional scale,
Geoinformatica (Dordrecht) 13 (2009): 277–289. doi_10.1007/s10707-008-0060-5,
DOI: 10.1007/s10707-008-0060-5
Abstract
Dealing with the evaluation of the risk connected to the formation of
landslide dams at regional ...
Dealing with the evaluation of the risk connected to the formation of
landslide dams at regional scale, it is important to estimate the volume of the
depleted material that can reach the riverbed. This information, combined with
other elements (river dimensions, valley width, landslide velocity, etc.) allows making
predictions on the possibility of river blockage. One of the problems of this approach
is the lack of data concerning the shape and position of the sliding surface; this does
not permit us to estimate the volume of the landslide material. The IFFI (Inventario
dei Fenomeni Franosi in Italia, i.e. Landslide Inventory in Italy) project furnishes
information, at different levels of precision, on nearly totality of the landslides
existing in Italy. The first level of the IFFI (compiled for all slides) does not contain
information on the depth of the sliding surface but contains data regarding the type
and the activity of the slope movement. Along with this information the IFFI project
also furnishes vector maps containing the boundary of each landslide and the main
sliding direction. This paper describes the implementation of an algorithm aimed to
define, with an adequate approximation, the 3D geometry of the sliding surface of
rotational slides for which, on the basis of geologic maps available at regional scale,
some geotechnical parameters can be known or estimated. The work also required
the creation of a computer code useful for the 3D analysis of slope stability (3D safety
factor) using the simplified Janbu method. All computer code has been created on
a GNU-Linux OS and using shell scripting, based on GRASS GIS and R statistical
software.
Reichenbach P., Mondini A.C., 2009, Test report_ as run – procedure di test s,
2009,
Reichenbach P., Mondini A.C., 2009, Test report_ as run – procedure di test s,
2009,