Innovative technologies at high environmental sustainability in the forest-based sector
(AmbiTecFilLegno)

Background
Millennium Ecosystems Assessment (ONU). Intergovernmental Convention on Climate and European Convention on the Protection of Forests. Integration of ground and remote technologies for Earth Observation and development of multi-resolution (spectral, spatial and temporal). Sustainable Forest Management (Ministerial Conference on the Protection of Forests in Europe). Decision support systems in the forest sector. Industrial technologies of the wood.
Purpose
The project aims at developing and integrating innovative technologies for exploiting environmental and forest resources in Calabria – namely of wood, a material characterized by high environmental sustainability – through through actions of industrial research and experimental development along all the aspects of the forest-wood-environment chain, from production to processing, to use of nanotechnologies.
Methods
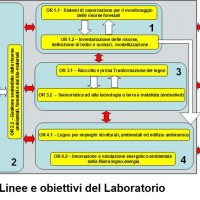
The activities will be developed according to 9 Objectives, articulated in 4 Lines:
- Monitoring and advanced inventory;
- Planning, biomass, environmental certification;
- Utilization, mechanization and logistics;
- Wood technology.
CNR-IRPI will analyze geo-hydrological risk models and will realize shallow-landslides susceptibility and soil erosion maps.
Results
Monitoring, inventory and scenarios: forest resources and “environmental services”. Integrated planning and management of the supply chain in the context of environmental sustainability. The protective role of forests against natural hazards and in the carbon cycle. Technologies for increasing availability and quality of wood, and for its transformation. Eco-certification and role of the forest-wood chain to environmental mitigation.
Products
Methods and application results, disseminated through technical reports, seminars and scientific articles. Impact on the socio-economic system of southern Italy, with exploitation of forest resources as drivers of innovation for small/medium industries. As regards CNR-IRPI, scenarios of geo-hydrological risk and maps of soil erosion will be produced, in presence/absence of forests.
Conclusions
The activities are very complex due to the wide spectrum of potential wood uses (construction, energy, furniture), with recent price tensions. The project enhances: growth, collection, characterization and processing of wood until the development of the final products, to improve quality and reduce costs. Environmental sustainability will be assessed also in terms of geo-hydrological processes and consequences.