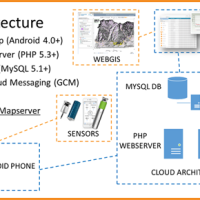
The management of natural hazards tends radically to distribute responsibilities at the local level, as the first civil protection actors. Prevention and preparedness are long-term goals, rooted in volunteer expertise, and awareness of local citizens, using solutions of "crowd-sourced mappers". The objective is designing mobile applications, sensors and dashboard for citizens and volunteers of civil protection, with pilot study cases selected ...

Producing knowledge implies the responsibility to divulge it with quality, making it available for everyone. With the advent of the Internet the possibilities to retransmit knowledge have grown, but the danger is also grown of a deterioration of its quality, as the Nobel prize Gell-mann already denounced in the nineties. The project intends to propose solutions to this kind of problem, contributing to improve the expressive capacity of thesis ...
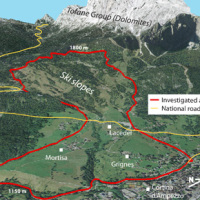
The study of the dynamics of large landslide is a heuristic process based on the integration of multiple investigation techniques: geological and geomorphological analysis, monitoring systems (traditional and innovative) and numerical models. Risk mitigation may require major interventions that call for detailed studies on the specific ...

Application of optical fibers is generally aimed at large bandwidth transmission. Few people know that the proposal of optical fibers as sensing elements is almost as old as their proposal as transmission media, and over the last two decades fibre optic sensor (FOS) technology has assumed a dominant role in several fields of application. As a matter of fact, FOSs offer many advantages with respect to legacy electronic and mechanic sensors. ...
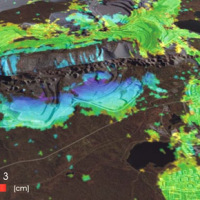
Space-borne radar interferometry or DInSAR (Differential Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar) is one of the latest techniques used for the detection and measurement of ground surface deformations caused by natural and / or man-made events. The DInSAR technique has been successfully used in the measurement of seismic deformations and of the effects of subsidence, unstable slopes and inflation of magma in volcanoes. The growth of space ...

Italy has a tradition of scientific research and technological development on hazardous natural phenomena in general, and specifically on geo-hydrological hazards. Within the CNR, the “Progetti Finalizzati” Soil Conservation and Geodynamics (in the ’70s and ’80s), and GNDCI – the National Group for the Defence from Hydrogeological Disasters (in the ’80s and ’90s), have contributed to the advancement of knowledge ...

The aim of the geomorphometric analysis is to derive indices capable of characterizing the spatial variability of specific hydro-geomorphological processes (e.g., sediment connectivity, erosion and deposit). The growing availability of high-resolution topographic data has increased the interest in geomorphometry and its applications. Debris-flow monitoring in instrumented areas and flash-flood documentation are invaluable ways to gather field ...

The project is focused on flood forecasting and hydraulic risk, i.e. the assessment of the effects of flooding in flood-prone areas also involving the vulnerability assessment of the hydraulic structures (dams, leaves, bridges, etc.).
The effects of flood events are not completely eliminated by structural measures, therefore it is necessary to develop complementary non-structural measures, such as real-time Flood Forecasting and Warning ...

The research topics involve the consideration of geological, geomorphological, hydrological, hydrogeological, and technology and the use of innovative methodologies to achieve the sustainability of the natural balance inherent inland waters, with a focus on groundwater and river water. Finally, we consider the effects of climate change on the hydrological cycle and anthropogenic modifications to emphasize the contribution of these modifications ...
The project concerns the mitigation of natural hazards (mainly the effects on the territory and the anthropic environment caused by rains, earthquakes, volcanism, and Radon gas). The geological characterization is essential to frame the contexts and the expected phenomena. Numerical modeling and monitoring allow to predict the spatio-temporal evolution of the phenomena, and therefore to evaluate the risk for mitigation ...
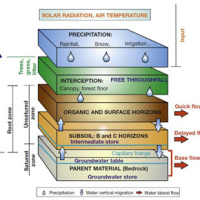
The area of interest specifically refers to the study of the following themes: extreme hydrological events and their interaction with slopes and watercourses; soil water erosion; debris flows; slope stability; triggering instability mechanisms; evolution of slope movements; monitoring systems for gravitational movements for the purpose of alerting for the mitigation of geo-hydrological risk. The activities proposed in the module are therefore ...

The urbanisation of seismically active areas, coupled with the ongoing change in climate patterns, require a shift in the approaches to land/infrastructure instability hazard assessment and risk reduction. This is particularly relevant in seismically active regions where the recurrent damage from landsliding, subsidence and ground deformations can be widespread. Geotechnical investigations and in situ monitoring of land prone to instability are ...
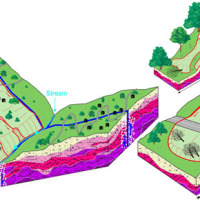
A Geo-hydrological event (EDId) (landslides, mass movements, floods, etc.) can result in a high social and economic impact, especially if it is generated by multiple simultaneous phenomena, when it is able to produce social hardships and economic damage characterized by important and lasting effects. The identification of the typical elements of the phenomena that can contribute to an EDId (typify) is essential to adequately define the risk ...

Climate change in the Greater Alpine Region is seriously affecting glacial and periglacial areas, especially for the presence of snow, glaciers and permafrost (cryosphere), with relevant consequences on slope stability. Cryosphere degradation, changes of the precipitation and temperature patterns and of the hydrological regimes, are some of the main terrestrial indicators of climatic change. Moreover, the increasing number of tourists and human ...

In Italy landslides and floods are frequent, widespread and dangerous phenomena, that cause fatalities and serious economic damage. In our country, landslides and floods pose major problems of scientific interest and of social and economic relevance.
The Institute is a Competence Centre for the Italian national Civil Protection Department, an Office of the Prime Minister. For the Department of Civil Protection we execute research and ...

Critical and depositional friction angles are characteristic for the deposition of a granular mass; the wrong angle adoption determines the ineffectiveness of a containment basin. The term is used with different meanings and measured by various procedures. The numerical simulation is a useful tool for the hazard assessment, but the definition of friction needed parameters requires insights on their ...

Nel 2014 ricorrono vent’anni dalla tragica alluvione che nel novembre 1994 colpì gran parte del territorio piemontese, con perdita di vite umane, di beni mobili ed immobili. L’alluvione 1994 costituì altresì un momento storico nel campo della pianificazione territoriale, prevenzione e gestione della pericolosità e rischio geologico-idraulico, che si tradusse in dettami normativi, per l’epoca avanzati e lungimiranti. Da quell’evento ...

Monitoring of debris flows in instrumented areas is carried out since many years in different Countries worldwide. It is still missing, however, an adequate standardization of methodologies, instrumentations and procedures. The instrumented areas are also employed for testing warning systems. Even though these latter have been more and more employed, a systematic experimentation of these systems has not yet been carried ...
Climate change in the Greater Alpine Region is seriously affecting glacial and periglacial areas, with relevant consequences on slope stability. Cryosphere degradation, changes of the precipitation and temperature patterns and of the hydrological regimes, are some of the main terrestrial indicators of climatic change. Moreover, the increasing number of tourists and human activities rise the level of ...
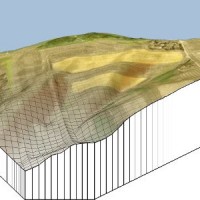
The application of distributed physically based models is possible on relatively small areas, typically hundreds or few thousands of km2. Distributed modelling of slope dynamics requires many sufficiently detailed information. Knowledge of geotechnical parameters and land use, digital terrain models, medium/high resolution cartography, temporal evolution of soil moisture conditions, are ...
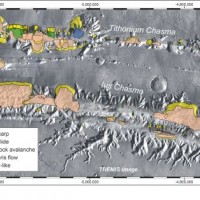
Landslides play an important role in the evolution of landscapes on Earth and on other solid planets of the Solar System. Surface gravity is the main factor driving landslides in solid planets. On Earth, landslides have been recognized in all continents, and in subaerial and submarine environments. The spatial and temporal range of the observed slope failures is extremely large on Earth. We are conducting a systematic mapping of landslides in ...

The high fragility of karst terrains, and the deriving vulnerability to a number of possible events, together with the presence of significant natural (first and foremost, groundwater), landscape and historical resources, are at the origin of the project activities, aimed at the safeguard of karst environments and the mitigation of the related ...

Sinkholes are among the main features of karst areas, and are extremely widespread in Florida, one of the sites most known for their occurrence and the likely interaction with the built-up environment. The Tampa area, in turn, shows an high frequency of events, which origin derives from different types of ...

Some geological phenomena of high pressure shearing show an unusual low friction during rock on rock slipping, like the abnormally long rock avalanches runout (hypermobility) or the slip of faults during earthquakes. The project aims to study the effect of the dynamic fragmentation of rock granules on the motion shear resistance, starting from the consideration that dynamic fragmentation is ubiquitous in geological processes subject to shearing ...
 The management of natural hazards tends radically to distribute responsibilities at the local level, as the first civil protection actors. Prevention and preparedness are long-term goals, rooted in volunteer expertise, and awareness of local citizens, using solutions of "crowd-sourced mappers". The objective is designing mobile applications, sensors and dashboard for citizens and volunteers of civil protection, with pilot study cases selected ...
The management of natural hazards tends radically to distribute responsibilities at the local level, as the first civil protection actors. Prevention and preparedness are long-term goals, rooted in volunteer expertise, and awareness of local citizens, using solutions of "crowd-sourced mappers". The objective is designing mobile applications, sensors and dashboard for citizens and volunteers of civil protection, with pilot study cases selected ...  Producing knowledge implies the responsibility to divulge it with quality, making it available for everyone. With the advent of the Internet the possibilities to retransmit knowledge have grown, but the danger is also grown of a deterioration of its quality, as the Nobel prize Gell-mann already denounced in the nineties. The project intends to propose solutions to this kind of problem, contributing to improve the expressive capacity of thesis ...
Producing knowledge implies the responsibility to divulge it with quality, making it available for everyone. With the advent of the Internet the possibilities to retransmit knowledge have grown, but the danger is also grown of a deterioration of its quality, as the Nobel prize Gell-mann already denounced in the nineties. The project intends to propose solutions to this kind of problem, contributing to improve the expressive capacity of thesis ...  Application of optical fibers is generally aimed at large bandwidth transmission. Few people know that the proposal of optical fibers as sensing elements is almost as old as their proposal as transmission media, and over the last two decades fibre optic sensor (FOS) technology has assumed a dominant role in several fields of application. As a matter of fact, FOSs offer many advantages with respect to legacy electronic and mechanic sensors. ...
Application of optical fibers is generally aimed at large bandwidth transmission. Few people know that the proposal of optical fibers as sensing elements is almost as old as their proposal as transmission media, and over the last two decades fibre optic sensor (FOS) technology has assumed a dominant role in several fields of application. As a matter of fact, FOSs offer many advantages with respect to legacy electronic and mechanic sensors. ...  Space-borne radar interferometry or DInSAR (Differential Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar) is one of the latest techniques used for the detection and measurement of ground surface deformations caused by natural and / or man-made events. The DInSAR technique has been successfully used in the measurement of seismic deformations and of the effects of subsidence, unstable slopes and inflation of magma in volcanoes. The growth of space ...
Space-borne radar interferometry or DInSAR (Differential Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar) is one of the latest techniques used for the detection and measurement of ground surface deformations caused by natural and / or man-made events. The DInSAR technique has been successfully used in the measurement of seismic deformations and of the effects of subsidence, unstable slopes and inflation of magma in volcanoes. The growth of space ...  The project is focused on flood forecasting and hydraulic risk, i.e. the assessment of the effects of flooding in flood-prone areas also involving the vulnerability assessment of the hydraulic structures (dams, leaves, bridges, etc.).
The effects of flood events are not completely eliminated by structural measures, therefore it is necessary to develop complementary non-structural measures, such as real-time Flood Forecasting and Warning ...
The project is focused on flood forecasting and hydraulic risk, i.e. the assessment of the effects of flooding in flood-prone areas also involving the vulnerability assessment of the hydraulic structures (dams, leaves, bridges, etc.).
The effects of flood events are not completely eliminated by structural measures, therefore it is necessary to develop complementary non-structural measures, such as real-time Flood Forecasting and Warning ...  The research topics involve the consideration of geological, geomorphological, hydrological, hydrogeological, and technology and the use of innovative methodologies to achieve the sustainability of the natural balance inherent inland waters, with a focus on groundwater and river water. Finally, we consider the effects of climate change on the hydrological cycle and anthropogenic modifications to emphasize the contribution of these modifications ...
The research topics involve the consideration of geological, geomorphological, hydrological, hydrogeological, and technology and the use of innovative methodologies to achieve the sustainability of the natural balance inherent inland waters, with a focus on groundwater and river water. Finally, we consider the effects of climate change on the hydrological cycle and anthropogenic modifications to emphasize the contribution of these modifications ...  The project concerns the mitigation of natural hazards (mainly the effects on the territory and the anthropic environment caused by rains, earthquakes, volcanism, and Radon gas). The geological characterization is essential to frame the contexts and the expected phenomena. Numerical modeling and monitoring allow to predict the spatio-temporal evolution of the phenomena, and therefore to evaluate the risk for mitigation ...
The project concerns the mitigation of natural hazards (mainly the effects on the territory and the anthropic environment caused by rains, earthquakes, volcanism, and Radon gas). The geological characterization is essential to frame the contexts and the expected phenomena. Numerical modeling and monitoring allow to predict the spatio-temporal evolution of the phenomena, and therefore to evaluate the risk for mitigation ...  The area of interest specifically refers to the study of the following themes: extreme hydrological events and their interaction with slopes and watercourses; soil water erosion; debris flows; slope stability; triggering instability mechanisms; evolution of slope movements; monitoring systems for gravitational movements for the purpose of alerting for the mitigation of geo-hydrological risk. The activities proposed in the module are therefore ...
The area of interest specifically refers to the study of the following themes: extreme hydrological events and their interaction with slopes and watercourses; soil water erosion; debris flows; slope stability; triggering instability mechanisms; evolution of slope movements; monitoring systems for gravitational movements for the purpose of alerting for the mitigation of geo-hydrological risk. The activities proposed in the module are therefore ...  A Geo-hydrological event (EDId) (landslides, mass movements, floods, etc.) can result in a high social and economic impact, especially if it is generated by multiple simultaneous phenomena, when it is able to produce social hardships and economic damage characterized by important and lasting effects. The identification of the typical elements of the phenomena that can contribute to an EDId (typify) is essential to adequately define the risk ...
A Geo-hydrological event (EDId) (landslides, mass movements, floods, etc.) can result in a high social and economic impact, especially if it is generated by multiple simultaneous phenomena, when it is able to produce social hardships and economic damage characterized by important and lasting effects. The identification of the typical elements of the phenomena that can contribute to an EDId (typify) is essential to adequately define the risk ...  In Italy landslides and floods are frequent, widespread and dangerous phenomena, that cause fatalities and serious economic damage. In our country, landslides and floods pose major problems of scientific interest and of social and economic relevance.
The Institute is a Competence Centre for the Italian national Civil Protection Department, an Office of the Prime Minister. For the Department of Civil Protection we execute research and ...
In Italy landslides and floods are frequent, widespread and dangerous phenomena, that cause fatalities and serious economic damage. In our country, landslides and floods pose major problems of scientific interest and of social and economic relevance.
The Institute is a Competence Centre for the Italian national Civil Protection Department, an Office of the Prime Minister. For the Department of Civil Protection we execute research and ...  Nel 2014 ricorrono vent’anni dalla tragica alluvione che nel novembre 1994 colpì gran parte del territorio piemontese, con perdita di vite umane, di beni mobili ed immobili. L’alluvione 1994 costituì altresì un momento storico nel campo della pianificazione territoriale, prevenzione e gestione della pericolosità e rischio geologico-idraulico, che si tradusse in dettami normativi, per l’epoca avanzati e lungimiranti. Da quell’evento ...
Nel 2014 ricorrono vent’anni dalla tragica alluvione che nel novembre 1994 colpì gran parte del territorio piemontese, con perdita di vite umane, di beni mobili ed immobili. L’alluvione 1994 costituì altresì un momento storico nel campo della pianificazione territoriale, prevenzione e gestione della pericolosità e rischio geologico-idraulico, che si tradusse in dettami normativi, per l’epoca avanzati e lungimiranti. Da quell’evento ...  Climate change in the Greater Alpine Region is seriously affecting glacial and periglacial areas, with relevant consequences on slope stability. Cryosphere degradation, changes of the precipitation and temperature patterns and of the hydrological regimes, are some of the main terrestrial indicators of climatic change. Moreover, the increasing number of tourists and human activities rise the level of ...
Climate change in the Greater Alpine Region is seriously affecting glacial and periglacial areas, with relevant consequences on slope stability. Cryosphere degradation, changes of the precipitation and temperature patterns and of the hydrological regimes, are some of the main terrestrial indicators of climatic change. Moreover, the increasing number of tourists and human activities rise the level of ...  The application of distributed physically based models is possible on relatively small areas, typically hundreds or few thousands of km2. Distributed modelling of slope dynamics requires many sufficiently detailed information. Knowledge of geotechnical parameters and land use, digital terrain models, medium/high resolution cartography, temporal evolution of soil moisture conditions, are ...
The application of distributed physically based models is possible on relatively small areas, typically hundreds or few thousands of km2. Distributed modelling of slope dynamics requires many sufficiently detailed information. Knowledge of geotechnical parameters and land use, digital terrain models, medium/high resolution cartography, temporal evolution of soil moisture conditions, are ...  The high fragility of karst terrains, and the deriving vulnerability to a number of possible events, together with the presence of significant natural (first and foremost, groundwater), landscape and historical resources, are at the origin of the project activities, aimed at the safeguard of karst environments and the mitigation of the related ...
The high fragility of karst terrains, and the deriving vulnerability to a number of possible events, together with the presence of significant natural (first and foremost, groundwater), landscape and historical resources, are at the origin of the project activities, aimed at the safeguard of karst environments and the mitigation of the related ...  Sinkholes are among the main features of karst areas, and are extremely widespread in Florida, one of the sites most known for their occurrence and the likely interaction with the built-up environment. The Tampa area, in turn, shows an high frequency of events, which origin derives from different types of ...
Sinkholes are among the main features of karst areas, and are extremely widespread in Florida, one of the sites most known for their occurrence and the likely interaction with the built-up environment. The Tampa area, in turn, shows an high frequency of events, which origin derives from different types of ... 










