
On 28 May 2025, at15:24 (CEST), the frontal part of the Birch Glacier in Valais (CH), estimated at around 3 million m3, collapsed, dragging with it over 6 million m3 of debris that had accumulated on its surface over the previous weeks, following a sequence of rockfalls from the northern slope of the Kleines Nesthorn (3335 m a.s.l.). The ice mass disintegrated immediately after detachment, giving rise to a catastrophic ice-rock avalanche with a ...

Climate changes affecting the planet need to pay great attention to evaluate the related effects, primarily in mountain territories, first sentinels of climate change. The actively involvement of high-altitude refuges, a precious asset for weather and climate surveillance of the Italian mountains, need to increase and improve knowledges about climate change effects on these infrastructures, requiring specific assessment and investigation ...

Between the late 19th and early 21st century, in the Alps the average air temperature has increased by about 2 °C, more than twice the increase in temperature in the northern hemisphere, of 0.8 °C. In the same period, precipitation showed a tendency towards an increase in the northern part of the Alps, and a tendency towards a decrease in the southern sector of the Alps.
Since the end of the Little Ice Age (about 1850), glaciers in the ...

ALMOND-F is an innovative unit for the microseismic detection of debris flows using a network of geophones.
The microseismic detection of debris flows is more complex than other types of monitoring. Use of the geophones requires: (1) the selection of the level of amplification of the signal, which depends on the distance from the stream; (2) the selection of the sampling frequency of the seismic signal, which must be sufficiently high; (3) ...

The researches at high-elevation sites continues, thanks to the RiST2 project (co-financed by Fondazione CRT of Torino). The study area is the Bessanese glacial basin. The Alpine environment and in particular the cryosphere, is responding quickly and with great intensity to climate change. The air temperature increase observed in the Alps urge the scientific communities involved in natural instability studies to consider not only air ...

Environmental sensor monitoring is continuously developing, both in terms of quantity (i.e. measurement sites), and quality (i.e. technological innovation). Environmental monitoring is carried out by either public or private entities for their own specific purposes, such as scientific research, civil protection, support to industrial and agricultural activities, services for citizens, security, education and information.
The left Cenischia ...

The Alpine environment, and in particular the high-altitude one, is responding quickly and with great intensity to climate change, through evidences of geomorphological, hydrological and ecological type. Mountain glacier shrinkage and related outcropping of rock walls and debris, changes of the precipitation and temperature patterns, are some of the main terrestrial indicators of climatic ...
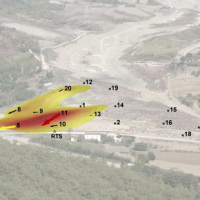
The 3DA software is a new procedure that allows retrieving in near-real-time 3D surface deformation models starting from data acquired via robotized total stations or others system that acquire the surface displacements. The measurements are first pre-processed and then implemented on 3D maps that include vector arrows representative of the intensities and of the real directions of motion in a given system of coordinates. The 3D surface ...
Glaciers are widely recognized as the best terrestrial indicator of climate change. Nevertheless, occurred changes, even in recent times, are often poorly known. Italy has a unique, secular history of glaciological documentation that, jointly with a rich wealth of spatial, multitemporal data, allows an accurate reconstruction of recent glacier evolution. Unfortunately, these data are dispersed and/or difficult to ...
Climate change in the Greater Alpine Region is seriously affecting glacial and periglacial areas, with relevant consequences on slope stability. Cryosphere degradation, changes of the precipitation and temperature patterns and of the hydrological regimes, are some of the main terrestrial indicators of climatic change. Moreover, the increasing number of tourists and human activities rise the level of ...
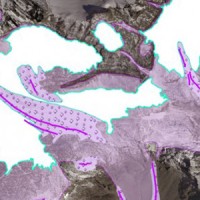
The project is included in Operative Program of the European cross-border territorial cooperation "Alcotra 2007-2013". It brings together specialized scientific expertise Italian and French that deal to study the mountain and its dangerousness. It is divided into a part of studies conducted on the entire framework of the Western Alps and in actions on the pilot sites identified by the ...

The observed increase in disastrous events over the last decades, associated with a low perception of risk by the communities involved, along with the lack of efficient, socially accepted and environmentally sound remedial measures are amongst the motivation behind this research project. The adaptation of a combined multi-risk-oriented analysis, in which the investigations focus more on the interdependence of events rather than on single event, ...
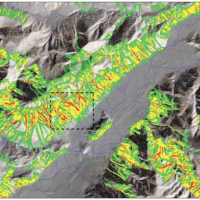
Debris flows and rockfalls are a familiar hazard in European mountain areas and regularly cause loss of life, livelihood and property. Hazard assessment is therefore increasingly required in land use planning. However, there are no standard techniques and existing operational techniques are qualitative.
DAMOCLES developed quantitative technologies for assessing the distribution of rapid slope failures and their hazard, for determining the ...
 On 28 May 2025, at15:24 (CEST), the frontal part of the Birch Glacier in Valais (CH), estimated at around 3 million m3, collapsed, dragging with it over 6 million m3 of debris that had accumulated on its surface over the previous weeks, following a sequence of rockfalls from the northern slope of the Kleines Nesthorn (3335 m a.s.l.). The ice mass disintegrated immediately after detachment, giving rise to a catastrophic ice-rock avalanche with a ...
On 28 May 2025, at15:24 (CEST), the frontal part of the Birch Glacier in Valais (CH), estimated at around 3 million m3, collapsed, dragging with it over 6 million m3 of debris that had accumulated on its surface over the previous weeks, following a sequence of rockfalls from the northern slope of the Kleines Nesthorn (3335 m a.s.l.). The ice mass disintegrated immediately after detachment, giving rise to a catastrophic ice-rock avalanche with a ...  Between the late 19th and early 21st century, in the Alps the average air temperature has increased by about 2 °C, more than twice the increase in temperature in the northern hemisphere, of 0.8 °C. In the same period, precipitation showed a tendency towards an increase in the northern part of the Alps, and a tendency towards a decrease in the southern sector of the Alps.
Since the end of the Little Ice Age (about 1850), glaciers in the ...
Between the late 19th and early 21st century, in the Alps the average air temperature has increased by about 2 °C, more than twice the increase in temperature in the northern hemisphere, of 0.8 °C. In the same period, precipitation showed a tendency towards an increase in the northern part of the Alps, and a tendency towards a decrease in the southern sector of the Alps.
Since the end of the Little Ice Age (about 1850), glaciers in the ...  ALMOND-F is an innovative unit for the microseismic detection of debris flows using a network of geophones.
The microseismic detection of debris flows is more complex than other types of monitoring. Use of the geophones requires: (1) the selection of the level of amplification of the signal, which depends on the distance from the stream; (2) the selection of the sampling frequency of the seismic signal, which must be sufficiently high; (3) ...
ALMOND-F is an innovative unit for the microseismic detection of debris flows using a network of geophones.
The microseismic detection of debris flows is more complex than other types of monitoring. Use of the geophones requires: (1) the selection of the level of amplification of the signal, which depends on the distance from the stream; (2) the selection of the sampling frequency of the seismic signal, which must be sufficiently high; (3) ...  The researches at high-elevation sites continues, thanks to the RiST2 project (co-financed by Fondazione CRT of Torino). The study area is the Bessanese glacial basin. The Alpine environment and in particular the cryosphere, is responding quickly and with great intensity to climate change. The air temperature increase observed in the Alps urge the scientific communities involved in natural instability studies to consider not only air ...
The researches at high-elevation sites continues, thanks to the RiST2 project (co-financed by Fondazione CRT of Torino). The study area is the Bessanese glacial basin. The Alpine environment and in particular the cryosphere, is responding quickly and with great intensity to climate change. The air temperature increase observed in the Alps urge the scientific communities involved in natural instability studies to consider not only air ...  Environmental sensor monitoring is continuously developing, both in terms of quantity (i.e. measurement sites), and quality (i.e. technological innovation). Environmental monitoring is carried out by either public or private entities for their own specific purposes, such as scientific research, civil protection, support to industrial and agricultural activities, services for citizens, security, education and information.
The left Cenischia ...
Environmental sensor monitoring is continuously developing, both in terms of quantity (i.e. measurement sites), and quality (i.e. technological innovation). Environmental monitoring is carried out by either public or private entities for their own specific purposes, such as scientific research, civil protection, support to industrial and agricultural activities, services for citizens, security, education and information.
The left Cenischia ...  The Alpine environment, and in particular the high-altitude one, is responding quickly and with great intensity to climate change, through evidences of geomorphological, hydrological and ecological type. Mountain glacier shrinkage and related outcropping of rock walls and debris, changes of the precipitation and temperature patterns, are some of the main terrestrial indicators of climatic ...
The Alpine environment, and in particular the high-altitude one, is responding quickly and with great intensity to climate change, through evidences of geomorphological, hydrological and ecological type. Mountain glacier shrinkage and related outcropping of rock walls and debris, changes of the precipitation and temperature patterns, are some of the main terrestrial indicators of climatic ...  Glaciers are widely recognized as the best terrestrial indicator of climate change. Nevertheless, occurred changes, even in recent times, are often poorly known. Italy has a unique, secular history of glaciological documentation that, jointly with a rich wealth of spatial, multitemporal data, allows an accurate reconstruction of recent glacier evolution. Unfortunately, these data are dispersed and/or difficult to ...
Glaciers are widely recognized as the best terrestrial indicator of climate change. Nevertheless, occurred changes, even in recent times, are often poorly known. Italy has a unique, secular history of glaciological documentation that, jointly with a rich wealth of spatial, multitemporal data, allows an accurate reconstruction of recent glacier evolution. Unfortunately, these data are dispersed and/or difficult to ...  Climate change in the Greater Alpine Region is seriously affecting glacial and periglacial areas, with relevant consequences on slope stability. Cryosphere degradation, changes of the precipitation and temperature patterns and of the hydrological regimes, are some of the main terrestrial indicators of climatic change. Moreover, the increasing number of tourists and human activities rise the level of ...
Climate change in the Greater Alpine Region is seriously affecting glacial and periglacial areas, with relevant consequences on slope stability. Cryosphere degradation, changes of the precipitation and temperature patterns and of the hydrological regimes, are some of the main terrestrial indicators of climatic change. Moreover, the increasing number of tourists and human activities rise the level of ...  The project is included in Operative Program of the European cross-border territorial cooperation "Alcotra 2007-2013". It brings together specialized scientific expertise Italian and French that deal to study the mountain and its dangerousness. It is divided into a part of studies conducted on the entire framework of the Western Alps and in actions on the pilot sites identified by the ...
The project is included in Operative Program of the European cross-border territorial cooperation "Alcotra 2007-2013". It brings together specialized scientific expertise Italian and French that deal to study the mountain and its dangerousness. It is divided into a part of studies conducted on the entire framework of the Western Alps and in actions on the pilot sites identified by the ...  The observed increase in disastrous events over the last decades, associated with a low perception of risk by the communities involved, along with the lack of efficient, socially accepted and environmentally sound remedial measures are amongst the motivation behind this research project. The adaptation of a combined multi-risk-oriented analysis, in which the investigations focus more on the interdependence of events rather than on single event, ...
The observed increase in disastrous events over the last decades, associated with a low perception of risk by the communities involved, along with the lack of efficient, socially accepted and environmentally sound remedial measures are amongst the motivation behind this research project. The adaptation of a combined multi-risk-oriented analysis, in which the investigations focus more on the interdependence of events rather than on single event, ... 




