Models of geo-hydrological processes
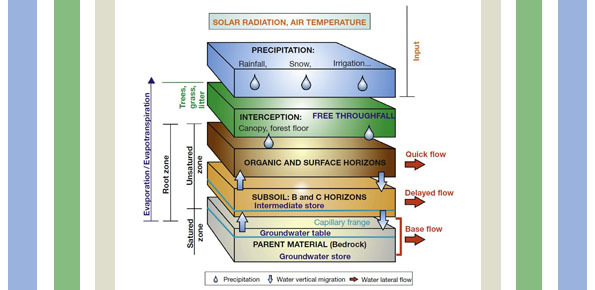
Background
The area of interest specifically refers to the study of the following themes: extreme hydrological events and their interaction with slopes and watercourses; soil water erosion; debris flows; slope stability; triggering instability mechanisms; evolution of slope movements; monitoring systems for gravitational movements for the purpose of alerting for the mitigation of geo-hydrological risk. The activities proposed in the module are therefore aimed at improving the knowledge for risk assessment deriving from geo-hydrological processes, also for the purpose of proposing mitigation and reduction measures.
Purpose
The objective is to evaluate the risk from natural processes that can potentially cause victims, damage human assets and, more generally, negative for socio-economic progress. Modeling of geo-hydrological processes can provide an useful tool to mitigate and reduce risk.
Methods
Mathematical modeling, together with an ever increasing availability of environmental information with a high spatio-temporal detail that integrates with that of sophisticated mathematical tools and powerful calculation, offers continuous progress investigation tools, useful for the understanding and simulation of physical mechanisms of interaction between precipitation and slopes.
Results
Mathematical models for landslide triggering, landslide inventory, susceptibility maps, risk maps, soil erosion evaluation.
Products
Mathematical models for landslide triggering, landslide inventory, susceptibility maps, risk maps, soil erosion evaluation.
Conclusions
The activities proposed in the module contribute to improve the knowledge for risk assessment deriving from geo-hydrological processes, also for the purpose of proposing mitigation and reduction measures.



 Internal contact person: oreste giuseppe terranova -
Internal contact person: oreste giuseppe terranova -