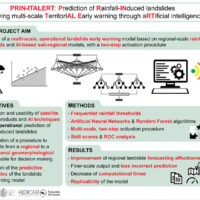
Predicting the occurrence of rainfall-induced landslides is a crucial task for civil protection purposes. Several landslide early warning systems are currently operating worldwide at different spatial scales. In Italy, landslide alerts are issued for territorial units named Alert Zones, covering a few thousand km². Usually, regional-scale warning models rely on rainfall thresholds, which require a few parameters and provide clear results in ...
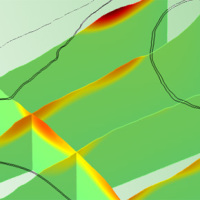
We experiment the application of 3D numerical modelling techniques for the analysis of the kinematics of slow-moving active landslides. The activity assesses the hazards posed by slow-moving landslides, determines the factors controlling the slope processes, investigates the potential evolution of the active slopes, and helps selecting appropriate slope mitigation strategies.
We exploit modern numerical modelling techniques based on finite ...
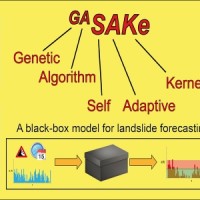
We developed GASAKe, Genetic Algorithm-based Self-Adaptive Kernel, a new model to predict the time of occurrence of rainfall induced landslides.
GASAKe predicts the time of occurrence of single landslides or groups of similar landslides, both shallow and deep-seated, using a threshold than when exceeded determines the initiation of the landslides. The triggering threshold is defined using historical information on rainfall and ...

The research activity aims at defining a coherent and unambiguous framework for the assessment and zonation of seismically induced landslides, at different geographical, temporal and management scales. To this end, the project works at the pre-event temporal scale, concerning spatial planning and soil protection and corresponding to years to decades time periods, and at the real-time or civil protection scale, corresponding to time periods ...
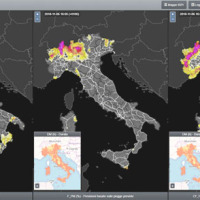
SANF-RFI is a landslide early warning system along the RFI national railway Infrastructure. The system forecasts the possible occurrence of landslides by comparing rainfall measurements and forecasts with empirical rainfall thresholds for the possible occurrence of landslides. Specifically, the system consists of three components: (i) for rainfall and other data input and storage, (ii) for data processing and analysis, and (iii) for the ...
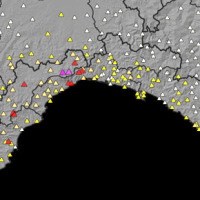
Since 2013, CNR IRPI went in with the collection of information on rainfall events that have resulted in landslides in the Liguria region. Rainfall thresholds can be used in early warning systems for the prediction of the occurrence of rainfall-induced landslides. To respond to a request of the Italian national Department for Civil Protection (DPC), CNR IRPI designed and developed SANF, an Italian acronym for National Early Warning System for ...

The project focuses on climate predictions from seasonal-to-decadal timescales for the Mediterranean region (here defined as the domain encompassing the Mediterranean basin and the surrounding areas), and their applications in different sectors. The IRPI contribution will cover this aspect of the project, with specific reference to the conditions and evolution of cryosphere resources (WP4, Task ...
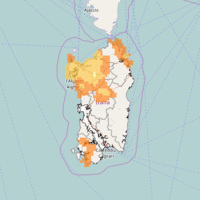
In Italy, landslides are triggered by intense and/or prolonged rainfall. The spatial and temporal forecast of multiple landslides triggered by rainfall in wide areas relies primarily on empirical rainfall thresholds. It is widely believed that the thresholds are influenced by the local topographic (morphological), lithological, soil, and climatic settings. For this reason, it is necessary to define local rainfall thresholds. Reliable local ...
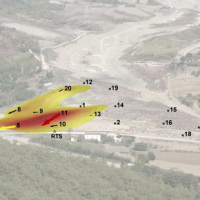
The 3DA software is a new procedure that allows retrieving in near-real-time 3D surface deformation models starting from data acquired via robotized total stations or others system that acquire the surface displacements. The measurements are first pre-processed and then implemented on 3D maps that include vector arrows representative of the intensities and of the real directions of motion in a given system of coordinates. The 3D surface ...
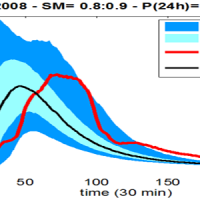
Semi-distributed continuous hydrological model (MISDc) for real-time soil moisture estimate and river discharge prediction in the Upper-Middle Tiber River basin; flood wave routing model (STAFOM-RCM) for stage hydrograph forecasting at some selected hydrometric stations in the Tiber River basin; Rainfall-runoff database coupled with the kinematic model KS for an expeditious estimate of probability flooding ...
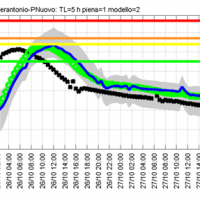
The project activities concern:
development and implementation of: 1) a semi-distributed continuous hydrological model (MISDc) for real-time soil moisture estimate and river discharge prediction in the Upper-Middle Tiber River basin; 2) a flood wave routing model (STAFOM-RCM) for stage hydrograph forecasting at some selected hydrometric stations in the Tiber River basin;
support for installation of soil moisture sensors in the ...
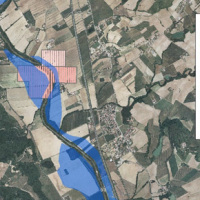
On 25-27 November 2005, the territory of central Italy was affected by heavy rainfall that hit the Tiber River basin and, mainly, the province of Perugia. The meteoric event had a significant phase with a duration of approximately 48 hours with widespread precipitation up to a maximum accumulated value higher than 100 mm. Significant increases in water levels occurred in most rivers of Upper-Middle Tiber
causing extended flooding in ...
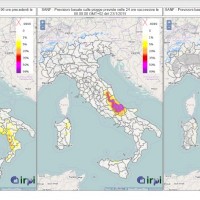
SANF is a landslide early warning system based on the comparison between rainfall measurements and forecasts and empirical rainfall thresholds. Specifically, the system consists of three components: (i) for rainfall and other data input and storage, (ii) for data processing and analysis, and (iii) for the production and delivery of the ...
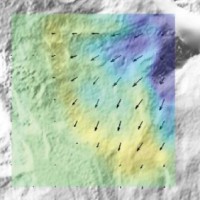
Based on the application of numerical modelling techniques, CNR – IRPI can provide consulting services on stability/instability conditions and kinematical evolution of potentially unstable slopes, underground caves, embankments, open-pit mines, landfills and any other type of natural or man-made soil/rock structure at ...

In Italy rainfall are among the main causes of trigger of shallow landslides, that yearly cause fatalities, damage, and severe economic losses. Identification of the amount of rainfall needed to trigger landslides, and the forecasting of rainfall-induced landslides, are of interest for the scientific community, as well as for the whole ...
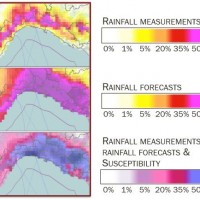
In Italy, landslides are triggered by intense and/or prolonged rainfall. The spatial and temporal forecast of multiple landslides triggered by rainfall in wide areas relies primarily on empirical rainfall thresholds. It is widely believed that the thresholds are influenced by the local topographic (morphological), lithological, soil, and climatic settings. For this reason, it is necessary to define local rainfall thresholds. Reliable local ...
Hydrometeorological monitoring and flood forecasting are indispensable in preventing hydraulic hazard and ensuring civil protection. Implementing a sustainable plan to combat floods requires further activities, such as best practices for agricultural, forestry and land use management in flood risk areas. Methodologies must be developped within a transnational context, transending local ...
 The project focuses on climate predictions from seasonal-to-decadal timescales for the Mediterranean region (here defined as the domain encompassing the Mediterranean basin and the surrounding areas), and their applications in different sectors. The IRPI contribution will cover this aspect of the project, with specific reference to the conditions and evolution of cryosphere resources (WP4, Task ...
The project focuses on climate predictions from seasonal-to-decadal timescales for the Mediterranean region (here defined as the domain encompassing the Mediterranean basin and the surrounding areas), and their applications in different sectors. The IRPI contribution will cover this aspect of the project, with specific reference to the conditions and evolution of cryosphere resources (WP4, Task ...  Semi-distributed continuous hydrological model (MISDc) for real-time soil moisture estimate and river discharge prediction in the Upper-Middle Tiber River basin; flood wave routing model (STAFOM-RCM) for stage hydrograph forecasting at some selected hydrometric stations in the Tiber River basin; Rainfall-runoff database coupled with the kinematic model KS for an expeditious estimate of probability flooding ...
Semi-distributed continuous hydrological model (MISDc) for real-time soil moisture estimate and river discharge prediction in the Upper-Middle Tiber River basin; flood wave routing model (STAFOM-RCM) for stage hydrograph forecasting at some selected hydrometric stations in the Tiber River basin; Rainfall-runoff database coupled with the kinematic model KS for an expeditious estimate of probability flooding ...  The project activities concern:
development and implementation of: 1) a semi-distributed continuous hydrological model (MISDc) for real-time soil moisture estimate and river discharge prediction in the Upper-Middle Tiber River basin; 2) a flood wave routing model (STAFOM-RCM) for stage hydrograph forecasting at some selected hydrometric stations in the Tiber River basin;
support for installation of soil moisture sensors in the ...
The project activities concern:
development and implementation of: 1) a semi-distributed continuous hydrological model (MISDc) for real-time soil moisture estimate and river discharge prediction in the Upper-Middle Tiber River basin; 2) a flood wave routing model (STAFOM-RCM) for stage hydrograph forecasting at some selected hydrometric stations in the Tiber River basin;
support for installation of soil moisture sensors in the ...  On 25-27 November 2005, the territory of central Italy was affected by heavy rainfall that hit the Tiber River basin and, mainly, the province of Perugia. The meteoric event had a significant phase with a duration of approximately 48 hours with widespread precipitation up to a maximum accumulated value higher than 100 mm. Significant increases in water levels occurred in most rivers of Upper-Middle Tiber
causing extended flooding in ...
On 25-27 November 2005, the territory of central Italy was affected by heavy rainfall that hit the Tiber River basin and, mainly, the province of Perugia. The meteoric event had a significant phase with a duration of approximately 48 hours with widespread precipitation up to a maximum accumulated value higher than 100 mm. Significant increases in water levels occurred in most rivers of Upper-Middle Tiber
causing extended flooding in ...  Based on the application of numerical modelling techniques, CNR – IRPI can provide consulting services on stability/instability conditions and kinematical evolution of potentially unstable slopes, underground caves, embankments, open-pit mines, landfills and any other type of natural or man-made soil/rock structure at ...
Based on the application of numerical modelling techniques, CNR – IRPI can provide consulting services on stability/instability conditions and kinematical evolution of potentially unstable slopes, underground caves, embankments, open-pit mines, landfills and any other type of natural or man-made soil/rock structure at ...  Hydrometeorological monitoring and flood forecasting are indispensable in preventing hydraulic hazard and ensuring civil protection. Implementing a sustainable plan to combat floods requires further activities, such as best practices for agricultural, forestry and land use management in flood risk areas. Methodologies must be developped within a transnational context, transending local ...
Hydrometeorological monitoring and flood forecasting are indispensable in preventing hydraulic hazard and ensuring civil protection. Implementing a sustainable plan to combat floods requires further activities, such as best practices for agricultural, forestry and land use management in flood risk areas. Methodologies must be developped within a transnational context, transending local ... 












